Standard 3 Component 1 Objective 1 Compare rocks and minerals
advertisement

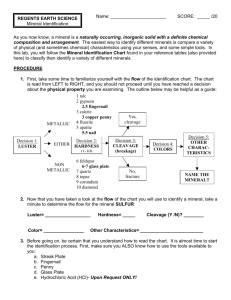
Standard 3 Component 1 Objective 1 Compare rocks and minerals and describe how they are related. A.Recognize that most rocks are composed of minerals. B.Observe and describe the minerals found in rocks (e.g., shape, color, luster, texture, hardness). Vocabulary: Mineral: A solid inorganic substance of natural occurrence Luster: Describes how a mineral appears to reflect light, and how brilliant or dull the mineral is. Texture: The shape or pattern on the surface of a mineral. Hardness: A minerals resistance to scratching Streak: The color of the powder left by a mineral Cleavage: The tendency of a mineral to break along flat surfaces in a geometric repetitive manner. Mohs Hardness Scale: Describes the scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of a harder material to scratch a softer material Learning Activities Analogies/Bridge Map Notes SMARTNotes with thinking map integration Mineral ID Lab Standard 3 Module 1 Essential Questions 1.) Explain how minerals and rocks are related. 2.) Give 3 analogies that have the same relationship as minerals do to rocks. Example: minerals are to rocks as words are to sentences 1.) 2.) 3.) 3.) Explain each of the following mineral physical properties and how you identified each in the lab. Luster Cleavage Streak Hardness Texture 4.) What is Moh’s Hardness Scale? 5.) Use the mineral identification chart below. A mineral has a white streak, no special properties, can be any color, has no cleavage, has a non-metallic luster, and a hardness of 7. What mineral is this? EXPLAIN how you came up with your answer. Standard 3 Module 1 Practice Content Quiz key 1. A mineral was found on an expedition to the Andes Mountains in South America. The physical properties are listed below. Use the key to determine the name of the mineral. This unknown mineral scratches glass, is not metallic, and does not have cleavage, and is not granular. What is the identity of this mineral? 2. A. Horneblend B. Calcite C. Quartz D. Olivine Metallic Luster Scratches glass Cleavage No Cleavage PYRITE Brass- MAGNETITE yellow; black streak; cubic crystals; Hardness: 6-6.5 Black; strongly magnetic; Hardness: 6 Does not scratch glass Cleavage No Cleavage Nonmetallic Luster Scratches glass Cleavage No Cleavage CHALCO PYRITE Brass yellow; black streak; Hardness: 3.5-4 GRAPHITE HORNBLENDE Black to dark green; oblong cleavage planes with splinters; hardness:5-6 OLIVINE CALCITE BAUXITE Shades of green granular masses; Hardness: 6-7 Colorless to white; rhombohedral cleavage; fizzes in HCl acid; Hardness: 3-4 Made of dark rounded spheres which are the mineral; Hardness: 2-4 HEMATITE Black-grey: red streak, hardness of 6 GALENA FELDSPAR QUARTZ Any Shiny Gray; black streak; very heavy; cubic crystals; Hardness: 2.5 Flesh-colored or white; two cleavage planes at nearly right angles; Hardness: 6 color, white or clear; glassy luster; Hardness: 7 DOLOMITE Colorless to white; fizzes in HCl Acid if powder; Hardness: 3.5-4 KAOLINITE White to rust; earthy odor when wet; uneven fracture; Hardness: 1 Lead-Pencil; black streak; leaves lots of smudges on hands, Hardness: 1 Does not scratch glass Cleavage No Cleavage 3. What is the name of the mineral with the physical and chemical properties listed below? Physical Properties Chemical Properties cleavage- present does not oxidize or rust luster- non-metallic reacts with HCl acid in powder form hardness- does not scratch glass streak- white A. Bauxite B. Dolomite Metallic Luster Scratches glass Cleavage No Cleavage PYRITE Brass- MAGNETITE yellow; black streak; cubic crystals; Hardness: 6-6.5 Black; strongly magnetic; Hardness: 6 C. Calcite D. Feldspar Does not scratch glass Cleavage No Cleavage Nonmetallic Luster Scratches glass Cleavage No Cleavage CHALCO PYRITE Brass yellow; black