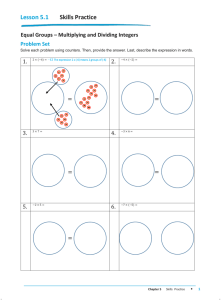
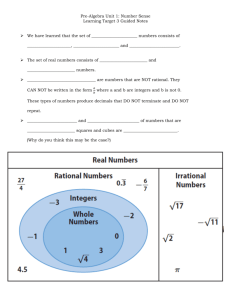
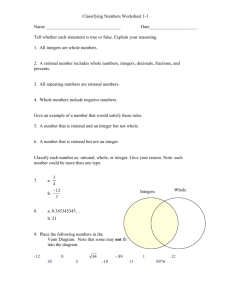
Grade 7 Unit 1 World Explorers - mathseminar7
advertisement

Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar Unit 1: 7th Grade World Explorers! Unit Overview In this unit of study, students will apply their understanding of fractions and integers to the real world, by exploring cities around the world. Students will research and chart facts about various cities across the world, comparing facts to the city of Baltimore. The unit will end with a final project where students will research a city of their choice and create a presentation sharing the data and information to Baltimore using integer and rational numbers to compare. This unit is expected to take 9 weeks (approximately 45 days). Common Core Content Standards 7.NS Apply and extend previous understandings of operations with fractions to add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. (7.NS.A) 4. Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. a. Describe situations in which opposite quantities combine to make 0. For example, a hydrogen atom has 0 charge because its two constituents are oppositely charged. b. Understand p + q as the number located a distance from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. c. Understand subtraction of rational numbers as adding the additive inverse. Show that the distance between two rational numbers on the number line is the absolute value of their difference, and apply this principle in real-world contexts. d. Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers. 5. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. a. Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Interpret products of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. b. Understand that integers can be divided, provided that the divisor is not zero, and every quotient of integers (with non-zero divisor) is a rational number. If p and q are integers. Interpret quotients of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar c. Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational numbers. d. Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division; know that the decimal form of a rational number terminates in 0s or eventually repeats. 6. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. Unit Guide Week 1 2 Focus Build background knowledge on city research City focus: Baltimore Opposites and Zero Pairs City focus: New Orleans Adding Integers 3 City focus: Denver Subtracting integers 4 City focus: Jerusalem Subtracting integers 5 City focus: Lhasa Multiplying and dividing integers 6 City focus: Death Valley Adding and subtracting rational numbers, including negatives 7 City focus: Melbourne Adding and subtracting rational numbers, including negative 8 City focus: Mumbai Multiplying and dividing rational numbers including negatives Final project Skills review 9 Content Standard(s) 7.NS.A.1a 7.NS.A.1a 7.NS.A.1b 7.NS.A.1d 7.NS.A.1a 7.NS.A.1c 7.NS.A.1d 7.NS.A.1 7.NS.A.1c 7.NS.A.1d 7.NS.A.2a 7.NS.A.2b 7.NS.A.2c 7.NS.A.1a 7.NS.A.1b 7.NS.A.1c 7.NS.A.1d 7.NS.A.1a 7.NS.A.1b 7.NS.A.1c 7.NS.A.1d 7.NS.A.2a 7.NS.A.2b 7.NS.A.2c 7.NS.A.3 Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar Facilitator Notes – Week 1 Day 1: Exploring Cities across the World 1. Begin the class with a brief introduction of the expectations and theme for this unit. Explain to students that with every unit, students will work together to complete a culminating project. 2. Explain that each week students will gather data on a different city in the world for a total of 8 cities. The first week, the class will focus on the city of Baltimore; each city researched in the weeks that follow will be compared to Baltimore. To compare each cities elevation level, students will place the name of each city at the appropriate place on a number line. To compare when each city was founded, students will place the name of each city at the appropriate location on a timeline. 3. Explain that at the end of the 8 weeks the students will gather data on a city of their choice. Display Exploring Cities Chart to see the data that the students will gather using a variety of websites. Display the Final Project Criteria for students to see the culminating final project for this unit. 4. Have students work in small groups to research information on the computer. Distribute copies of the Exploring Cities Chart. Students will gather information on the city of Baltimore this first week. 5. Designate half the groups to design the class timeline for the dates founded and the other half to design the class number line for the elevation level (refer to resource for guidance). Students can design the timeline and number line with various materials, such as poster paper, bulletin paper, on a side whiteboard or chalkboard. Just be sure that it will be accessible and visible each week to update with each new city. 6. Use the following sites as resources: ● To find the date founded, elevation, coordinates, and population refer to Wikipedia http://www.wikipedia.org ● To find average temperatures for the month of September and average rainfall, refer to The Weather Channel http://www.weather.com (Note: To get the averages for the month go to the website and type in the city name in the search tool. Then on the left side under forecast go to Monthly. Scroll down to the bottom of the month and click averages and collect data for the month of September. To determine the average rainfall stay in the averages section, scroll down below the monthly temperature averages. There will be a bar graph displaying the average rainfall here the students should add up the total averages for each month and divide by 12 to get the mean (students should include the months with 0 average rainfall into the mean.)) ● To find information on time zones refer to Time Zone Map http://www.timeanddate.com/time/map. (Note: Be sure to go over the time zone legend and map for this website with students. The map is divided into 24 main time zones. Each time zone is defined by the current time difference – or offset – from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), shown in whole hours at the bottom of the map. Example: +3 means that the time zone is 3 hours ahead of UTC.) ● To find information on money conversions refer to XE Currency http://www.xe.com (Note: Here students will determine how much the US Dollar is worth in another Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar city. Also, be aware that the Exploring Cities Chart Key may not be as up to date as the information on the website for the value of money is constantly changing.) ● To find information on the distances from Baltimore, MD to cities in the US and around the world use the Distance Calculator http://distancecalculator.globefeed.com/World_Distance_Calculator.asp (Note: When students enter in the city and county name they may be directed to a more specific search below and have to select the exact location. Make sure they are selecting the correct city and country.) 7. Place Baltimore on the appropriate location on the number line and timeline. Collect students’ Exploring Cities Charts, as they will build upon it each week. 8. If time allows, demonstrate how to visit Baltimore, MD using Google Earth. The Google Earth Tour begins with an aerial view of Baltimore City, and then zooms into the Inner Harbor, Camden Yards and M&T Stadium. After the tour, demonstrate for students how to travel the city through aerial and street view. (Note: You will want to download and view the tour prior to the students viewing. Also on the sidebar under Layers, please check only Borders and Labels and 3D Buildings. While viewing the tour, pause at locations and under Layers check Photos to view pictures provided of the areas.) ● Have students locate the Transamerica building on Google Earth, they will learn about the building on Day 2. ● Looking for visual images for the world explorer cities, search Flickr http://www.flickr.com/ by typing the city into the search box in the upper right corner. For safe content filtering, you will need to create an account or login and adjust your content filters http://www.flickr.com/help/filters/. Online Resources for Baltimore (Have students explore websites throughout the week) 1. Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baltimore 2. Visit Baltimore http://baltimore.org/ Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar 3. Oriole Park at Camden Yards http://baltimore.orioles.mlb.com/bal/ballpark/index.jsp 4. Baltimore Ravens M&T Stadium http://www.baltimoreravens.com/gameday/mt-bankstadium.html 5. Emporis - Transamerica Tower (Tallest Building in Baltimore) http://www.emporis.com/building/transamerica-tower-baltimore-md-usa Day 2: Comparing Integers (Student Computers Optional) 1. Show students the Transamerica Tower through a guided practice describing and comparing integers on the Comparing Integers PowerPoint (Slides 1-4). 2. Have students use the integer cards from slide 5 of Comparing Integers PowerPoint to place themselves in order from least to greatest and answer questions from slide 6. Lead them to the discussion of absolute value on slides 7 and 8. 3. Have students answer the questions from the Mathopolis sites listed below or on the Comparing Integers Power Point (slide 9). This can be done individually on computers or as a whole class. http://www.mathopolis.com/questions/q.php?id=1669&site=1&ref=/numbers/absolutevalue.html&qs=1669_1670_1671_1672_2212_2213_2214 http://www.mathopolis.com/questions/q.php?id=1661&site=1&ref=/numberline.html&qs=1661_1662_1663_1664_1665_1666 4. Show students the first 40 seconds of the Wizard of Oz clip (slide 10 from Comparing Integers Power Point) and have the students answer the following question: When the scarecrow says, “We can go both ways,” how does this relate to absolute value? Wizard of Oz Clip http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yejtZgzB5Ik Day 3: Number line and t-charts 1. Introduce the various methods to create zero pairs (a pair of numbers with a positive and negative sign whose sum is zero). To introduce, have students watch the YouTube video “A Zero Pair Love Story” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V4KESAhST9I 2. Display the picture of the Baltimore Ravens Football field on your document camera. Discuss how the field is similar to a number line. As a class, discuss the following situations and have students come up and represent each number on the field. ● The Ravens are going for a touchdown and are at their 30 yard line. How many more yards until they score? ● The Ravens are at the 20 yard line after the kickoff. If they lost 20 yards, where would they end up? ● Does the 30 yard line on both sides of the field represent a zero pair? Why or why not? Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar ● The Ravens are on the 40 yard line and make the first down within inches. On their next play, they get a 10 yard penalty. Where are they now? ● The Ravens run for 15 yards, but then lose 15 yards on the next play. Why is this a zero pair? ● Have students create their own horizontal and/or vertical number line using construction paper to use for practice today and for the future if needed. Demonstrate how to use the number line to make zero pairs. Have students use their fingers, chips or small post-it notes to designate their answers on the number line. Have students represent the following situations on the number line: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. In Buffalo, New York the temperature in the morning is -14 degrees F. A gain of 15 yards. The opposite of -6. Represent the integer that will make a zero pair with 18. Represent the integer that will make a zero pair with -7. Represent a zero pair of your choice by marking two integers. Maggie has $12 in her wallet, but owes her sister $12. Represent this situation on the number line. Why is this a zero pair? 3. Next have students create their own t-chart using construction paper or use the provided T-Chart. Demonstrate how to use the two-colored chips to make zero pairs and give students time to practice with sample problems. 4. At the end of class, have students write a real-life situation where zero pairs are used on a sticky note and placed on the chalkboard. Share and discuss each situation with the class. 5. Be sure that students save their number lines and t-charts for the following weeks. Day 4: Skill Review Day (Opposites and zero pairs) Skill Review lessons are opportunities to offer targeted, differentiated support for students based on their current understanding of content standards. Prior to this lesson, determine the instructional needs of your students for opposites and zero pairs. Plan a differentiated lesson using strategies that meet the needs of the class (strategic grouping, stations, two-group model, all pupil response, etc.). For ideas for creating and responding to formative assessment data, visit: Let the Data Be Your Guide http://letthedatabeyourguide.wikispaces.com/ For differentiation strategies, visit: Dare to Differentiate http://daretodifferentiate.wikispaces.com/ HCPSS Instructional Strategies http://media.hcpss.org/newcode/strategies/strategies.php For ideas for teaching/re-teaching opposites and zero pairs, use the following Moving with Math: Algebra (MH5) activities: Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar ● ● Positive and Negative Numbers: Lesson Plan p. 2 - 4 The Opposite of a Number: Lesson Plan p. 6 - 8 Online Resources for Teaching/Re-teaching: ● NCTM Illuminations Zip Zero Zilch Lesson http://illuminations.nctm.org/LessonDetail.aspx?id=L819 ● Illustrative Mathematics 7.NS Distance on the Number Line 2 Task http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/310 ● A Math Dictionary for Kids Zero Pairs (Click on Z to find Zero Pairs) http://www.amathsdictionaryforkids.com/dictionary.html Online Teacher Resources: 1. Teaching Channel Zero Pairs, Manipulatives, and a Real-World Scenario https://www.teachingchannel.org/videos/teaching-subtracting-integers Day 5: Integer Game 1. Have students review comparing integers, absolute value, and zero pairs. Give each student an integer card. Students need to find their classmate who has their zero pair. This will be their partner for the review game. Use the Integer Review PowerPoint for the game (slides 13-16 pre-assess their knowledge for the next week). 2. Provide white boards and markers for students to reveal answers, but have each student work out problems on their own paper. 3. To end class, have students write down the zero pair with Baltimore’s elevation level and one thing they learned about Baltimore. Facilitator Notes – Week 2 Day 1: Welcome to New Orleans 1. Have students work in small groups to research information on the computer. Redistribute students’ copies of the Exploring Cities Chart. Have students gather information on the city of New Orleans. Helpful sites to refer to: ● To find the date founded, elevation, coordinates, and population refer to Wikipedia http://www.wikipedia.org ● To find average temperatures for the month of September and average rainfall refer to The Weather Channel http://www.weather.com ● (Note: To get the averages for the month go to the website and type in the city name in the search tool. Then on the left side under forecast go to Monthly. Scroll down to the bottom of the month and click averages and collect data for the month of September. Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar 2. 3. 4. 5. ● To find information on time zones refer to Time Zone Map http://www.timeanddate.com/time/map ● To find information on money conversion refer to XE Currency http://www.xe.com Designate half the group to update the timeline for the dates founded and the other half to update the number line for the elevation level. Place New Orleans on the appropriate location on the number line and timeline. If time allows have students visit New Orleans, LA using Google Earth. The Google Earth Tour begins with an aerial view of Baltimore and flies the class to New Orleans, Louisiana. Then zooms into the Superdome (Home to the New Orleans Saints and many other events), the Battle of New Orleans (Final Major Battle of War of 1812), and Jackson Square (Located in the French Quarter, where Mardi Gras is often celebrated). After the tour, demonstrate for students how to travel the city through aerial and street view to visit points of interest. (Note: You will want to download and view the tour prior to the students viewing. Also on the sidebar under Layers, please check only Borders and Labels and 3D Buildings. While viewing the tour, pause at locations and under Layers check Photos to view pictures provided of the areas.) Have students locate the Mardi Gras parade routes on Google Earth (Krewe Delusion and Krewe du Vieux), refer to the Mardi Gras Parade Route website http://www.mardigrasneworleans.com/schedule/parade-route/krewe-du-vieux.html Online Resources for New Orleans (Have students explore websites throughout the week) 1. Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Orleans 2. New Orleans NOLA http://www.neworleansonline.com/ 3. American Library - Battle of New Orleans War of 1812 http://www.americaslibrary.gov/aa/jackson/aa_jackson_icon_1.html 4. Superdome http://www.superdome.com/site.php 5. Jackson Square http://www.experienceneworleans.com/jackson-square.html 6. Mardi Gras http://www.mardigrasneworleans.com/ Day 2: Adding Integers introduction 1. To share information regarding Mardi Gras, show the following videos. http://www.mardigrasneworleans.com/videos.html (Mardi Gras In and Out Volume 33rd one)- show for about a minute or two http://www.neworleansonline.com/tools/videos/mardigras.php (AskNOLA: Mardi Gras in New Orleans with Barry Kern) - explains the parade and how to make the floats 2. Distribute the Mardi Gras resource and have students read directions. Explain to students that they will only be selecting their parade choice, at least 2 souvenirs to buy, and how many beads they plan to sell. As they select, they are to place each item under the appropriate column (profit or debit). After collect the sheets from them, as they will use it on Day 5. ● Explain that today students will practice combining integers. Recall the last three questions from the review game last week Integer Review PowerPoint (Slides Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar 14-16). Place each slide up again and have students write their answers on the whiteboards. Have a class discussion for students to explain their answers. ● Distribute the t-charts and number lines that students have used from the previous week. Students will review strategies of adding integers conceptually by using the number line and t-charts. Give students a handful of the two-colored chips. If students have a preference of their method, have them practice with the one they prefer. ● Have students write the problem to represent the real-world situation: “you have $5 and your mom gives you $3.” Tell students to solve the problem using either the number line or t-chart. As a class, have students explain how they got their answers. ● Have students write the problem to represent the real-world situation: “you have $5 and owe your mom $3.” Before having students solve the problem, ask them what the differences are in this problem to the one prior. Students may come up with either 5 + (-3) or 5 - 3. Use this as a discussion for the class to see they are the same problem. Emphasize that in both problems, the 3 has a negative value, so the problem is the same. Explain that today’s focus is on adding integers, so have them focus on 5 + (-3). Ask the students if the answer will be the same answer as 5 + 3 and have them explain their answers. Have students solve the problem using their number line or t-chart. As a class go over the answer and have students explain how they got their answer. ● Display the problem -3 + 5. Ask the class if this solution will be the same as 5 + (-3). Have them explain reasoning. Tell them to write a real-world situation to match the problem. Have them check their predictions using one of the integer strategies. ● Have students write the problem to represent the real-world situation: “you owe your mom $5 and you owe your dad $3.” Before going over the answer, have students explain the differences between this problem and the others and to predict if it will have the same answer as any of them. Instruct them to solve the problem using one of the strategies. As a class go over the answer and have students explain how they got their answer. ● Have students compare the problems 5 + (-3) and -5 + 3. Have them discuss the differences in the solutions and reasons why they are different. ● Display all the problems of the day. 5+3 5 + (-3) (-5) + 3 (-5) + (-3) As a class, discuss any patterns they observe and any generalizations they can make. 4. Have students complete the Adding Integers Generalizations to see if their generalizations hold true. 5. At the end of class, have students share and discuss generalizations. Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar Day 3: Adding Integers Practice (*Students will need access to computers) 1. Students will observe New Orleans elevation level. Display the article from http://www.uwec.edu/jolhm/eh3/group7/WhyNOVulnerable.htm. Read through the information as a class and discuss the elevation levels with students. 2. For the warm-up, display each problem below individually. Without actually solving, have students determine whether the sum will be positive or negative, by holding thumbs up (positive) or thumbs down (negative). For each problem, have students explain how they determined the sign. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. -8 + -4 9 + (-2) 12 + 14 -18 + 15 -11 + (-22) -25 + 13 3. Have students decide whether they want to practice the t-chart strategy or number line strategy. Have students get on the appropriate site below to practice. Have students play for about 15 minutes. 1. T-chart Strategy http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_161_g_2_t_1.html 2. Number line Strategy http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/mathgames/integers/FS_NumberLine_integer. htm 4. After students have had enough time to practice on the website, distribute the Circle Zero resource. Have them go to www.nlvm.usu.edu and select Virtual Manipulatives. Select the square for Number and Operations, 6 – 8. Scroll down and click on the game Circle 0. Students will play for the remaining time in class. Day 4: Skill Review (Adding Integers) Skill Review lessons are opportunities to offer targeted, differentiated support for students based on their current understanding of content standards. Prior to this lesson, determine the instructional needs of your students for adding integers. Plan a differentiated lesson using strategies that meet the needs of the class (strategic grouping, stations, two-group model, all pupil response, etc.). For ideas for creating and responding to formative assessment data, visit: Let the Data Be Your Guide http://letthedatabeyourguide.wikispaces.com/ For differentiation strategies, visit: Dare to Differentiate http://daretodifferentiate.wikispaces.com/ Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar HCPSS Instructional Strategies http://media.hcpss.org/newcode/strategies/strategies.php For ideas for teaching/re-teaching adding integers, use the following Moving with Math activities: MH5 Algebra Operations with Integers (Addition): Lesson Plan p. 13 - 16 Online Resources for Teaching/Re-teaching: Arcademic Skill Builders Orbit Integers http://www.arcademics.com/games/orbitintegers/orbit-integers.html ● Arcademic Skill Builders Spider Match http://www.arcademics.com/games/spidermatch/spider-match.html Online Teacher Resources 3. Teaching Channel Adding Integers https://www.teachingchannel.org/videos/mathteaching-techniques Day 5: Adding Integer Review Games 5. To review integers, students will be playing two different games. Have students get into pairs to play the games. Have students play the first game for about 15-20 minutes. Then have them switch partners and play the second game. Game 1: Integer War- Distribute a deck of cards evenly between the pairs. Each player turns over two cards and finds the sum of the cards. Each card is the value of it’s number; black cards are positive numbers, red cards are negative, Ace is 1, Jokers are 0, Jacks are 11, Queens are 12, and Kings are 13. The player with the greater sum wins that round and takes all four cards. Who ever gets all the cards first wins! Game 2: Race to 10 (Directions on game) 2. For a closure activity in the last 10 minutes of class, return students’ Mardi Gras papers. Based on the items in their table, students are to determine how much money they have left. Have a few students share the information from their sheets and explain why they selected their parade and souvenirs. Facilitator Notes – Week 3 Day 1: Welcome to Denver 1. Have students work in small groups to research information on the computer. Redistribute students’ copies of the Exploring Cities Chart. Have students gather information on the city of Denver. Helpful sites to refer to: ● To find the date founded, elevation, coordinates, and population refer to Wikipedia http://www.wikipedia.org ● To find average temperatures for the month of September and average rainfall refer to The Weather Channel http://www.weather.com Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar ● (Note: To get the averages for the month go to the website and type in the city name in the search tool. Then on the left side under forecast go to Monthly. Scroll down to the bottom of the month and click averages and collect data for the month of September. ● To find information on time zones refer to Time Zone Map http://www.timeanddate.com/time/map ● To find information on money conversion refer to XE Currency http://www.xe.com 2. Designate half the group to update the timeline for the dates founded and the other half to update the number line for the elevation level. 3. Place Denver on the appropriate location on the number line and timeline. 4. If time allows have students visit Denver using Google Earth. The Google Earth Tour begins with an aerial view of New Orleans and flies the class to Denver, Colorado, The Mile-High City (It is exactly one mile above sea level). Then zooms into the Denver International Airport (Recently experiencing a tornado in June 2013), Chipotle (The first location opened in 1993 near the University of Denver Campus), the Sports Authority Mile High Field (Home of the Denver Broncos and many other events) and Genessee Park (Largest Denver Mountain Park with Genessee Mountain at 8,284 feet above sea level and Bald Mountain at 7,988 feet above sea level). After the tour, demonstrate for students how to travel the city through aerial and street view to visit points of interest. (Note: You will want to download and view the tour prior to the students viewing. Also on the sidebar under Layers, please check only Borders and Labels and 3D Buildings. While viewing the tour, pause at locations and under Layers check Photos to view pictures provided of the areas.) Online Resources for Denver (Have students explore websites throughout the week) Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Denver Denver Mile High City http://www.denver.org/ Sports Authority Field at Mile High http://www.sportsauthorityfieldatmilehigh.com/ Chipotle - How it all started http://www.chipotle.com/enus/chipotle_story/steves_story/steves_story.aspx Denver International Airport http://flydenver.com/doyouknowdia Genesee Park http://mountainparkshistory.org/Parks/genesee.html Genesee Park - Beaver Brook Trail (Use Evernote Cleary (Google Chrome Extension) to remove Ads) http://www.examiner.com/article/hike-of-the-week-genesee-park-beaverbrook Day 2: Subtracting Integers 1. Review with students why Denver is called the Mile-City and show them the picture of the State Capitol Building steps on the website http://www.denver.org/metro/highaltitude-tips and the significance. Discuss the difference in elevations between Denver and New Orleans and challenge students to find the difference. 2. To learn about the effects of Denver’s high elevations, have students read the first page of the article “Denver and the Colorado Mountains” from Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. http://www.hemophilia.org/NHFWeb/Resource/StaticPages/menu0/menu6/menu10/menu 13/DenverAltitude.pdf. Ask students to share their thoughts on the information. To introduce subtracting integers, have students complete the Frayer Model with the word Integer in the center and share with partners. Distribute a set of 15 positive and negative counters to each group member. Ensure that all group members have a integer counter mat on which to place the counters. Explain to students that they will use the counters to model integers and integer equations with integer answers. Remind students of the four important ground rules to keep in mind when modeling integers with the counters and integer mats: ● All modeling is to be done on the integer counter mat ● The integer counter mat always has a value of zero when there are no counters on it. ● When one positive counter is paired with one negative counter on the mat, the combination is called a zero pair and has a value of zero. ● Zero pairs can always be added and removed from the mat without changing the collective value of the counters on the mat. Explain to students that the class is going to now explore modeling integer subtraction expressions. Demonstrate how to model (-4) – (-2) on the integer mat. Explain to students that counters representing the first number only should be placed initially on the mat. Place four negative counters on the mat. Explain that the counters that collectively represent the value of the second number must be removed from the counters already on the mat. Remove two negative counters from the mat. Write the expression and integer answer on the board. (-4) – (-2) = (-2). Explain to students that this answer is negative on the mat since there are still two negative counters. Demonstrate to students how to model (-4) – (+2) with the counters and mat. Explain to students that after the four negative counters have been added to the mat, by visual inspection it is obvious that there are no positive counters on the mat. So as presently represented, two positive counters cannot be removed from the mat. Remind students that zero pairs can be added to the mat without changing the value of the counters currently displayed on the mat. Model adding two zero pairs onto the mat such that there are now six negative counters and two positive counters. Explain to students that adding the zero pairs creates the positive counters needed to perform the operation as indicated in the expression. Remove the two positive counters from the mat. Write the expression and answer on the board (-4) – (+2) = -6 since there are six negative counters remaining on the mat. Distribute the Modeling Subtracting Integers to students and have them use the integer mat and counters to model each integer expression. Before they begin, have students think about and record predictions on whether or not the answer will be positive or negative. Then have students use the counters to model the expression and find solutions. Days 3-4: Subtracting Integers 1. Display the website Genesee Park http://mountainparkshistory.org/Parks/genesee.html and review some basic facts of Denver’s popular Genesee park. Either print the article or display on projector the article from http://www.examiner.com/article/hike-of-the-weekHoward County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar 2. 