Intro to the Integumentary System MLP English
advertisement

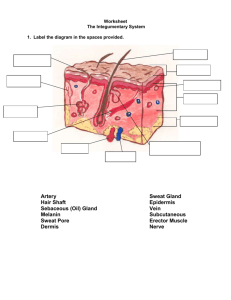
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System Instructor Serial/Semester Location Start/Finish Time Date LESSON OBJECTIVE Performance: To gain an understanding of the anantomy and physiology of the integumentary system. Conditions: The student will be presented a powerpoint presentation by the instructor and will have all necessary references made available to him/her. Standard: 1. Given the five elements of the nursing care process and a scenario of a patient with a skin disorder by correctly responding to written, oral, and experiential assessment measures. TEACHING POINTS 1. Define key terms related to the integumentary system. 2. Describe the functions of the skin. 3. 4. 5. Identify the layers and appendages of the skin. Describe age related changes in the skin. List the components of a nursing assessment of the skin. 6. 7. Describe tests used in the diagnosis of skin disorders Identify various types of therapies used in the treatment or management of skin disorders. (Timby) 8 9. 10. INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGY Interactive Lecture Method: Instructor Media: Classroom Environment: OTHER LESSON SPECIFICATIONS Knowledge Lesson Type of Lesson: 1/50 Ratio: Resources: . End of Lesson Test: None Minutes Instructional Time: 153 Reference(s): ISBN 0-323-01728-2 Adult Health Nursing, 4th Edition 01 Jan 2003 ISBN 0-7817-3553-X Introductory Medical-Surgical Nursing, 8th Edition 01 Jan 2002 LESSON PLAN APPROVAL Signature of Standards Officer Date AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System INTRODUCTION Allocated Time: Review: 5 Minutes You have had previous anatomy and physiology lectures in your combat medic training, this lecture will build upon prior instruction. Objective: To discuss/describe topics related to the nursing process. Importance: Nurses work in various health care settings so it is important to gain an understanding of this subject as it will apply to your clinical practice. Fit: The term "integument" means covering. The skin, composed of a variety of tissues, is the largest organ of the body. An adult's skin weighs 5 to 8 pounds (about 3 to 4 kilograms). If you spread out your skin, it would measure around 20 square feet. In your 91W program you learned that 1/3 of the sick call load is related to skin disorders. In this block we will review many of the skin diseases that you learned to treat as a 91W and in addition focus on the nursing assessment and management of the patient with a skin disorder. Approach: You will be presented the subject in lecture format and will be tested using a written exam at a later date. Control Statement: If you have any questions during the lesson please feel free to ask. BODY 1. Teaching Point: Define key terms related to the integumentary system. Minutes Allocated Time: Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Skill Lesson Learning Support: a. Alopecia - loss of hair b. Angioma - a tumor-like mass formed by a group of dilated blood vessels c. Crust - scab on an abrasion d. Carbuncle - cluster of furuncles. Infection of several hair follicles that spreads to surrounding tissue e. Dermatitis - superficial infection of the skin f. Eczema - lesions surrounded by erythema. They rupture then dry and itch. Associated with allergies g. Erythema - redness or inflammation of the skin h. Excoriation - surface layer injury caused by scratching or abrasion 1 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System i. Furuncle - boil j. Keloid - raised, hard, shiny scar k. Necrosis - dead tissue l. Nodule - an elevated solid mass deeper than a papule m. Macule - a flat area that is a change in the color of the skin (freckles) n. Papule - elevated, firm area less than 1 cm in diameter o. Pruritus - itching p. Pustule - elevated lesion filled with purulent fluid q. Tinea pedis - athlete's foot r. Tumor - outgrowth of skin cells s. Vesicle - circumcised elevation containing serous fluid (chicken pox, herpes zoster) t. Wheal - hives, irregularly shaped, elevated Knowledge Lesson: Question: Answer: Skill Lesson: Check on Learning In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class. What two terms refer to elevated solid masses with the difference being size and depth? Papule and Nodule In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill. 2. Teaching Point: Describe the functions of the skin. Minutes Allocated Time: Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Skill Lesson Learning Support: a. Homeostatis and protection of the internal organs are the broad functions of the integumentary system. These are broken down into the following: (1) Barrier against infection: prevents microorganisms and foreign substances from coming in contact with the underlying organs and body parts (2) Serves as a sensory organ that