Cell Reproduction
advertisement

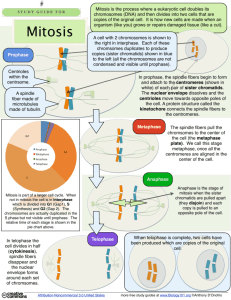
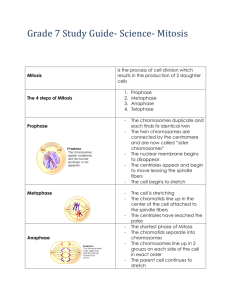
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – the organic compound in all organisms which contains all the instructions for making and operating the organism. In eukaryotic organisms DNA is stored in the nucleus. Nitrogen bases – make up the center of DNA molecules and are responsible by their arrangement for the making of proteins when DNA opens up. Nitrogen Base pairs – The DNA molecule has four nitrogen bases that always connect only one way at the molecule’s center: Adenine always connects with Thymine Cytosine always connects with Guanine Chromatin – DNA in a nucleus before it is formed into chromosomes for cell division. Chromosomes - DNA strands organized in the beginning of cell reproduction. Diploid – Organisms contain paired chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs (46 chromosomes). Each chromosome in a pair is very much alike (called homologous). Each parent contributes one chromosome to each pair. Genes - specific sections of the DNA strands that make specific proteins Allele – there maybe more than one type of construction of a gene. Each different type is called an allele. For instance, a gene for eye color may have one allele that produces brown eyes and another allele that produces green eyes. Chromatids – chromosome copies (1 copy for each chromosome) made just before mitosis Centromere – the joining point of chromatids Cell Life Cycle - The development of a cell from birth to death.. Interphase - The time of growth and development of a cell. This phase may last 90% of the cell’s life. Chromosomes will be copied, forming chromatids, in a nucleus in preparation for cell reproduction (mitosis). Mitosis - The copying of DNA in a Eukaryotic cell resulting in two cells from one. First two nuclei are made from one. Then a new membrane separates the two new nuclei with cytoplasm into two new cells. There are 4 phases to mitosis. In order they are: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase Prophase - the nucleolus and nucleus membrane breakdown. The chromatids are visible. The spindle fibers begin to stretch across the cell. Centrioles – a pair of organelles found only in animal cells. During prophase they move to opposite ends of the cell and organize the spindle fibers. Plant cells have no centrioles but have spindle fibers. Spindle fibers – pull apart chromatids by the centromere to opposite ends of the cell during anaphase. Metaphase – chromatid pairs line up in the center of the cell and spindle fibers attach to their centromeres from both sides of the cell. Anaphase – the chromatid pairs’ centromeres separate. The spindle fibers shorten moving the separated chromatids to opposite ends of the cell. Telophase – the cytoplasm begins to divide, spindle fibers disappear, as the chromosomes begin to uncoil and the two new nuclei form, one on each side of the divided cytoplasm. Asexual Reproduction – an organism produces another of its kind without mating. The DNA in the new organism is identical to the parent’s DNA. Budding – a form of asexual reproduction for some eukaryotic organisms involving mitosis. Fission – a form of asexual reproduction for prokaryotic organisms, like bacteria which have no nucleus