Chapter 7 Nervous System Notes
advertisement
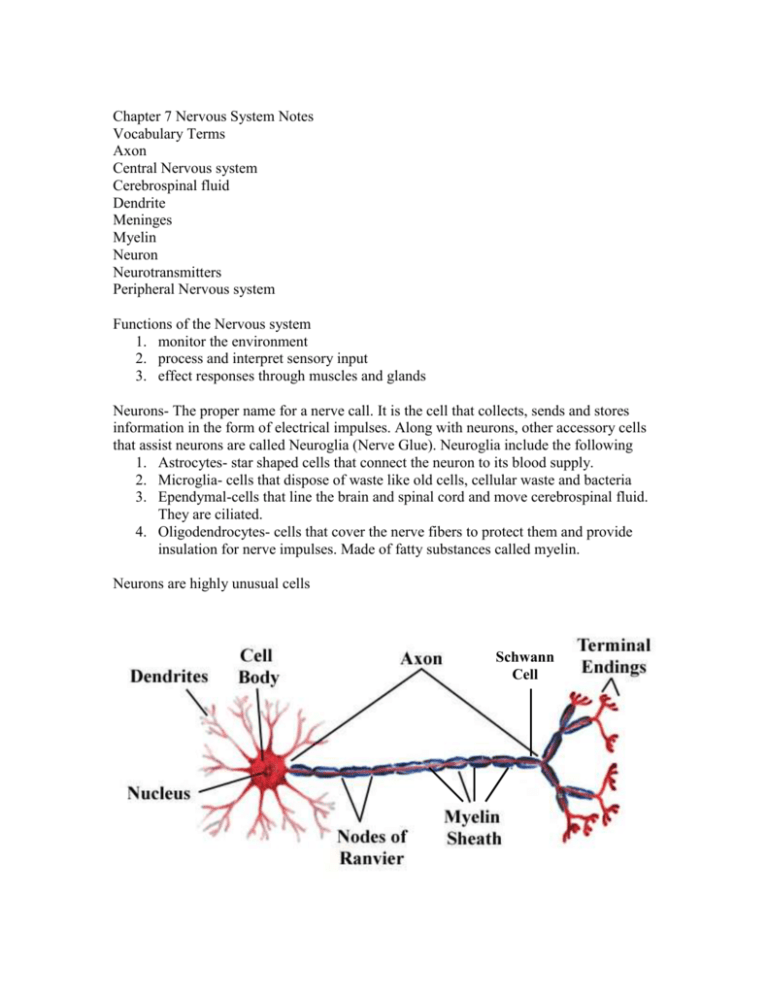
Chapter 7 Nervous System Notes Vocabulary Terms Axon Central Nervous system Cerebrospinal fluid Dendrite Meninges Myelin Neuron Neurotransmitters Peripheral Nervous system Functions of the Nervous system 1. monitor the environment 2. process and interpret sensory input 3. effect responses through muscles and glands Neurons- The proper name for a nerve call. It is the cell that collects, sends and stores information in the form of electrical impulses. Along with neurons, other accessory cells that assist neurons are called Neuroglia (Nerve Glue). Neuroglia include the following 1. Astrocytes- star shaped cells that connect the neuron to its blood supply. 2. Microglia- cells that dispose of waste like old cells, cellular waste and bacteria 3. Ependymal-cells that line the brain and spinal cord and move cerebrospinal fluid. They are ciliated. 4. Oligodendrocytes- cells that cover the nerve fibers to protect them and provide insulation for nerve impulses. Made of fatty substances called myelin. Neurons are highly unusual cells Schwann Cell 1. Neuron Anatomy: Cell Body- Metabolic center of the cell Dendrites- Receiving fibers of the neuron Axon- Sending fiber of the neuron Axon Terminals- One of the many ends of an axon Myelin Sheath- bundles of fatty cells that insulate nerve impulses Schwann cell- a single myelin bundle surrounding the axon Nodes of Ranvier- gaps between Schwann cells that accelerate and amplify nerve impulses Neurotransmitters- Chemicals that continue nerve impulses from one neuron to the next. 2. Neuron Classification- There are three primary ways Neurons are classified A) Function- Motor Nerve, Sensory nerve, Interneuron B) Structure- Number of dendrites and number of axons or branches C) Physiology-Is the nerve signal voluntary or involuntary, or a reflex? 3. Neuron Impulses- Nerve signals or Impulses are electrical signals that travel the length of the neuron from its dendrites to its axon. The signal is electrical in the sense that it is the change in cell membrane polarity as the signal travels the length of the cell. Sodium and Potassium are moved into and out of the cell creating the change in polarity. The nerve signal is also protected by the myelin covering of the cell. At the end of the axon, neurotransmitters like Acetylcholine (Ach) cross the gap (synapse) to the next cell and the signal is continued. http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter14/animation__the_nerve_im pulse.html CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain is the primary organ of the entire Nervous system. It is made up of four distinct regions listed below and detailed later. I. Cerebrum II. Diencephalon III. Brain Stem IV. Cerebellum I. Cerebrum (aka Cerebral Cortex) The largest region of the brain, it covers or partially covers the other parts. The outer surface of the cerebrum is grey colored and is covered with ridges and grooves. The deepest of the grooves are called fissures and the largest one divides the cerebrum into right and left halves. (interhemispheric fissure) The cerebrum is also divided into “Lobes”, named for the cranial bones that lie above them. Frontal Lobe- Primary motor area, personality, thought and reasoning Temporal Lobe- Primary auditory area Parietal Lobe- Primary sensory area Occipital Lobe- Primary visual area The cerebrum is the area associated with all thought processes and memory as well as sensory input. The cerebrum covers an underlying portion of white matter called the