3. 4. 5. genesee-park-beaver-brook. Ask students to point out the elevation gains and drops along the hike. Point out the highest elevation on different trails and have students find the difference. Ask them to share their strategies. Ask students what effects do higher elevation produce. They should be able to answer the air quality, which is from Day 1 article. Ask if they think there would be any difference in temperature and have a discussion. Explain that for about every 1000 feet in elevation, the temperature decreases about 3-5 degrees (http://www.onthesnow.com/news/a/15157/ask-a-weatherman--how-does-elevationaffect-temperature). Pose the following questions to students: As hikers began their hike at Genesee Mountain, the temperature was 59 degrees F. As they hiked up the mountain to the highest point at 7,915 feet, the temperature was 46 degree F. What is the difference in temperatures? Have students explain their strategy to find the solution. The temperature in Anchorage, Alaska was 8°F in the morning and dropped to -5°F in the evening. What is the difference between these temperatures? Have students show their solution to this problem using a number line (see below). Then have students share their diagram solutions with each other. ● Show students this chart of cities in Canada: City Lowest recorded temperature (C∘) Highest recorded temperature (C∘) Ottawa -37 +39 Toronto -32 +41 Montreal -38 +38 Calgary -36 +34 Vancouver -17 +35 Winnipeg -44 +42 Churchill -49 +37 6. Have students mark the lowest and highest temperatures for Ottawa on a number line and Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar draw an arrow from the lowest temperature to the highest temperature. Then have students write the subtraction question their arrow represents. How far away is the highest temperature from the lowest temperature? 7. Next assign each pair a different city or 2 cities and have them create a number line and draw an arrow from the lowest temperature to the highest temperature and write the subtraction expression. 8. Have students in pairs compare the lowest to the highest temperature for 3 pairs of different cities listed and create a number line and draw an arrow from the lowest temperature to the highest temperature and then write the subtraction expression. 9. Note: Before you do this next activity with students, read the activity available at http://www.yummymath.com/2012/hot-summer-cold-winter-2/. Distribute the HotSummer-Cold-Winter resource to groups and have students work through this Yummy Math activity. Day 5: Skill Review (Subtracting Integers) Skill Review lessons are opportunities to offer targeted, differentiated support for students based on their current understanding of content standards. Prior to this lesson, determine the instructional needs of your students for subtracting integers. Plan a differentiated lesson using strategies that meet the needs of the class (strategic grouping, stations, two-group model, all pupil response, etc.). For ideas for creating and responding to formative assessment data, visit: http://letthedatabeyourguide.wikispaces.com/ For differentiation strategies, visit: http://daretodifferentiate.wikispaces.com/ http://media.hcpss.org/newcode/strategies/strategies.php For ideas for teaching/re-teaching subtracting integers use the following Moving with Math: Algebra (MH5) activities: Operations with Integers (Subtraction): Lesson Plan p. 17 - 19 Online Resources for Teaching/Re-teaching: ● Vimeo Maisonet Math Addition and Subtraction Integers http://vimeo.com/25506148 ● National Library of Virtual Manipulatives Number Line Bounce (Addition and Subtraction) http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_107_g_1_t_1.html?from=topic_t_1.html ● Math Play Subtracting Integers http://www.math-play.com/math-racing-subtracting-integersgame/math-racing-subtracting-integers-game.html ● Sheppard Software Fruit Shoot Subtracting Integers http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/mathgames/integers/FS_Integer_subtraction.htm Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar Facilitator Notes – Week 4 Day 1: Welcome to Jerusalem 1. Have students work in small groups to research information on the computer. Redistribute students’ copies of the Exploring Cities Chart. Have students gather information on the city of Jerusalem. Helpful sites to refer to: ● To find the date founded, elevation, coordinates, and population refer to Wikipedia http://www.wikipedia.org ● To find average temperatures for the month of September and average rainfall refer to The Weather Channel http://www.weather.com ● (Note: To get the averages for the month go to the website and type in the city name in the search tool. Then on the left side under forecast go to Monthly. Scroll down to the bottom of the month and click averages and collect data for the month of September. ● To find information on time zones refer to Time Zone Map http://www.timeanddate.com/time/map ● To find information on money conversion refer to XE Currency http://www.xe.com 2. Designate half the group to update the timeline for the dates founded and the other half to update the number line for the elevation level. 3. Place Jerusalem on the appropriate location on the number line and timeline. 4. If time allows have students visit Jerusalem, Israel using Google Earth. The Google Earth Tour begins with an aerial view of Denver and flies the class to Jerusalem, Israel, one of the oldest cities in the world. Then zooms into The Knesset (The legislative branch of the Israel Government), Jerusalem Chords Bridge (A suspended bridge that serves as the entry way of the city), the Mahane Yehud Market (A fresh market with cafes and restaurants), Mamilla Mall (An outside promenade mall with fashion stores, boutiques, many brand name shops and restaurants) and Old City (Surrounded by a wall and divided into four religious quarters Muslim, Christian, Armenian and Jewish). After the tour, demonstrate for students how to travel the city through aerial and street view to visit points of interest. (Note: You will want to download and view the tour prior to the students viewing. Also on the sidebar under Layers, please check only Borders and Labels and 3D Buildings. While viewing the tour, pause at locations and under Layers check Photos to view pictures provided of the areas.) Online Resources for Jerusalem (Have students explore websites throughout the week) ● Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jerusalem ● i Travel Jerusalem http://www.itraveljerusalem.com ● Jerusalem Official Website https://www.jerusalem.muni.il/jer_main/defaultnew.asp?lng=2 ● Go Israel Jerusalem Map http://goisrael.com/Tourism_Eng/Tourist%20Information/Planning%20your%20trip/Onli ne%20tools/Documents/jerusalemNew.pdf ● The Knesset http://main.knesset.gov.il/Pages/default.aspx Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar ● ● ● ● Jerusalem Chords Bridge http://jerusalem.com/videos/chords_bridge Mahane Yehuda Market http://jerusalem.com/videos/jerusalem_market Mamilla Mall http://jerusalem.com/videos/mamilla_jerusalem Old City and New City http://jerusalem.com/articles/travel/jerusalem_info_the_old_and_new_city_of_jerusalema6245 ● Jerusalem 3D Tours http://jerusalem.com/tour Day 2: Subtracting Integers in the Real World 1. Note: Before class have the movie clip (1:19) “Jerusalem” from http://jerusalem.com/videos set-up on your computer. To see an overview of the city, show the clip to students. Discuss Jerusalem’s date founded and have students point out the difference between their previous cities date founded. Challenge students to find the difference in years between Denver and Jerusalem’s date founded. 2. Divide the class into two groups. Give one group a print out of the Owing Money slide (slide 2) from the Subtracting Integers PowerPoint. Give the other group a print out of the Quiz Corrections slide (slide 3) from the Subtracting Integers PowerPoint. 3. Direct students to read through the given situation and determine how to represent it as an equation using integers and operations. Students may use counters and/or the number line to assist them. 4. Then have students partner up with a student from another group. Each student will present their scenario and have the other one determine the equation. (This can be done if scenarios are put into page protectors or just by having enough copies for each student in the class). 5. Have students think of another way to look at these two scenarios using slides 4 and 5 as a guide. 