Physics 184 Exp 2 Ohms
advertisement

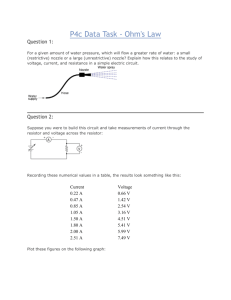
Physics 184 Experiment 2 OHM'S LAW AND POWER OBJECT: To verify Ohm's Law, to study the transfer of power from a voltage source to a load resistor, to find the emf and the internal resistance of a battery. APPARATUS: Voltage supply, ammeter, voltmeter, switch, resistance box, connecting wires and a 10 mm to 1 cm linear graph paper. THEORY: Ohm's Law states that the voltage across a conductor is proportional to the current in the conductor: V=IR, where V is the voltage in volts, I is the current in am peres, and R is the proportionality constant which is known as the resistance of the conductor whose unit is in ohms. The power dissipated in the conductor is the product of the current in the conductor and the voltage across it: P = I V, where P is the power in watts, I is in amperes, and V is in volts. A voltage source may be considered as consisting of a perfect battery in series with a resistor. A perfect battery supplies the same voltage no matter what current is supplied, but the current in the series resistor produces a voltage drop (Ohm's Law). The voltage from the perfect battery is known as the Emf (for Electro-motive force). In practice, any voltage source will have some internal resistance and its voltage may be represented by Vsource =- I Rint where is the Emf, I is the current in amperes, and Rint is the resistance in ohms. It should be noted that IRint is the voltage drop caused by the internal resistance. PROCEDURE: 1. Connect the apparatus as indicated in the diagram on the next page. In this experiment, the resistance box serves as the external load of the circuit. Never close the switch at zero-ohm on the resistance box. 2. Set the resistance box at 20-ohm and dose the switch. Measure the current and the voltage and calculate the power dissipated in the resistor. Do not hold the switch closed for long periods of time as that may overheat the resistances and the energy from the battery will be overdrawn. 3. Repeat step 2 using resistances of 30, 40, 50, 70, 100, 200, and 300 ohms, respectively. Record your data on the data page. DATA ANALYSIS 1. From you data for the current and the voltage, plot the voltage across the resistance box versus the current in the circuit. Draw the best straight line through your data points. 2. From your graph, determine the emf and the internal resistance of the voltage source. The emf will be the intercept on the voltage axis and the internal resistance is absolute value of the slope of the line. 3. From you data for the current and the voltage calculate the power delivered by the power supply for different values of the load resistor. 4. Plot the power in the load resistor versus the load resistance and find the maximum power. The resistance read at the maximum power is R int ,the internal resistance. 5. Compare the internal resistance values obtained in step 2 and in step 4.