Requirements Management REQM

Requirements Management REQM
Purpose
: to manage the requirements of the project’s products and product components and to identify inconsistencies between those requirements and the project’s plans and work products.
SG1 Manage Requirements
Requirements are managed and inconsistencies with project plans and work products are identified
SP1.1 Obtain an Understanding of the Requirements
Develop an understanding with the requirements providers on the meaning of the requirements
Official sources for requirements should be identified and utilized to receive requirements. Acceptance criteria should be created and used to evaluate the requirements. The criteria might include, properly stated, complete, consistent, appropriate to implement, verifiable (testable) and traceable.
An understanding of the requirements should be reached with the requirements provider.
SP1.2 Obtain Commitment to Requirements
Obtain commitment to the requirements from the project participants
This deals with agreements and commitments among those who have to carry out the activities necessary to implement the requirements. The impact of requirements on existing commitments should be established and commitments negotiated and recorded.
SP1.3 Manage Requirements Changes
Manage changes to the requirements as they evolve during the project
All requirements change requests received or generated by the project must be captured and their impact on the project and stakeholders evaluated. Again, acceptance is an issue but once accepted, the requirements change history and rationale need to be carefully maintained.
SP1.4 Maintain Bidirectional Traceability of Requirements
Maintain bidirectional traceability of requirements and the project plans and work products.
It is important here to trace requirements from their source to the lower level derived requirements and vice versa. The same applies to tracing requirements to other entities such as design documentation, test plan and work products.
Traceability is important in conducting impact analysis whenever a change request is received.
SP1.5 Identify Inconsistencies between Project Work and Requirements
Identify inconsistencies between the project plans and work products and the requirements.
The project’s plans, activities and work products need to be reviewed to determine consistency with current requirements. The source and rationale of any inconsistency needs to be defined and corrective actions initiated.
Requirements Development RD
Purpose: to produce and analyse customer, product and product-component requirements.
SG1 Develop Customer Requirements
Stakeholder needs, expectations, constraints and interfaces are collected and translated into customer requirements
SP1.1 Elicit Needs
Elicit stakeholder needs, expectations, constraints and interfaces for all phases of the product life cycle
This goes beyond collecting requirements by proactively identifying additional requirements not explicitly provided by customers.
SP1.2 Develop the Customer Requirements
Transform stakeholder needs, expectations, constraints and interfaces into customer requirements
The information gathered is translated into documented customer requirements.
Constraints are defined for verification and validation
SG2 Develop Product Requirements
Customer requirements are refined and elaborated to develop product and productcomponent requirements
SP2.1 Establish Product and Product Component Requirements
Establish and maintain product and product component requirements which are based on the customer requirements
Develop requirements in technical terms necessary for product and component design.
For example a customer may have expressed a requirement for a HCI to be simple and easy to understand. This must be stated in terms of the actual technical requirement for the interface.
Requirements that result from design decisions should be derived. A requirement might be derived for example for a component that has to interface with an off-theshelf database so the component must comply. Such a derived requirement is not traceable to higher level requirements.
Relationships between requirements should be established and maintained, to aid change management
SP2.2 Allocate Product Component Requirements
Allocate the requirements for each product component
This implies that some basic architecture exists such that the requirements can be mapped to sub-components of this architecture This might be achieved with requirements allocation sheets.
SP2.3 Identify Interface Requirements
Identify interface requirements both internal and external
Interfaces between functions (or objects) are identified and requirements for these interfaces developed.
SG3 Analyse and Validate Requirements
The requirements are analysed and validated and a definition of required functionality is developed
SP3.1 Establish Operational Concepts and Scenarios
Establish and maintain operational concepts and associated scenarios
Identify and develop scenarios in which the proposed product is expected to operate.
Fully define this environment to include boundaries and any constraints the environment imposes.
Scenarios and operational concepts should be reviewed to uncover requirements.
Note the distinction between scenarios and operational concepts. Scenarios are operational sequences as viewed by the customer. Use Cases in fact; they are a sequence of events that might occur in the life-time of the product. Operational sequences are related to concept. The operational sequence of a helicopter is different to that of an aeroplane. The scenarios should be considered in light of operational alternatives. This may yield constraints which impact on requirements.
SP3.2 Establish a Definition of Required Functionality
Establish and maintain a definition of required functionality
This is a description of what the product is intended to do and may involve the use of a functional architecture, activity diagrams, use cases and class models with services identified.
This may well evolve from consideration of scenarios.
SP3.3 Analyse Requirements
Analyse requirements to ensure that they are necessary and sufficient
Analyse requirements to ensure that they are complete, feasible, realisable and verifiable and that they can satisfy the objectives of any higher level requirements .