6. If time allows have students visit Bank of Israel Currency http://www.boi.org.il/en/Currency/CurrentCurrencySeries/Pages/Default.aspx and create situations/equations that represent owing money using NIS (New Sheqel) and Agora, the currency of Israel. For market exchange rates, to compare the value of a dollar, visit Bank of Israel Market http://www.boi.org.il/en/Markets/ExchangeRates/Pages/Default.aspx. Day 3: Subtracting Integers in the Real World (Students need computer access) 1. Have students rotate through the following two stations: Station A: Virtual Classroom Provide the following links for students to visit: http://www.mathgoodies.com/lessons/vol5/challenge_vol5.html http://www.mathgoodies.com/games/integer_game/football.html http://hoodamath.com/games/integer.php http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_162_g_2_t_1.html Station B: Word Problem Creation (index cards needed) Directions for students: ● Create a word problem that could be used by subtracting integers on the front of your card. Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar ● Write the answer on the back of the card. ● Quiz the other member 2. Have students share something they learned about subtracting integers in the real world. Day 4: Skill Review (Subtracting Integers) Skill Review lessons are opportunities to offer targeted, differentiated support for students based on their current understanding of content standards. Prior to this lesson, determine the instructional needs of your students based for subtracting integers. Plan a differentiated lesson using strategies that meet the needs of the class (strategic grouping, stations, two-group model, all pupil response, etc.). For ideas for creating and responding to formative assessment data, visit: Let the Data Be Your Guide http://letthedatabeyourguide.wikispaces.com/ For differentiation strategies, visit: Dare to Differentiate http://daretodifferentiate.wikispaces.com/ HCPSS Instructional Strategies http://media.hcpss.org/newcode/strategies/strategies.php For ideas for teaching/re-teaching subtracting integers use the following Moving with Math: Algebra (MH5) activities: Operations with Integers (Subtraction): Lesson Plan p. 17 - 19 Online Resources for Teaching/Re-teaching: ● Vimeo Maisonet Math Addition and Subtraction Integers http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_107_g_1_t_1.html?from=topic_t_1.html ● National Library of Virtual Manipulatives Number Line Bounce (Addition and Subtraction) http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_107_g_1_t_1.html?from=topic_t_1.html ● Math Play Math Racing Integers http://www.math-play.com/math-racing-subtractingintegers-game/math-racing-subtracting-integers-game.html ● Sheppard Software Fruit Shoot Subtraction Integers http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/mathgames/integers/FS_Integer_subtraction.htm Day 5: Subtracting Integers in the Real World: Elevator Story 1. Note - Have videos set-up prior to class. Explain to students that many people travel to Jerusalem to visit various religious sites, such as The Dome of the Rock and the Western Wall. Show the video clip (1:10) of the Temple Mount from http://jerusalem.com/videos. Optional - on the same site, you may also have students view the video on The Kotel- the Western Wall or view the 3-D tours. 2. Assign students to pairs. Distribute each pair an Elevator Story paper. Explain to students that there’s has been an increase of tourists in Jerusalem, so they are in need of another hotel. The American Colony is a popular hotel in Jerusalem. Optional - Have Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar students explore the hotel http://www.americancolony.com/. Other hotels in the area include The David Citadel Hotel http://www.thedavidcitadel.com/, The King David Hotel http://www.danhotels.com/JerusalemHotels/KingDavidJerusalemHotel/ and the Mamilla Hotel http://www.mamillahotel.com/. 3. Explain to students that they will be creating their own dream hotel that has 15 levels and will compete with other hotels in the area. There will be the “Start” floor, which is at level zero, and then 7 floors above and 7 floors below. 4. Have students name each level of the hotel with the appropriate name and number next to it given the options on the paper (Ex. Pool Level 2, Souvenir Shop Level -3). Students may create their own ideas for floors as well. Have students develop a story that goes with their hotel that includes directions as to which floor they are traveling to next. Next to each line of the story that has them moving, have students include the equation that models the situation. (See example below for clarification). Ex. Beginning at the start, Tim traveled down 3 levels to get souvenirs from the shop. 0 - 3 = -3 Next he decided to travel up 5 levels to go swimming at the pool. -3 + 5 = 2 5. If time allows have pairs share their story and elevator board with another group. As students are reading the story, the other pair will mark the travels using a chip or a clothespin and also record the equations that model the situation in the story. Facilitator Notes – Week 5 Day 1: Welcome to Lhasa 1. Have students work in small groups to research information on the computer. Redistribute students’ copies of the Exploring Cities Chart. Have students gather information on the city of Jerusalem. Helpful sites to refer to: ● To find the date founded, elevation, coordinates, and population refer to Wikipedia http://www.wikipedia.org ● To find average temperatures for the month of September and average rainfall refer to The Weather Channel http://www.weather.com ● (Note: To get the averages for the month go to the website and type in the city name in the search tool. Then on the left side under forecast go to Monthly. Scroll down to the bottom of the month and click averages and collect data for the month of September. ● To find information on time zones refer to Time Zone Map http://www.timeanddate.com/time/map ● To find information on money conversion refer to XE Currency http://www.xe.com 2. Designate half the group to update the timeline for the dates founded and the other half to update the number line for the elevation level. 3. Place Lhasa on the appropriate location on the number line and timeline. 4. If time allows have students visit Lhasa, China using Google Earth. The Google Earth Tour begins with an aerial view of Jerusalem and flies the class to Lhasa, Tibet (Republic of China), one of the highest cities in the world. Then zooms into Barkhor Street (The Barkhor Street Market surrounds the famous Jokhang Temple), Norbulingka Palace (Served as the Dalai Lama’s summer palace prior to being exiled by the China during the Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar Tibetan Uprising 1959), the Namtso Lake (The largest saltwater lake at a high elevation 15,479 feet above sea level), and Potala Palace (The primary residence of the Dalai Lama prior to the Tibetan Uprising 1959, he now resides in India). After the tour, demonstrate for students how to travel the city through aerial and street view to visit points of interest. (Note: You will want to download and view the tour prior to the students viewing. Also on the sidebar under Layers, please check only Borders and Labels and 3D Buildings. While viewing the tour, pause at locations and under Layers check Photos to view pictures provided of the areas.) Online Resources for Lhasa (Have students explore websites throughout the week) Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lhasa,_Tibet Tibet Discovery http://www.tibetdiscovery.com/lhasa-travel/ Lhasa Travel Guide http://www.travelchinaguide.com/cityguides/tibet/lhasa/ Lhasa Attractions http://www.beijingtolhasa.com/china-tibetguide/lhasa/attractions/index_2.html Geobeats Johkang Temple http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m9az6hERGWQ Namtso Lake http://www.tibetdiscovery.com/what-to-see/namtso-lake/ Potala Palace http://www.potala-palace.com/ Norbulingka Palace http://www.tibettours.com/norbulingka.html Day 2: Multiplying Integers Conceptually 1. *Note - Have the YouTube video of Potala Palace set up http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iu8Xtk7TX3g for students to view. 2. Show the video to students and then display the Potala Palace PowerPoint. 3. Distribute two-colored chips to students and the Multiplying Integers Conceptually handout. Have students answer questions 1 and 2. As a class, have students discuss their answers. Make sure that students have remembered that multiplication is a short cut to repeated addition. 4. Using the chips (yellow-side up), have students represent the problem to find the solution to 3 x 2, making 3 groups of 2. Have students share how they got their answer. 5. Have them complete 2a and then discuss students’ answers to determine the correct answer. Then have them write the definition of the Commutative Property: If you change the order of numbers when adding or multiplying, it doesn’t change the sum or product. 6. Inform students to keep in mind both the definition of multiplication and the commutative property to understand the signs of the product when multiplying with integers. 7. Have students complete #3 either on their own or in pairs. Have students share and discuss their answers. Make sure all students understand that to determine the answer, they should have made 3 groups of -2 (red side up), resulting with a product of -12 (12 negative sided chips). Have students explain why the product was a negative sign. 8. Have students answer #4a and then discuss answers as a class. After student discussion, explain why they are the same. 2 x 3 means two groups of three; since there’s a negative sign in front of the 2, it means “the opposite of 2 groups of three.” This means after you Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar make 2 groups of positive 3, you flip the counters over, making the product a negative sign. Have students fill in #4b and use the chips to determine the product. 9. Have students determine the answer #5a and predict the sign of the product. Discuss predictions as a class. After discussion, have students fill in the blank for #5b. 3 • (2) means “ three groups of two.” In the problem -3 • (-2), since both the 3 and the 2 are negative, it means “the opposite of three groups of negative two.” This means after you make 3 groups of negative 2 (red side up), you flip the counters over (since the 3 was negative and means opposite), make the product positive. Have students demonstrate the problem with the chips. Complete #5c together. 