streak; Hardness: 3.5-4 GRAPHITE HORNBLENDE Black to dark green; oblong cleavage planes with splinters; hardness:5-6 OLIVINE CALCITE BAUXITE Shades of green granular masses; Hardness: 6-7 Colorless to white; white streak rhombohedral cleavage; fizzes in HCl acid; Hardness: 3-4 Made of dark rounded spheres which are the mineral; Hardness: 2-4 HEMATITE Black-grey: red streak, hardness of 6 GALENA FELDSPAR QUARTZ Any Shiny Gray; black streak; very heavy; cubic crystals; Hardness: 2.5 Flesh-colored or white; two cleavage planes at nearly right angles; Hardness: 6 color, white or clear; glassy luster; Hardness: 7 DOLOMITE Colorless to white; white streakfizzes in HCl Acid if powdered; Hardness: 3.5-4 KAOLINITE White to rust; earthy odor when wet; uneven fracture; Hardness: 1 Lead-Pencil; black streak; leaves lots of smudges on hands, Hardness: 1 Does not scratch glass Cleavage No Cleavage 4. What analogy best describes the relationship between minerals and rocks? A. cars to road B. student to desk C. policeman to firefighter D. words to sentences 5. What analogy best describes the relationship between minerals and rocks? A. water to drink B. trees to forest C. plastic to computer D. book to chapter 6. What analogy best describes the relationship between minerals and rocks? A. cells to tissue B. bone to arm C. teacher to student D. car to tunnel Standard 3 Module 1 Practice Vocab Quiz 1. A solid inorganic substance of natural occurrence A. Texture B. Cleavage C. Mineral D. Luster 2. Describes the scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of a harder material to scratch a softer material A. Luster B. Mohs Hardness Scale C. Mineral D. Texture 3. A minerals resistance to scratching A. Texture B. Cleavage C. Hardness D. Luster 4. The color of the powder left by a mineral A. Streak B. Cleavage C. Texture D. Luster 5. The tendency of a mineral to break along flat surfaces in a geometric repetitive manner. A. Streak B. Cleavage C. Texture D. Luster 6. The shape or pattern on the surface of a mineral. A. Streak B. Cleavage C. Texture D. Luster 7. Describes how a mineral appears to reflect light, and how brilliant or dull the mineral is. A. Streak B. Cleavage C. Texture D. Luster Standard 3 Module 1 Essential Questions Key 1.) Explain how minerals and rocks are related. Minerals make up rocks. Minerals are the building blocks of rocks 2.) Give 3 analogies that have the same relationship as minerals do to rocks. Example: minerals are to rocks as words are to sentences 1.) sentences are to paragraphs 2.) cells are to tissue 3.) students are to class 3.) Explain each of the following mineral physical properties and how you identified each in the lab. Luster how a mineral reflects light cleavage a minerals tendency to break in a geometric repetitive pattern streak the color of the powder that a mineral leaves behind on a streak plate Hardness a minerals resistance to scratching Texture The appearance of the surface of a mineral 4.) What is Moh’s Hardness Scale? A scale that shows the relative hardness of various materials and minerals. 5.) Use the mineral identification chart below. A mineral has a white streak, no special properties, can be any color, has no cleavage, has a non-metallic luster, and a hardness of 7. What mineral is this? EXPLAIN how you came up with your answer. Quartz because the only other one that is close has a green color only. Standard 3 Module 1 Practice Content Quiz key 1. A mineral was found on an expedition to the Andes Mountains in South America. The physical properties are listed below. Use the key to determine the name of the mineral. This unknown mineral scratches glass, is not metallic, and does not have cleavage, and is not granular. What is the identity of this mineral? A. Horneblend B. Calcite C. Quartz D. Olivine Metallic Luster Scratches glass Cleavage No Cleavage PYRITE Brass- MAGNETITE yellow; black streak; cubic