Corpus Callosum, which connects the diencephalon to the cerebrum. II. Diencephalon- (Interbrain ) Is the area of the brain directly over the brain stem but enclosed by the cerebrum. Area is filled with 4 open areas called ventricles that are filled with cerebrospinal fluid Area has three main endocrine glands that produce hormones (pituitary, hypothalamus and pineal) The thalamus is the primary relay station for incoming nerve messages. It chooses what information to pass on to the cerebrum. The Hypothalamus regulates the autonomic nervous system and regulates the Pituitary Gland. The pineal gland regulates sleep patterns and is in the rear of the region. III. Brain Stem The top three inches of the spinal cord and includes the following……. The Midbrain controls partial vision and hearing The Pons is a bridge of nerve fibers The Medulla Oblongata controls aggression, pulse rate, blood pressure, breathing and swallowing. IV. Cerebellum- A large Cauliflower shaped structure that is found below the occipital lobe of the cerebrum. It coordinates all motor activity, balance and equilibrium. Injury to this area produces awkward, clumsy movements. Alcohol also affects this area affecting balance. Brain Waves- Electrical impulses travel through the brain in various wave lengths and frequencies. They are measured by an Electroencephalograph (EEG) Alpha waves- produced in awake but relaxed state Beta waves- produces in awake and alert state Theta waves- produced in children but not adults Delta waves- produced during sleep The Spinal Cord The white extension of the brain stem that runs from the Magna Foramen through the L2 vertebrae. The spinal cord is approximately 17 inches long and is the thickness of your little finger. The base of the Spinal cord divides into many smaller nerves called the “Cauda Equina” (Horses Tail) that branch downward to the pelvis and legs. There are 31 pairs of Spinal nerves that branch laterally from each gap in the vertebral column. The Spinal cord is responsible for the “Reflex Arc”, that protects you from danger and injury. Is protected by three layers of meninges (dura mater, pia mater and archnoid mater) Grey matter inside the spinal cord is Butterfly shaped in cross section. A central canal runs the length of the spinal cord internally and circulates CSF Four Protective structures of the Brain and Spinal cord. 1. bone 2. meninges 3. cerebrospinal fluid 4. blood brain barrier Peripheral Nervous system Is made up of any nerve that is not a part of the CNS. Cranial nerves- any of 12 pairs of nerves that leave the brain other than by the spinal cord. Most control senses and muscles of the face and head 1. optic nerve- vision 2. vestibulocochlear nerve- hearing and balance 3. olfactory nerve- smell 4. facial nerve- senses and muscles of the face 5. oculomotor nerve- muscles of the eyes 6. vagus nerve- heart rate, digestive system and reproductive systems Spinal Nerves- 31 pairs of nerves that branch from the spinal cord. Most control sensory and motor functions from the same nerve. Part of the reflex arc with the spinal cord. Typical nerve diagram- Nerves contain fatty myelin, blood vessels and both sensory and motor nerves. The outer covering of a nerve is called the Epineurium. Motor and Sensory Nerves Blood Vessels Myelin Diseases and Disorders of the Nervous system Multiple Sclerosis Huntington’s disease Parkinson’s disease Alzheimers disease Ataxia Meningitis Hydrocephlia Cerebrovascular accident (stroke) Concussion Paralysis Cerebral Palsy Anencephaly Spina Bifida Epilepsy Rabies Polio