10. Have students complete the practice problems in #6 independently or with peers. Review answers as a class. Day 3: Dividing Integers Conceptually 1. Have students take out the Multiplying Integers Conceptually resource from the day before to review what the students completed. Distribute the Dividing Integers resource (2 copies on one sheet) and have them fill out the multiplying chart. Ask students to predict if the sign rules will be the same for dividing. 2. Using the chips (yellow side up), have students represent the 6 ÷ 3 to find the solution. Have students discuss what they did, and the relationship between multiplication and division. Remind students that division is the inverse of multiplication. 3. Have students represent -6 ÷ 3 to find the solution. Have students share out answers and what the sign of the quotient is. They should have 6 chips red side up and split into 3 even groups. Have students explain why the quotient is negative. Ask if they see the connection when multiplying the inverse. 4. If necessary, use the chips to answer the remaining problems. If students see the pattern, have them complete the table. Have students discuss their conclusions of multiplying and dividing integers. 5. Next distribute a Who Has card to each student. (The game is set-up for 16 students. You may need to adjust the numbers if you have less or more so it will come back around.) After the first round, have students exchange cards, and play again. Play the game for about 10 minutes. 6. Give each pair the Integer Tournament Scoreboard, Spinner resource, a paperclip, and 2 dice. Have students play the Integer Tournament in pairs to review integer operations. Day 4: Skill Review (Multiplying and Dividing Integers) Skill Review lessons are opportunities to offer targeted, differentiated support for students based on their current understanding of content standards. Prior to this lesson, determine the instructional needs of your students based for multiplying and dividing integers. Plan a differentiated lesson using strategies that meet the needs of the class (strategic grouping, stations, two-group model, all pupil response, etc.). For ideas for creating and responding to formative assessment data, visit: http://letthedatabeyourguide.wikispaces.com/ Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar For differentiation strategies, visit: http://daretodifferentiate.wikispaces.com/ http://media.hcpss.org/newcode/strategies/strategies.php For ideas for teaching/re-teaching multiplying/dividing integers, use the following Moving with Math: Algebra (MH5) activities: Operations with Integers (Multiplying/Dividing): Lesson Plan (p. 20 - 24) Online Resources for Teaching/Re-teaching: Illustrative Mathematics 7.NS Operations on a Number Line http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/46 Arcademic Skill Builders Integer Warp http://www.arcademics.com/games/integerwarp/integer-warp.html Visual Fractions Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Dividing Fractions http://www.visualfractions.com/ Day 5: Review Game (Students need access to computers.) 1. Distribute the Lhasa Trip Warm-up to students. Have them complete either independently or in pairs. Then review solutions as a class. 2. Students will review all integer operations today by playing Integer Jeopardy on the computer. The link is http://www.math-play.com/Integers-Jeopardy/IntegersJeopardy.html.You can either play as a whole class, up to four teams, or have students play against one another in pairs. 3. If you have extra time, students can play various integer operation games on the computer. Multiplying integers: http://www.arcademics.com/games/integer-warp/integer-warp.html Dividing Integers: http://www.xpmath.com/forums/arcade.php?do=play&gameid=16#.UZ5gluBwY20 Dividing Integers: http://www.slidermath.com/integer/SlamnD.shtml All operations: http://www.quia.com/cb/64603.html Facilitator Notes – Week 6 Day 1: Welcome to Death Valley 1. Have students work in small groups to research information on the computer. Redistribute students’ copies of the Exploring Cities Chart. Have students gather information on the city of Death Valley. Helpful sites to refer to: ● To find the date founded, elevation, coordinates, and population refer to Wikipedia http://www.wikipedia.org Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar ● To find average temperatures for the month of September and average rainfall refer to The Weather Channel http://www.weather.com ● (Note: To get the averages for the month go to the website and type in the city name in the search tool. Then on the left side under forecast go to Monthly. Scroll down to the bottom of the month and click averages and collect data for the month of September. ● To find information on time zones refer to Time Zone Map http://www.timeanddate.com/time/map ● To find information on money conversion refer to XE Currency http://www.xe.com 2. Designate half the group to update the timeline for the dates founded and the other half to update the number line for the elevation level. 3. Place Death Valley on the appropriate location on the number line and timeline. 4. If time allows have students visit Death Valley National Park, CA using Google Earth. The Google Earth Tour begins with an aerial view of Lhasa and flies the class to Death Valley National Park, CA. It is the hottest place on Earth which holds the world’s highest air temperature record of 134 degrees Fahrenheit. Then zooms into Ubehebe Crater (A large volcanic crater 600 feet deep and half a mile across), Mesquite Sand Dunes (Sand dunes rise to 100 feet and are rumored to be the one of many locations used in the Star Wars Films), Dante’s View (A “breathtaking” view point 5,476 ft above sea level on Coffin Peak that overlooks Death Valley), Badwater Basin (The lowest point in North America) and Telescope Peak (The highest point in Death Valley 11,049 feet above sea level allows viewers to see over one hundred miles in any direction). After the tour, demonstrate for students how to travel the city through aerial and street view to visit points of interest. (Note: You will want to download and view the tour prior to the students viewing. Also on the sidebar under Layers, please check only Borders and Labels and 3D Buildings. While viewing the tour, pause at locations and under Layers check Photos to view pictures provided of the areas.) Online Resources for Death Valley (Have students explore websites throughout the week) ● Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Death_Valley ● Death Valley National Park http://www.nps.gov/deva/index.htm ● Nat Geo Death Valley http://travel.nationalgeographic.com/travel/national-parks/deathvalley-national-park/ ● Ubehebe Crater http://www.nps.gov/deva/planyourvisit/ubehebe-crater.htm ● Sand Dunes http://www.nps.gov/deva/naturescience/sand-dunes.htm ● Death Valley National Park (10 minutes) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X6PRC6PYolk ● Frying an Egg in Death Valley http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hwQq8yRruCM Day 2: Applying Rational Numbers using a Number Line 1. Prior to lesson- Either display the article from http://www.nps.gov/deva/planyourvisit/upload/Weather%20and%20Climate.pdf or print Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar 2. 3. 4. 5. out a copy for students to read. Read the article as a class and discuss the information from it. Have students create either a vertical and/or horizontal number line that includes rational numbers. The number line can include equivalent rational numbers on the same number line or students can create a decimal number line and then also create a fraction number line. The number line should include negative values going from -10 to 10. Using the Temperature and Precipitation Table from the article, have students place the average precipitation values (in cm) and the record low temperatures (in C) in the appropriate place on the number line. Have students write down three situations in which opposite quantities of rational numbers combine to make 0. They should use values that are on the number line. Have students share their situations with a partner. Day 3: Adding and Subtracting Rational Numbers Materials: Addition and Subtraction of Rational Numbers Handout *Prior to lesson, either print out the Death Valley Visitor Guide resource or have link for students (go to http://www.nps.gov/deva/index.htm and then click Visitor Guide link) and print the article from Day 2 or have link for students http://www.nps.gov/deva/planyourvisit/upload/Weather%20and%20Climate.pdf 1. Either distribute the print out of articles to students or have them access on the computer. In pairs, have students complete the Discovering Death Valley resource sheet (Answer key on the second page) using the information from the articles. Students will discover Death Valley and then answer mathematical questions pertaining to it. 2. Go over answers and strategies as a class. 