13-Integrative and Eclectic Therapies
advertisement

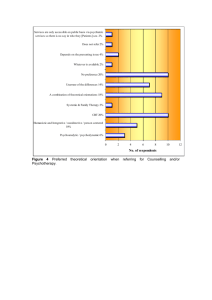
Integrative and Eclectic Therapies Transtheoretical Therapy Future of Psychotherapy Integrative and Eclectic Therapies Psychotherapy integration is motivated by a desire to look past the confines of a singlesystem approach so that clients may benefit from other approaches. Why have Integrative and Eclectic approaches become popular? 1. Proliferation of therapies 2. Inadequacy of any single theoretical system for all patients and problems 3. External socioeconomic contingencies 4. Growing popularity of short-term, problem-focused treatments 5. Opportunities for therapists to observe and experiment with various treatments 6. Recognition that therapeutic commonalities play major roles in determining therapy outcome 7. Identification of specific treatments of choice 8. Development of professional societies for integration Technical Eclecticism versus Theoretical Integration See Table 14.2 Technical Eclecticism – Theoretical Integration – - - Most common combos are o Cognitive and behavioral o Humanistic and cognitive o Psychoanalytic and cognitive Transtheoretical Therapy This theory allows the clinician to use different techniques depending on the client’s stage of change. 1. This therapy draws on the common factors from all therapies as well as the unique aspects of each. 2. It is based on empirical findings. 3. Accounts for change inside and outside of therapy. 4. Generalizes to a broad range of behavior changes, including physical health changes. 5. Encourages psychotherapists to become innovators, not just borrowers. Processes of Change Covert or overt activities that people engage in to alter emotion, thinking, behavior, or relationships. 10 Processes of change with the most empirical support: 1. Consciousness Raising 2. Catharsis 3. Self-reevaluation 4. Environmental reevaluation 5. Self-liberation 6. Social liberation 7. Counterconditioning 8. Stimulus Control 9. Contingeny Management 10. Helping relationship Across the board, most therapies agree on the processes; they most often disagree on the problem that needs to be changed. Table 15.1 Consciousness raising is most often used in a variety of therapies. Client expectation or placebo may account for 10-40% of change. Stages of Change 1. Precontemplation – a. b. c. “I don’t really have any problems that need changing” 2. Contemplation a. b. c. d. “I’ve been thinking I might want to change something about myself” 3. Preparation a. b. c. 4. Action a. b. c. d. “I am really working hard to change” 5. Maintenance a. b. Spiral pattern Relapse is Termination Integration of Stages and Processes Doing the right thing at the right time. Using insight-oriented techniques for a person not yet ready to change; using behavior-oriented techniques for the person ready to take action. Specific processes work better during specific stages. Precontemplation - consciousness raising o o o - catharsis o Contemplation - consciousness raising o - self-re-evaluation o - environmental re-evaluation o Preparation - self-liberation o Action - counterconditioning - contingency management - stimulus control Maintenance - continuing processes that have worked so far Levels of Change 1. Symptom/situational problems 2. Maladaptive cognitions 3. Current interpersonal conflicts 4. Family/systems conflicts 5. Intrapersonal conflicts A symptom can be the result of any of the previous levels (or multiple levels). The deeper, more historical the cause, the more resistant the symptom will be to change. Therapists should try to explain symptoms using the lowest level of change appropriate. Three basic strategies 1. Shifting levels: 2. Focus on key levels: 3. Maximum impact: TTT Relationship - Therapist is expert on change. - Relationship depends on the stage. - Move from nurturing parent to Socratic teacher, experienced coach, consultant. Future of Psychotherapy Twelve Emerging Directions 1. Industrialization of Mental Health Care – a. 2. Practice and Treatment Guidelines – a. b. 3. Prescriptive Matching a. 4. Cultivation and Customization of the Therapeutic Relationship a. b. 5. Technological Applications a. Behavioral e-health – b. Virtual therapy – c. Telepsychotherapy – 6. Treatment of Health Behaviors a. Over of health costs are due to behaviors 7. Proactive Outreach to Entire Populations a. Increase the percentage of high-risk people receiving services b. Getting out into the community, primary care 8. Self-Help Resources a. Can be used in conjunction with therapy 9. Relapse Prevention a. Most used with 10. Decline of Personality in Psychotherapy Systems a. Less focus on _______________________, more focus on __________________________ 11. Incorporation of Spiritual and Religious a. 92% of Americans are affiliated with a religion b. 96% profess belief in God or universal spirit c. Research supports the inclusion of client’s religion 12. Psychotherapy Works! a. Effect size = .80 (79% of clients are better off than those not seeking tx)