Skeletal Project Objectives
advertisement

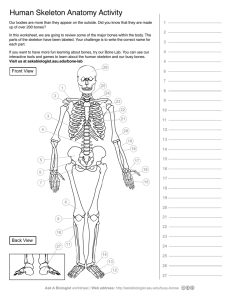
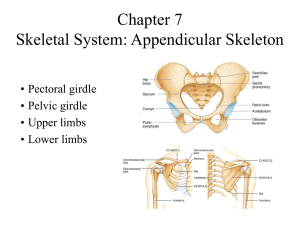
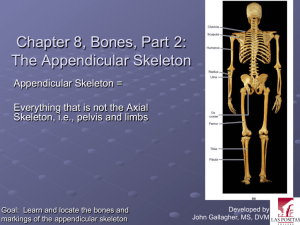
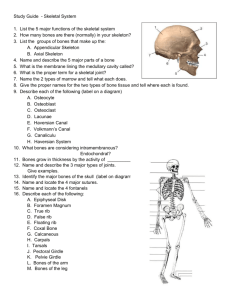
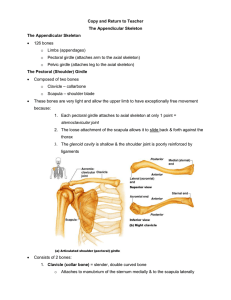
The Skull Learning Objectives: 1. Identify the following bones/structures of the skull: Frontal, Parietal, Mandible, Maxilla, Sphenoid, Ethmoid, Temporal, Zygomatic, Palatine, Occipital, Nasal, Lacrimal, Vomer 2. Explain the bone markings Process and Meatus and identify the Zygomatic Process, Mastoid Process, and External Auditory Meatus 3. Explain the term suture and identify the Coronal Suture and Squamous Suture 4. Explain what a sinus is 5. Identify the Frontal sinus, Sphenoid sinus, Ethmoid sinus, and Maxillary sinus 6. Describe the purpose of sinuses and explain why they are so susceptible to infection The Axial Skeleton (minus the skull) 1. Identify the types of vertebrae: Cervical, Thoracic, and Lumbar, Sacral 2. Identify the specific vertebrae: Atlas, Axis, Sacrum, Coccyx 3. Know how many of each type of vertebrae there are in a human backbone 4. Describe the following disorders: Kyphosis, Scoliosis 5. Describe the discs between the vertebrae and what their function is 6. Identify the structures on the rib cage: True Ribs, False Ribs, Floating Ribs, Costal Cartilages, Sternum, Manubrium, Body, Xiphoid Process 7. Describe the function of the rib cage The Appendicular Skeleton (Pectoral Girdle) 1. Identify the bones of the pectoral girdle: Clavicle, Scapula, Arms 2. Explain the bone markings Spine, Process, and Fossa and identify them on the scapula 3. On the humerus, identify the Head, Capitulum, Trochlea, Shaft. Explain where the humerus connects with other bones of the skeleton 4. On the radius and ulna, identify the Olecranon Process, Coronoid Process, Semilunar Notch, and Radial Tuberosity. Explain where the forearm connects with other bones of the skeleton 5. Identify the Carpals, Metacarpals and Phalanges 6. Describe how the clavicle, scapula, and humerus form the socket of the shoulder and why the shoulder can be prone to dislocation and injury The Appendicular Skeleton (Pelvic Girdle) 1. Explain the following bone markings: Tuberosity, Notch, Trochanter, Crest, Malleolus, Foramen 2. Describe how the pelvis and femur fit together to form the hip socket and why the hip must sometime be replaced as an individual ages 3. Identify the structures on the pelvis: Coxal Bone, Sacrum, Pubic symphisis, Acetabulum, Iliac Crest, False Pelvis, True Pelvis, Ischial Spine, Pelvic Brim, Pubic Ramus, Obturator Foramen 4. Explain the difference between a male pelvis and a female pelvis 5. Identify the Tibia, Fibula, and Femur and the regions on them: Head of femur, Intercondylar Eminence, Tibial Tuberosity, Anterior Crest of Tibia, Lesser Trochanter, Greater Trochanter, Head of Fibula, Medial Malleolus, lateral Malleolus 6. Explain how the three leg bones fit together to form the knee joint 7. Identify the Tarsals, Metatarsals, and Phalanges