3. If time, have students complete the Addition and Subtraction of Rational Numbers closure. Day 4: Skill Review (Operations with Rational Numbers & Mixed Numbers) Skill Review lessons are opportunities to offer targeted, differentiated support for students based on their current understanding of content standards. Prior to this lesson, determine the instructional needs of your students for operations with rational numbers. Plan a differentiated lesson using strategies that meet the needs of the class (strategic grouping, stations, two-group model, all pupil response, etc.). For ideas for creating and responding to formative assessment data, visit: Let the Data Be Your Guide http://letthedatabeyourguide.wikispaces.com/ For differentiation strategies, visit: Dare to Differentiate http://daretodifferentiate.wikispaces.com/ HCPSS Instructional Strategies http://media.hcpss.org/newcode/strategies/strategies.php http://media.hcpss.org/newcode/strategies/strategies.php Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar For ideas for teaching/re-teaching operations with rational numbers and mixed numbers, use the following Moving with Math Fractions and Decimals (MH2) activities: Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions: Lesson Plan (p. 13-14) Like Mixed Numbers: Lesson Plan (p. 15-16) Unlike Fractions: Lesson Plan (p. 17-20) Estimating with Fractions: Lesson Plan (p. 21-23) Adding and Subtracting Decimals: Lesson Plan (p. 56 Making Change p.57 Estimating with Mixed Numbers: Lesson Plan (p. 34-35). Online Resources for Teaching/Re-teaching: ● Illustrative Mathematics 7.NS Compare Freezing Points Task http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/314 ● Illustrative Mathematics 7.NS Distance Between Houses Task http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/591 ● National Library of Virtual Manipulatives Fractions (Adding) http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_106_g_3_t_1.html?from=topic_t_1.html ● Visual Fractions Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Dividing Fractions http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_106_g_3_t_1.html?from=topic_t_1.html ● Worksheet Works Fractions http://www.worksheetworks.com/math/fractions.html ● Worksheet Works Decimals http://www.worksheetworks.com/math/decimals.html Day 5: Adding Rational Numbers Puzzle 1. Distribute the Adding Rational Numbers Puzzle. Have students solve the puzzle by finding the path through the table so that the numbers add up to the sum. 2. If students finish early they can create their own puzzle using rational numbers. 3. As a closure, have students find the difference in elevation between Death Valley and New Orleans. Facilitator Notes – Week 7 Day 1: Welcome to Melbourne! 1. Have students work in small groups to research information on the computer. Redistribute students’ copies of the Exploring Cities Chart. Have students gather information on the city of Death Valley. Helpful sites to refer to: ● To find the date founded, elevation, coordinates, and population refer to Wikipedia http://www.wikipedia.org ● To find average temperatures for the month of September and average rainfall refer to The Weather Channel http://www.weather.com ● (Note: To get the averages for the month go to the website and type in the city name in the search tool. Then on the left side under forecast go to Monthly. Scroll down Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar to the bottom of the month and click averages and collect data for the month of September. ● To find information on time zones refer to Time Zone Map http://www.timeanddate.com/time/map ● To find information on money conversion refer to XE Currency http://www.xe.com 2. Designate half the group to update the timeline for the dates founded and the other half to update the number line for the elevation level. 3. Place Melbourne on the appropriate location on the number line and timeline. 4. If time allows have students visit Melbourne, Australia using Google Earth. The Google Earth Tour begins with an aerial view of Death Valley and flies the class to Melbourne, Australia, the capital of the Australian state Victoria, and the second largest city in Australia. Then zooms into Flinders Street Station (The oldest and busiest railway station in Australia, construction first began in 1900 and currently there is a design competition in its final phase to reimagine Flinders Station), Queen Market Victoria (A historic landmark spread over two blocks, it has been opened since 1878, where you can shop for a variety of items from food to clothing), Melbourne Park (Melbourne is home to the Australian Open - Grand Slam Tennis, The Melbourne Cup - Horse Racing, and The Australian Grand Prix - Formula One Racing), Eureka Skydeck (The highest building in Melbourne, 91 stories, with a skydeck overlooking the city and the 50th tallest building in the world), and Phillip Island Penguin Parade (Where visitors can view penguins return home each night after a day of fishing). After the tour, demonstrate for students how to travel the city through aerial and street view to visit points of interest. (Note: You will want to download and view the tour prior to the students viewing. Also on the sidebar under Layers, please check only Borders and Labels and 3D Buildings. While viewing the tour, pause at locations and under Layers check Photos to view pictures provided of the areas.) Online Resources for Melbourne (Have students explore websites throughout the week) ● Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melbourne ● Visit Melbourne http://www.visitmelbourne.com/ ● Melbourne http://www.melbourneaustralia.org/ ● Flinder Street Station Redesign http://www.majorprojects.vic.gov.au/flinders-streetstation-design-competition/home ● Queen Victoria Market http://www.qvm.com.au/ ● Melbourne Park http://www.mopt.com.au/desktopdefault.aspx/tabid-36/46_read-21/ ● Eureka Sky Deck http://www.eurekaskydeck.com.au/ ● Eureka Sky Deck Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xZuXZyZsczY ● Phillip Island http://www.visitphillipisland.com/ ● Phillip Island Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EMM8ap0bg3E ● Penguin Parade http://penguins.org.au/ Day 2: Adding and Subtracting Rational Numbers **Optional- Student computers Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar 1. For an overview of the city of Melbourne, have students watch the youtube clip Melbourne Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_oQTZuKpi1M (2:22). 2. Students will practice adding and subtracting decimals by balancing a checkbook. Distribute the Balancing Your Checkbook handout. Discuss with students what debit (a negative number), credit (a positive number), and balance means. 3. Complete Situation #1 as a class. 4. Have students complete Situation #2 in pairs. Check answers as a class. 5. As a closure activity, have students plan a trip to Luna Park in Melbourne. Distribute the Luna Park Closure to students and either explore the website http://www.lunapark.com.au/ with them as a class or have them explore on their own. Have students use the site to help them complete the activity. Day 3: Adding and Subtracting Rational Numbers 1. *Prior to class have the video of Penguin Parade set-up http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WhDHOxl5X2g (2:59). (This video only discusses the Penguin Parade; if you would like to show more of Phillip Island show this video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EMM8ap0bg3E). 2. After watching the video, have the Philip Island website up (http://penguins.org.au/) and browse through it with students. Explain to students they will plan a trip there as a class. 3. Discuss the ticket options, and explain they will purchase the 3 Parks Pass https://penguins.org.au/buy-tickets/category/id/36 (you will need to select a date to show ticket prices). To practice adding decimals, decide how many of each type your class would need to buy and find the total cost. 4. Next show the map of Phillip Island http://penguins.org.au/assets/Visit-Us/pdf-visitus/PINP-Map-website-A4dld.pdf. Either print out copies for students or display from your computer. Distribute the Phillip Island Tour resource to students. Students will practice adding and subtracting fractions with negatives by mapping out their tour. 5. Read the situation to students and complete #1 as a class. Either make a large number line on the chalkboard or poster and have students transfer to their sheets. 6. Have students complete the rest in pairs. Check answers as a class. Day 4: Skill Review (Operations with Rational Numbers & Mixed Numbers) Skill Review lessons are opportunities to offer targeted, differentiated support for students based on their current understanding of content standards. Prior to this lesson, determine the instructional needs of your students regarding operations with rational numbers and mixed numbers. Plan a differentiated lesson using strategies that meet the needs of the class (strategic grouping, stations, two-group model, all pupil response, etc.). For ideas for creating and responding to formative assessment data, visit: http://letthedatabeyourguide.wikispaces.com/ For differentiation strategies, visit: http://daretodifferentiate.wikispaces.com/ http://media.hcpss.org/newcode/strategies/strategies.php Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar For ideas for teaching/re-teaching operations with rational numbers and mixed numbers, use the following Moving with Math Fractions and Decimals (MH2) activities: Adding and Subtracting Like Fractions: Lesson Plan (p. 13-14) Like Mixed Numbers: Lesson Plan (p. 15-16) Unlike Fractions: Lesson Plan (p. 17-20) Estimating with Fractions: Lesson Plan (p. 21-23) Adding and Subtracting Decimals: Lesson Plan (p. 56) Making Change: Lesson Plan (p.57) Estimating with Mixed Numbers: Lesson Plan (p. 34-35). Online Resources for Teaching/Re-teaching: ● Illustrative Mathematics 7.NS Compare Freezing Points Task http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/314 ● Illustrative Mathematics 7.NS Distance Between Houses Task http://www.illustrativemathematics.org/illustrations/591 ● National Library of Virtual Manipulatives Fractions (Adding) http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_106_g_3_t_1.html?from=topic_t_1.html ● Visual Fractions Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Dividing Fractions http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_106_g_3_t_1.html?from=topic_t_1.html Day 5: Reviewing Adding and Subtracting Rational Numbers 1. Have students play Bingo to practice adding and subtracting rational integers. Prior to class, have the Bingo Questions cut up into cards. 2. Distribute the Integer Bingo Sheet and cubes for marking the Bingo cards. Have students fill numbers randomly in their Bingo squares making sure to use each number only once. They will use all but one number. 3. To play, randomly select a Bingo Question, and display under document camera. Students should solve the problem and then locate the answer on their square. If they have the answer, they should mark it with a cube. The first player to get 5 in a row wins. Replay if time allows. Facilitator Notes – Week 8 Day 1: Welcome to Mumbai, India! 