SP3.4 Analyse Requirements to Achieve Balance
Analyse requirements to achieve stakeholder needs and constraints
Use models (simulation, prototyping) to analyse the balance of stakeholder needs and perform a risk management on the requirements and functional architecture.
SP3.5 Validate Requirements
Validate requirements to ensure the resulting product will perform appropriately in its intended-use environment
Determine the risk that the product will not perform appropriately in its intended-use environment
Explore the adequacy and completeness of requirements by developing product representations (e.g. prototypes, simulations, scenarios and storyboards) and by obtaining feedback about them from stakeholders.
Technical Solution TS
Purpose : to design, develop and implement solutions to requirements. Solutions, designs and implementations encompass products, product components and product related life cycle processes either singly or in combination as appropriate.
S G1 Select Product-Component Solution
Product or product-component solutions are selected from alternative solutions
SP1.1 Develop Alternative Solutions and Selection Criteria
Develop alternative solutions and selection criteria
A process for identifying solution alternatives and selection criteria needs to be established and maintained. Design issues for each alternative solution need to be considered and any risks characterised. The requirements of the system need to be allocated for each alternative solution
SP1.3 Select Product-Component Solutions
Select the product-component solutions that best satisfy the criteria collected
The rationale for product component selection is identified and the relationship between requirements and product-components is documented.
SG2 Develop the Design
Product or product-component designs are developed
SP2.1 Design the Product or Product-Component.
Develop a design for the product or product-component
Establish and maintain criteria against which the design can be evaluated. Develop or acquire appropriate design methods and ensure that standards are adhered to in use.
Ensure that the design of each product and product-component adheres to the allocated requirements. Carefully document the design.
SP2.2 Establish a Technical Data Package
Establish and maintain a technical data package
A technical data package provides a comprehensive description of a product or product-component as it is developed. The data might include, architecture description, allocated requirements, product description, characteristics, interface requirements etc, allowing various view of the product to be established for developers and customers.
SP2.3 Design Interfaces Using Criteria
Design comprehensive product-component interfaces in terms of established and maintained criteria
The criteria for interfaces frequently reflect a comprehensive list of critical parameters that must be defined, or at least investigated to ascertain their applicability.
SP2.4 Perform Make, Buy or Reuse Analysis
Evaluate whether the product componenet should be developed, purchased or reused based on established criteria
Determination is based on analysis of the needs of the project. It can be conducted using a formal evaluation approach. Requirements can be used where necessary to establish a supplier agreement.
Factors influencing the decision may include, cost, fit, quality, supplier agreement terms and availability.
SG3 Implement the Product Design
Product components and associated support documentation are implemented from the designs
SP3.1-1 Implement the Design
Implement the designs of the product components
Once design has been completed, effective methods should be used to implement the product components. For example, object-oriented programming, structured programming, automatic code generation, code reuse etc. Standards should be adhered to and peer reviews of the implementation should be conducted. Unit testing needs to be carried out.
SP3.2-1 Develop Product Support Documentation
Develop and Maintain the end-use documentation
The documentation that is used to install, operate and maintain the product is developed and maintained.
Product Integration PI
Purpose: to assemble the product from the product components, ensure that the product, as integrated, functions properly, and deliver the product
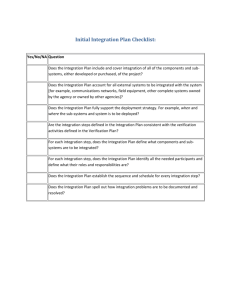
SG1 Prepare the Product Integration
Preparation for product integration is conducted
SP1.1 Determine Integration Sequence
Determine the product-component integration sequence.
All components to be integrated should be identified and all verifications carried out.
The definition of interfaces should be used during verifications. The best integration sequence should be established.
SP1.2 Establish the Product Integration Environment
Establish and maintain the environment needed to support the integration of the product components
NB: Not as significant for software development
SP1.3 Establish Product Integration Procedures and Criteria
Establish and maintain procedures and criteria for integration of the product components
Criteria can be defined for how the components are to be verified and the functions they are expected to have. Criteria can be defined for how the assembled components and final integrated product are to be validated and delivered
S G2 Ensure Interface Compatibility
The product-component interfaces, both internal and external, are compatible
SP2.1 Review Interface Descriptions for Completeness
Review interface descriptions for coverage and completeness
Review interface data for completeness and compatibility and ensure complete coverage of all interfaces
SP2.2 Manage Interfaces
Manage internal and external interface definitions, designs and changes for products and product components .