crystals; Hardness: 6-6.5 Black; strongly magnetic; Hardness: 6 Does not scratch glass Cleavage No Cleavage Nonmetallic Luster Scratches glass Cleavage No Cleavage CHALCO PYRITE Brass yellow; black streak; Hardness: 3.5-4 GRAPHITE HORNBLENDE Black to dark green; oblong cleavage planes with splinters; hardness:5-6 OLIVINE CALCITE BAUXITE Shades of green granular masses; Hardness: 6-7 Colorless to white; rhombohedral cleavage; fizzes in HCl acid; Hardness: 3-4 Made of dark rounded spheres which are the mineral; Hardness: 2-4 HEMATITE Black-grey: red streak, hardness of 6 GALENA FELDSPAR QUARTZ Any Shiny Gray; black streak; very heavy; cubic crystals; Hardness: 2.5 Flesh-colored or white; two cleavage planes at nearly right angles; Hardness: 6 color, white or clear; glassy luster; Hardness: 7 DOLOMITE Colorless to white; fizzes in HCl Acid if powder; Hardness: 3.5-4 KAOLINITE White to rust; earthy odor when wet; uneven fracture; Hardness: 1 Lead-Pencil; black streak; leaves lots of smudges on hands, Hardness: 1 Does not scratch glass Cleavage No Cleavage 2. What is the name of the mineral with the physical and chemical properties listed below? Physical Properties Chemical Properties cleavage- present does not oxidize or rust luster- non-metallic reacts with HCl acid in powder form hardness- does not scratch glass streak- white A. Bauxite B. Dolomite Metallic Luster Scratches glass Cleavage No Cleavage PYRITE Brass- MAGNETITE yellow; black streak; cubic crystals; Hardness: 6-6.5 Black; strongly magnetic; Hardness: 6 C. Calcite D. Feldspar Does not scratch glass Cleavage No Cleavage Nonmetallic Luster Scratches glass Cleavage No Cleavage CHALCO PYRITE Brass yellow; black streak; Hardness: 3.5-4 GRAPHITE HORNBLENDE Black to dark green; oblong cleavage planes with splinters; hardness:5-6 OLIVINE CALCITE BAUXITE Shades of green granular masses; Hardness: 6-7 Colorless to white; white streak rhombohedral cleavage; fizzes in HCl acid; Hardness: 3-4 Made of dark rounded spheres which are the mineral; Hardness: 2-4 HEMATITE Black-grey: red streak, hardness of 6 GALENA FELDSPAR QUARTZ Any Shiny Gray; black streak; very heavy; cubic crystals; Hardness: 2.5 Flesh-colored or white; two cleavage planes at nearly right angles; Hardness: 6 color, white or clear; glassy luster; Hardness: 7 DOLOMITE Colorless to white; white streakfizzes in HCl Acid if powdered; Hardness: 3.5-4 KAOLINITE White to rust; earthy odor when wet; uneven fracture; Hardness: 1 Lead-Pencil; black streak; leaves lots of smudges on hands, Hardness: 1 3. What analogy best describes the relationship between minerals and rocks? A. cars to road B. student to desk C. policeman to firefighter D. words to sentences 4. What analogy best describes the relationship between minerals and rocks? A. water to drink B. trees to forest C. plastic to computer D. book to chapter Does not scratch glass Cleavage No Cleavage 5. What analogy best describes the relationship between minerals and rocks? A. cells to tissue B. bone to arm C. teacher to student D. car to tunnel Standard 3 Module 1 Practice Vocab Quiz key 1. A solid inorganic substance of natural occurrence A. Texture B. Cleavage C. Mineral D. Luster 2. Describes the scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of a harder material to scratch a softer material A. Luster B. Mohs Hardness Scale C. Mineral D. Texture 3. A minerals resistance to scratching A. Texture B. Cleavage C. Hardness D. Luster 4. The color of the powder left by a mineral A. Streak B. Cleavage C. Texture D. Luster 5. The tendency of a mineral to break along flat surfaces in a geometric repetitive manner. A. Streak B. Cleavage C. Texture D. Luster 6. The shape or pattern on the surface of a mineral. A. Streak B. Cleavage C. Texture D. Luster 7. Describes how a mineral appears to reflect light, and how brilliant or dull the mineral is. A. Streak B. Cleavage C. Texture D. Luster