1. Have students work in small groups to research information on the computer. Redistribute students’ copies of the Exploring Cities Chart. Students will gather information on the city of Mumbai. Helpful sites to refer to: ● To find the date founded, elevation, coordinates, and population refer to http://www.wikipedia.orghttp://www.wikipedia.com ● To find average temperatures for the month of September and average rainfall refer to http://www.weather.com Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar To get the averages for the month go to the website and type in the city name in the search tool. Then on the left side under forecast go to Monthly. Scroll down to the bottom of the month and click averages and collect data for the month of September.http://www.weather.com ● To find information on time zones refer to http://www.timeanddate.com/time/map http://www.timeanddate.com/time/map/ ● To find information on money conversion refer to http://www.xe.comhttp://www.xe.com 2. Designate half the group to update the timeline for the dates founded and the other half to update the number line for the elevation level. 3. Place Mumbai on the appropriate location on the number line and timeline. 4. If time allows have students visit Mumbai, India using Google Earth. The Google Earth Tour begins with an aerial view of Melbourne and flies the class to Mumbai, India, the capital of the Indian state Maharashtra. It is formerly known as Bombay and is the largest populated city in India. Then zooms into Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (Built in 1887, now a World Heritage site, it is the headquarters for Central Railways in Mumbai), Hanging Gardens (Built in 1880, it is a terraced garden built over a water reservoir), Chowpatty Beach (Located at the north end of Marine Drive, it is a famous public beach, though very polluted), Rajabai Clock Tower (Modeled after Big Ben in London, this clock sits on the University of Mumbai Campus), and the Gateway to India (Built in 1911 to welcome King George V and Queen Mary, it was the entryway to India for many decades). After the tour, demonstrate for students how to travel the city through aerial and street view to visit points of interest. (Note: You will want to download and view the tour prior to the students viewing. Also on the sidebar under Layers, please check only Borders and Labels and 3D Buildings. While viewing the tour, pause at locations and under Layers check Photos to view pictures provided of the areas.) Online Resources for Mumbai (Have students explore websites throughout the week) ● Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mumbai ● Nat Geo Mumbai http://travel.nationalgeographic.com/travel/city-guides/mumbai-india/ ● Mumbai Maharashtra http://www.maharashtratourism.gov.in/mtdc/HTML/MaharashtraTourism/Default.aspx?s trpage=../MaharashtraTourism/CitiestoVisits/Mumbai.html ● Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/945 ● India Videos Mumbai http://www.youtube.com/user/indiavideodotorg/search?query=mumbai ● Geo Beats Mumbai Videos http://www.youtube.com/user/geobeats/search?query=mumbai ● Gateway of India Panoramia http://www.earthpano.com/india/gatewaygross.htm Day 2: Multiplying and Dividing Rational Numbers Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar 1. Have students watch the video on Mumbai http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GMNxRf_mUa4 (3:41) and have students discuss any observations they have on the city. 2. Explain to students they are enrolled in an exchange program at the American School of Bombay http://www.asbindia.org/, a school assisted by the US Office of Overseas School located near the US Consulate http://mumbai.usconsulate.gov/. Their class would like to schedule a movie night outing to see an American movie; in India there are movie theatres that have Hindi and English movies. Display Time City’s Movies in Mumbai for students to view what movies are playing in Mumbai http://timescity.com/mumbai/movies. 3. Assign students into groups. Distribute the student resource A Trip to the Movies Mumbai to each student. Discuss Rupee, the Indian Currency, and use the Bank of India website to show students a visual of Rupee currency http://rbi.org.in/Scripts/ic_currency.aspx. Have students watch the video Mumbai Public Transportation, to learn about the four modes of transportation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VSWTof1HFRY (2:51). 4. While students are completing the student resource, display the map of Mumbai showing the location of the school and the two movie theaters Cinemax Sion and PVR Cinemas Kurla West. https://mapsengine.google.com/map/edit?mid=zj5jSdSMYjh8.kNe5hMJLCDnA 5. If time allows, distribute the student resource A Trip to the Movies Columbia. Prior to class you will have to determine the distance from your middle school to each theater, AMC Columbia Mall and UA Snowden Square, and add the information to the student resource. Provide each student with a budget, movie theater, showtime, number of tickets and mode of transportation. Have students determine if they have enough in their budget to go to the movies, and if they could purchase a snack. Day 3: Multiplying and Dividing Rational Numbers **Student Computers Optional 1. Explain to the class that India is very overpopulated and they will investigate how their population compares to Baltimore. For the warm-up, wither as a whole class activity or in paris, have students compare the population versus area of Mumbai and Baltimore by looking up the information on Wikipedia. Have students calculate the population per square km. After reading the article on http://www.city-data.com/world-cities/MumbaiBombay-Environment.html, have a class discussion about students’ observations of the article and information they discovered. The article states that 42% of the population lives in slum; challenge students to find out how many people that is. 2. For the next activity, have students work in small groups, either 2-3 students per group. Distribute the Medieval Times Field Trip handout and go over the scenario as class. Give groups about time to complete. 3. Discuss strategies as a class. Have each group share the fundraiser the PTA should select and explain how they came to their decision. 4. If time remains, have students independently write a real world scenario that would result in the problem 15.75 divided by 3. Have students share scenarios. Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar Day 4: Skill Review (Multiplying and Dividing Rational Numbers) Skill Review lessons are opportunities to offer targeted, differentiated support for students based on their current understanding of content standards. Prior to this lesson, determine the instructional needs of your students for multiplying and dividing fractions. Plan a differentiated lesson using strategies that meet the needs of the class (strategic grouping, stations, two-group model, all pupil response, etc.). For ideas for creating and responding to formative assessment data, visit: Let the Data Be Your Guide http://letthedatabeyourguide.wikispaces.com/ For differentiation strategies, visit: Dare to Differentiate http://daretodifferentiate.wikispaces.com/ HCPSS Instructional Strategies http://media.hcpss.org/newcode/strategies/strategies.php For ideas for teaching/re-teaching multiplying fractions, use: ● Moving with Math Fractions and Decimals (MH2) Multiplying Fractions: Lesson Plan (p. 24-33). ● Elementary and Middle School Mathematics: Teaching Developmentally by John Van de Walle (p.311-312 and 317-326) For ideas for teaching/re-teaching dividing fractions, use the following Hands-On Standards: Grades 5 & 6 activities: ● Multiply with Fractions: Lesson plan (p. 46-47) ● Meaning of Division: Lesson plan (p. 48-49) ● Divide with Fractions: Lesson plan (p. 50-51) Online Resources for Teaching/Re-teaching: View the Tim and Moby video and then take the quiz. http://www.glencoe.com/sec/math/brainpops/00112038/00112038.html Thinking blocks are used to review how to multiply fractions. http://www.thinkingblocks.com/tb_fractions/fractions.html Play soccer math - scroll to the dividing fractions game. http://www.math-play.com/soccermath.htmlhttp://www.thinkingblocks.com/tb_fractions/fractions.html Fraction Mystery Picture Game can be used to practice multiplying a fraction and a whole number. http://www.dositey.com/2008/math/mistery2.html Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. Grade 7 Mathematics Seminar National Library of Virtual Manipulatives Fraction Line Bars (Division) http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_265_g_1_t_1.html?open=activities&from=topic_t_1.html http://www. math-play.com/soccer-math.html Day 5: Reviewing Multiplying and Dividing Rational Numbers 1. Students will play Jeopardy to practice multiplying and dividing rational numbers. Prior to class, setup and display Rational Numbers Jeopardy PowerPoint. The power point includes practice with multiplying and dividing fractions and decimals, and a potluck category of all operations. 2. Have students work in small groups/teams. Provide students with whiteboards and markers to reveal answer, and require all students to work out problems on their own papers. Facilitator Notes – Week 9 Days 1-5: Final Project and Presentations Materials: Exploring Cities Chart, Final Project Criteria Resource, Groupwork Rubric 1. Place students into small groups for the final project. Each group will select a city of their choice to research and gather information needed to fill in on the last row of the Exploring Cities Chart. The criteria and rubric are located on the Final Project Criteria. Have students place a picture of their city on the appropriate location on the number line and timeline before presentation. 2. Distribute the Final Project Criteria to students and go over the information. Use the Groupwork Rubric if needed for students. Give students 2-3 days to research and create their presentations. Then have students share presentations with the class and have students fill out the Listener’s Guide. 3. If presentations finish early, have students select their favorite games from the unit (refer to resources or online games) to practice skills for the remaining time available. Howard County Public Schools Office of Secondary Mathematics Curricular Projects has licensed this product under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.