Developmental Psychology (MPTC/809-188)
advertisement

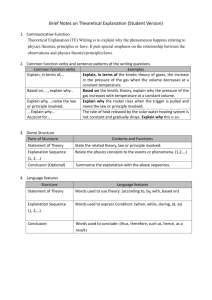
Elise Schmidt Theories of Development Chart Developmental Psychology 1 Learning Plan 1: Theories of Development Chart Theory Category Psychoanalytic Theories Cognitive Theory Description of the Theory Freud’s Theory Five Stages of psychosexual development; Oral stage (birth-1 ½), Anal stage (1 ½ to 3), Phallic Stage (3 to 6), Latency Stage (6 to puberty), and Genital Stage (Puberty+) Problems because of childhood experiences Adult personality based how we handle these experiences Erickson’s Theory Eight Stages of human development; trust vs. mistrust(first year), autonomy vs. shame(1-3), initiative vs. guilt (3-5), industry vs. inferiority (6-puberty), Identity vs. identity confusion (10-12), intimacy vs. isolation (20s&30s), generatively vs. stagnation (40s & 50s), and integrity vs. despair (60s+) Crisis in life are turning points More successful in handling the crisis the healthier development will be Piaget’s Four Stages; sensorimotor stage (birth to 2), Key Terms relevant to the Theory Oral Stage-pleasure center mouth Anal-focus on anus Phallic-focus on genitals Latency- represses sexual interest Genital- sexual reawaking, sexual pleasure from outside of family trust vs. mistrust-sets expectations of world autonomy vs. shamediscover independence initiative vs. guiltrequire new behavior industry vs. inferioritymastering knowledge Identity vs. identity confusion-finding who you are intimacy vs. isolationmaking intimate relationships generatively vs. stagnation-lead useful lives integrity vs. despairreview of life Sensorimotor Stage- Criticisms of the Theory Lack of scientific support Too much emphasis on sexual underpinnings Image of people too negative Contributions of the Theory Emphasis on a developmental framework, family relationships, and unconscious aspects of the mind Lack of scientific support Too much emphasis on sexual underpinnings Image of people too negative Emphasis on a developmental framework, family relationships, and unconscious aspects of the mind Skepticism about the Positive view of Elise Schmidt Theories of Development Chart Developmental Psychology 2 Theories Cognitive Development Theory preoperational stage(2 to 7), concrete operational stage(7 to 11), and formal operation stage (11 to 15) Child construct their understanding of the world Organization and adaptation Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Cognitive Theory Culture and social interaction guide cognitive development Learning to use inventions of society construct understanding by sensory Preoperational stagerepresent the world with words and images Concrete Operational Stage- reason logic Formal Operationreasons more abstract, idealistic, and logical ways Culture-behavior patterns, beliefs, and all other products of a group that are passed on from generation to generation pureness Too little attention to individuals variations development Emphasis on the active construction of understanding Too little attention to individuals variations Positive view of development Emphasis on the active construction of understanding Elise Schmidt Theories of Development Chart Developmental Psychology 3 Theory Category Key Terms relevant to the Theory Thinking- information processing Criticisms of the Theory Operant conditioning Rewards and punishments shape development Key factor is behavior Operant conditioningbehavior with rewarding stimulus more likely to happen again Too little emphasis on cognition Inadequate attention to developmental changes Emphasis on scientific research and environmental determinates of behavior Bandura’s Social Cognitive Theory Behavior, environment, and cognition are key factors to development Someone can control their success Development is learned Behavior- learned from observation Cognition- people represent the behavior of others; may adopt behaviors Inadequate attention to developmental changes Emphasis on scientific research and environmental determinates of behavior Ethological Theory Ethological Theory Presence or absence of certain experiences long-lasting effects Ethology Biological and evolutionary base of development Ethology- behavior influenced by biology, tied to evolution, characterized by critical periods Too much emphasis on biological foundations and beliefs the critical and sensitive periods may be too rigid Ecological Theory Ecological Theory Focus on five environmental systems; Microsystems, mesosystem, exosystem, macrosystem, and chronosystem Range of social context beyond family Microsystems-setting where person lives Mesosystemrelationships in microsystem Exosystem- links in social settings where person doesn’t have active role Inadequate attention to biological factors, too little emphasis on cognitive factors Focus on biological and evolutionary bias of development Use of careful observations in naturalistic