responds to pressure, pain, heat and cold 2 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System (3) Temperature control (a) Blood vessels near the surface constrict in response to cold to preserve heat (b) Dilate when hot to release body heat b. Prevention of dehydration c. Excretion of waste products d. Vitamin D synthesis: Cholesterol compounds located in the skin are converted to vitamin D when exposed to the ultraviolet rays of the sun. Vitamin D is necessary for bone development Knowledge Lesson: Question: Answer: Check on Learning In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class. What are the broad main functions of the skin? Homeostasis and protection Skill Lesson: In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill. 3. Teaching Point: Identify the layers and appendages of the skin. Minutes Allocated Time: Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Skill Lesson Learning Support: a. Layers of the Skin (1) Epidermis: composed of three layers (a) Stratum corneum, which is avascular and comprises the outer portion. These cells are flat and are filled with a protein called keratin, which makes the cells dry, tough and somewhat waterproof (b) Pigment layer composed of specialized cells called melanocytes, which give rise to melanin. Melanin is a pigment in the skin, which gives the skin color. The more melanin, the darker the skin (c) Stratum germinativum is the inner layer of the epidermis. These cells can reproduce by receiving a blood supply from the underlying dermis through the process of diffusion. New cells replace damaged cells in the stratum corneum. This allows the skin to repair itself (2) Dermis: just below the epidermis layer (a) Contains blood vessels, nerves, glands and hair follicles 3 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System (b) Cells are composed of connective tissue and elastic fibers (c) Cells are bathed in interstitial fluid (3) Subcutaneous Layer: layer below the dermis that connects the skin to the muscle surface (a) Composed of adipose tissue and loose connective tissue (b) Provides shape and contour to the body (c) Primary functions include 1) Store water and fat 2) Insulation 3) Protection of the body organs 4) Provides a pathway for nerves and blood vessels. Question: Which layer of the skin contains blood vessels? Answer: Dermis b. Appendages of the skin (1) Sudoriferous (sweat) glands: (a) Tube-like structures located in the dermis and subcutaneous layers (b) Excretion of sweat helps cool the body surface and (c) Rid the body of waste products such as uric acid, ammonia and other products (2) Ceruminous glands: (a) Secrete a waxlike substance called cerumen (b) Located in the external ear canal (3) Sebaceous (oil) glands: (a) Secrete sebum through the hair follicles (b) Function is to lubricate the skin and hair (c) Sebum also inhibits bacterial growth (4) Hair: composed of modified dead epidermal tissue (keratin) 4 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System (5) Nails: composed of tightly packed keratin Knowledge Lesson: Question: Answer: Check on Learning In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class. Which gland helps to cool the body's surface? Sudoriferous (sweat) gland Skill Lesson: In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill. 4. Teaching Point: Describe age related changes in the skin. Minutes Allocated Time: Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Skill Lesson Learning Support: a. Changes in the skin are the most readily recognized signs of aging (1) Aging changes include decreased tissue fluid, subcutaneous fat, and sebaceous secretions. Results in dryness, flaking, pruritus, loss of elasticity, altered turgor, and a wrinkled appearance (2) Skin of older persons more fragile and susceptible to impairment (3) Hyperkeratotic changes seen in nails, which make them thick (4) Localized clusters of melanocytes surrounded by areas of decreased pigmentation result in age spots (5) Incidence of basal and squamous cell carcinoma increases with age. Skin should be closely inspected for changes in the appearance of moles or warts Knowledge Lesson: Question: Answer: Check on Learning In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class. What are skin changes notes with aging? Decreased tissue fluid, subcutaneous fat, and sebaceous secretions. Skill Lesson: In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill. 5. Teaching Point: List the components of a nursing assessment of the skin. 15 Minutes Allocated Time: Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson 5 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System Skill Lesson Learning Support: a. Chief complaint and history of present illness (1) Complaint may be discomfort, pruritus, color changes, lesions, hair loss, or abnormal hair growth (2) Get history of present illness (a) Onset of symptoms and precipitating