Management of the interfaces includes maintenance of the consistency of the interfaces throughout the life of the product, coping with change by resolving noncompliance issues as they arise.
SG3 Assemble Product Components and Deliver the Pro duct
Verified product components are assembled and the integrated, verified and validated product is delivered.
SP3.1 Confirm Readiness of Product Components for Integration .
Confirm, prior to assembly, that each product component required to assemble the product has been properly identified, functions according to its description, and that the product-component interfaces comply with their descriptions.
The purpose here is to ensure that the properly identified product component that meets its description can actually be assembled according to the product integration sequence and available procedures.
SP3.2 Assemble Product Components
Assemble product components according to the product integration sequence and available procedures.
Ensure the assembly sequence is properly performed
SP3.3 Evaluate Assembled Product Components
Evaluate assembled product components for interface compatibility
SP3.4 Package and Deliver the Product or Product Component
Package the assembled product or product component and deliver it to the appropriate customer
Use effective methods to include Diskettes, CDs. Hardcopy documents etc and outline copyright, licensing and security issues.
Delivery and possible installation at customer site should be confirmed.
Verification VER
Purpose : to ensure that selected work products meet their specific requirements.
SG1 Prepare for Verification
Preparation for verification is conducted
SP1.1 Select Work Products for Verification
Select the work products to be verified and the verification methods that will be used for each
Work products are selected based on their contribution to meeting project objectives and requirements and to addressing risks.
Verification methods can vary but include, inspections, peer reviews, audits, walkthroughs, testing and simulation
SP1.2 Establish the Verification Environment
Establish and maintain the environment needed to support verification
The type of environment required will depend on the work products selected for verification and the verification methods used. A Peer Review may require little more than a package of materials, reviewers and a room. A product test may require simulators, scenario generators, interfaces with other systems etc.
SP1.3 Establish Verification Procedures and Criteria
Establish and maintain verification procedures and criteria for the selected work products
Once a comprehensive procedure for verification of a product has been established, the expected results from verification should be identified as should any tolerances allowed in the observation.
SG2 Perform Peer Reviews
Peer Review is performed on selected work products
SP2.1 Prepare for Peer Reviews
Prepare for peer reviews of selected work products
Identify the staff who will be invited to participate in the peer review of each work product, identifying the key reviewers who must participate. Prepare and update any materials (checklists and review criteria) and schedule.
SP2.2 Conduct Peer Reviews
Conduct peer reviews on selected work products and identify issues resulting from the peer review
The purpose is to remove defects early and the review may be performed on work products from specification, design, test and implementation activities. When issue aris they should be communicated to the primary developer of the work product for correction
SP2.3 Analyse Peer Review Data
Analyse data about presentation, conduct and results of the peer reviews.
Data to be recorded and analysed might include product name, product size, composition of the review team, preparation time per reviewer, length of the review meeting, number of defects found, type and origin of defect, etc.
SG3 Verify Selected Work Products
Selected work products are verified against their specified requirements
SP3.1 Perform Verification
Perform verification on the selected work products
Perform verification of selected work products against their requirements and identify resultant action items.
SP3.2 Analyse Verification Results and Identify Corrective Action
Analyse the results of all verification activities and identify corrective actions
Compare actual results to expected results, identifying products which have not met their requirements or identify problems with the methods, procedures, criteria and verification environment. Provide information on how defects are to be resolved and formalise it in a plan.
Validation VAL
Purpose: to demonstrate that a product or product component fulfils it intended use when placed in its intended environment.
SG1 Prepare for Validation
Preparation for validation is conducted
SP1.1 Select Products for Validation
Select product and product components to be validated and the validation methods that will be used for each
Products and product components are selected based on their relationship to user needs. Validation methods address the operation, maintenance, support and training for the product as appropriate to ensure that user needs are satisfied.
SP1.2 Establish the Validation Environment
Establish and maintain the environment needed to support validation .
SP1.3 Establish Validation Procedures and Criteria
Establish and maintain procedures and criteria for validation
Issues affecting validation of the product or component are identified and resolved.
The environment, operational scenario, procedures, inputs, outputs and criteria for the validation of the selected product are documented.
SG2 Validate Product or Product Components
The product or product components are validated to ensure that they are suitable for use in their intended operating environment
SP2.1 Perform Validation
Perform validation on the selected products and product components
Validation activities are performed and the resulting data are collected according to the established methods, procedures and criteria.
SP2.2 Analyse Validation Results
Analyse the results of the validation activities and identify issues
Analysis reports indicate whether the needs are met, they document the degree of success or failure and categorise probable cause of failure. The results are compared with established evaluation criteria to determine a course of action.