settings A systematic examination of macro and micro dimensions of environment systems Attention to connections between environment systems Behavioral and Social Cognitive Theories Theory Description of the Theory Information Processing Theory People manipulate information, monitor it, and strategize about it People develop gradually slowly increasing knowledge Skinner’s Operant Conditioning Too little attention to individuals variations Contributions of the Theory Positive view of development Emphasis on the active construction of understanding Elise Schmidt Theories of Development Chart Developmental Psychology 4 Eclectic Theoretical Orientation Eclectic Theoretical Orientation Does not follow any one theoretical approach Selects from theories what is considered best Use different theories to discover new information Macrosystem- culture where person lives Chronosystempatterning of environmental events and transions Scientific methodapproach used to find accurate information Theory- set of ideas that help explain and make predictions Hypotheses- prediction that can be tested Still theories and not facts Refined through scientific method Your preferred theory and reasons why…. The theory that I prefer is the Social Cognitive theory. Although I like how Erikson’s focuses on development and family I believe that behavior, environment, and cognition are key points. I strongly believe that observation of others, especially at young ages, effects who you are as person. Birth to puberty your environment and learned behavior from your parents sets the stage for your future in my eyes and during puberty what you observe from your peers and role models reflects what your actions are going to be. Criteria Values You summarize the psychodynamic (psychoanalytic) theoretical framework to development (definition, theories, theorists, contributions and criticism of the theoretical framework, and relevant concepts within the framework). 10 9 8 4 0 You summarize the cognitive theoretical framework to development (definition, theories, theorists, contributions and criticism of the theoretical framework, and relevant concepts within the framework). 10 9 8 4 0 You summarize the behavioral/social cognitive theoretical framework to development (definition, theories, theorists, contributions and criticism of the theoretical framework, and relevant concepts 10 9 8 4 0 Elise Schmidt Theories of Development Chart Developmental Psychology 5 within the framework). You summarize the ethological theoretical framework to development (definition, theories, theorists, contributions and criticism of the theoretical framework, and relevant concepts within the framework). 10 9 8 4 0 You summarize the ecological theoretical framework to development (definition, theories, theorists, contributions and criticism of the theoretical framework, and relevant concepts within the framework). 10 9 8 4 0 You summarize the eclectic theoretical framework to development (definition, theories, theorists, contributions and criticism of the theoretical framework, and relevant concepts within the framework). 10 9 8 4 0 You explain the theory you prefer and reasons why you selected the theory. 10 9 8 4 0 CORE ABILITIES - COMMUNICATE CLEARLY CORE ABILITIES COMMUNICATE CLEARLY You demonstrate mastery of grammar, spelling, punctuation, capitalization, word usage and sentence structure. 10 9 8 4 0 Your writing is organized (paragraphs, headings and subheadings, or other organizational devices), clear (it's easy to read and understand), concise (you use action verbs; you do not ramble or include irrelevant information), and cohesive (words and ideas flow logically from one idea, sentence and/or paragraph to another). 10 9 8 4 0 CORE ABILITIES - THINK CRITICALLY AND CREATIVELY You use language that is free from bias (including loaded language), obscenities, and absolutes (all, always, everyone, no one, totally, all of the time, CORE ABILITIES THINK CRITICALLY AND CREATIVELY 10 9 8 4 0 Elise Schmidt Theories of Development Chart Developmental Psychology 6 etc.). You provide sufficient, specific, valid, relevant support (i.e., facts. reasons, examples, details, statistics, anecdotes and quotes) to aid in understanding your ideas and information, and to support your conclusions and/or opinions. CORE ABILITIES - ACT RESPONSIBLY You follow directions (followed Formatting Requirements, APA Requirements, included name on assignment, saved document per directions). Total Points Possible 10 9 8 4 0 CORE ABILITIES ACT RESPONSIBLY 10 9 8 4 0 120 Total Points Earned Percent grade = Total Points Earned divided by Total Points Possible You meet deadlines. (Points subtracted from Points Earned score) Submitted without scoring guide (Points subtracted from Points Earned score) Final Grade/Percent - 5 percentage points if submitted after the due date - 5 percentage points if submitted without the scoring guide