factors (b) Changes in the progression of symptoms (3) Past History (a) When the disorder first began (b) Where is first appeared (c) How long has the lesion been present (d) Any changes in the disorder since it first appeared (4) Allergies (5) Medications (6) Family history of skin cancer (7) Diseases that may affect skin: (a) Diabetes (b) Cancer (c) Kidney failure (d) Thyroid disease (e) Liver disease (f) Anemia (8) Personal Issues: (a) Exposure to the sun or chemicals (b) Changes in work or living environment (c) Current stressors 6 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System b. Visual Inspection of the Skin (1) Skin must be exposed and checked in an orderly sequence (2) AM bath an excellent time to assess the skin (3) Expose the area being assessed while maintaining privacy (4) Important to remember to wear gloves when inspecting the skin or mucous membranes (5) Assess general appearance of the skin: texture, dryness and skin turgor (6) Observe the color. Affected by the following: (a) Amount of hemoglobin (pallor) (b) Oxygen saturation (cyanosis) (c) Amount of substances like bilirubin, urea, or other chemicals (jaundice) (d) Amount of melanin in the epidermis (7) Temperature and texture should be assessed by touch using the palms of hands to compare opposite body areas (8) Check the mucus membranes for color, moistness, swelling, lesions (9) Assess shape and contour of nails: (Timby) Normal nail convex at 160 degrees angle between the nail base and the skin (a) Assess for clubbing, due to long standing cardiovascular disease (b) Thickening may be due to a fungal infection or poor circulation (c) Concave shaped nails called spooning and are a sign of iron deficiency (d) Check for tissue perfusion by compressing the nail beds causing them to blanch, and then release them. Color should return in 3 seconds or less. Called capillary refill time (10) Assess the scalp and distribution of hair (11) Assess for the presence of rashes, scars, lesions, and ecchymoses NOTE: Sudden onset of urticaria (hives) accompanied by intense itching may indicate a severe drug reaction. The nurse must quickly assess the patient and immediately contact the physician c. Typical Clinical Manifestations of Skin Disorders (1) Carbuncle - Infection of several hair follicles that spreads to surrounding tissue 7 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System (2) Keloid - raised, hard, shiny scar (3) Nodule - an elevated solid mass deeper than a papule (e.g.wart) (4) Macule - flat, nonpalpable area, change in the color of the skin (freckles) (5) Papule - elevated, firm area less than 1 cm in diameter (e.g. elevated nevus) (6) Pustule - elevated lesion filled with purulent fluid (e.g. acne, staphylococcal infection) (7) Tumor - outgrowth of skin cells that extend through subcutaneous tissue (epithelioma) (8) Vesicle - circumcised elevation containing serous fluid (chicken pox, herpes zoster) (9) Wheal - irregularly shaped, elevated area or superficial localized edema (e.g. hives or mosquito bite) d. Additional Terms Used to Describe the Skin (1) Atheroma - a fatty plaque (2) Bleb - a blister filled with fluid (3) Cyst - a sac or capsule containing fluid or semi-solid material (4) Excoriation - an abrasion of the outer layer of the skin (5) Exfoliated cells - dead cells shed from the skin, mucous membranes, or bone (6) Exudate - fluid, usually containing pus or bacteria (7) Fissure - a groove, crack or slit (8) Hyperplasia - extra growth of normal tissue (9) Petechiae - thin hemorrhagic spots on the skin e. Assessment of dark skin: (1) Skin color results from the reflection of light as it strikes the underlying skin pigment. Increased amount of melanin in dark skin - acts as a natural shield from the sun resulting in less skin cancer in dark skinned people (2) Darker to skin the more difficult it is to assess. Assessment of color easier in areas where the epidermis is thin - lips and mucous membranes (3) To assess rashes and skin inflammation in dark-skinned individuals, rely on palpation for warmth and indurations rather than observation 8 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System (4) Dark skin predisposed to certain skin conditions such as pseudofolliculitis, keloids, and Mongolian spots Knowledge Lesson: Question: Answer: Check on Learning In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class. Identify three disease processes that may affect the skin. (a) Diabetes (b) Cancer (c) Kidney failure (d) Thyroid disease (e) Liver disease (f) Anemia Skill Lesson: In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill. 6. Teaching Point: Describe tests used in the diagnosis of skin disorders Minutes Allocated Time: Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Skill Lesson Learning Support: a. The diagnosis of skin disorders is made mainly by visual inspection b. Skin biopsy - may be performed to identify malignant or premalignant lesions. May also aid in identifying some skin disorders c. Allergy tests such as intradermal injection, scratch test, and patch test are used to confirm an allergy to one or more substances (1) Scratch test- Scratching of the skin and applying a small amount of the test allergen (2) Patch test-appling a substance to the skin and covering with a dressing then examined in 48 hours. d. Culture and sensitivity - to determine the causative microorganism 9 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System Knowledge Lesson: Question: Answer: Check on Learning In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class. How is the diagnosis of skin conditions generally made? Visual inspection. Skill Lesson: In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill. 7. Teaching Point: Identify various types of therapies used in the treatment or management of skin disorders. (Timby) Minutes Allocated Time: Introduction: Learner Participation: Knowledge Lesson Skill Lesson Learning Support: a. Drug therapy: (1) Corticsteroids - topically or administered systemically (2) Antihistamines - relieve itching and shorten the duration of an allergic reaction (3) Antibiotics, antifungal and antiviral agents - used to treat infectious disorders (4) Scabicides and pediculicides - used in the treatment of infestations with scabies and mite and lice (5) Local (topical) anesthetics are applied to relieve minor skin pain and itching. (6) Emolients, ointments, powders and lotions sooth, protect and soften the skin (7) Antiseborrheic agents are applied directly to the scalp or as part of a shampoo (8) Antiseptics are used to reduce bacteria on the skin (9) Keratolytics dissolve thickened, cornified skin such as warts, corns, and calluses. Treated area softens and swells, facilitation removal b. Wet to dry dressings (1) Used to soothe, soften and remove crusts, debris and necrotic tissue (2) Warm water is used and various agents may be added (3) Moisten wet dressing before removal to prevent traumatizing healthy tissue (4) After soak, gently dry the treated area, then apply topical medication as ordered c. Therapeutic Baths 10 AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System (1) Used to relieve inflammation and itching and to aid in the removal of crusts and scales (2) May use cornstarch, baking soda, oatmeal colloid bath preparations, and mineral oil (3) Fill tub with warm water and mix drug or product thoroughly (4) Use washcloth or compress to apply solution gently d. Surgical excision - Used to remove benign or malignant tissue e. Laser therapy - vaporizes tissue and coagulates bleeding. Must protect eyes f. Photo therapy (1) Ultraviolet light used to promote shedding of the epidermis (2) Used to treat chronic skin conditions such as psoriasis (3) After photo therapy patient may have pruritus and dry skin (4) Assess for signs and symptoms of photoxicity (redness, vesicles, pain) (5) Often combined with medications or other treatments g. Lifestyle changes (1) Fatigue and emotional stress may aggravate a skin condition (2) Diet may be a factor Knowledge Lesson: Question: Answer: Check on Learning In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class. What are some lifestyle risk factors for skin disease? (1) Fatigue and emotional stress may aggravate a skin condition (2) Diet may be a factor Skill Lesson: 11 In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill. AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP) Nursing Program Introduction to the Integumentary System END OF LESSON TEST Allocated Time: Instructions: Test Questions or Performance Expected: Test Key: 0 Minutes CONCLUSION Allocated Time: Summary: 5 Minutes Review and re-emphasize the difficult Teaching Points below. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Define key terms related to the integumentary system. Describe the functions of the skin. Identify the layers and appendages of the skin. Describe age related changes in the skin. List the components of a nursing assessment of the skin. Describe tests used in the diagnosis of skin disorders Identify various types of therapies used in the treatment or management of skin disorders. (Timby) Closing Statement: You will be presented the subject in lecture format and will be tested using a written exam at a later date. Re-motivating Statement: The term "integument" means covering. The skin, composed of a variety of tissues, is the largest organ of the body. An adult's skin weighs 5 to 8 pounds (about 3 to 4 kilograms). If you spread out your skin, it would measure around 20 square feet. In your 91W program you learned that 1/3 of the sick call load is related to skin disorders. In this block we will review many of the skin diseases that you learned to treat as a 91W and in addition focus on the nursing assessment and management of the patient with a skin disorder. 12