UNIT-5
advertisement
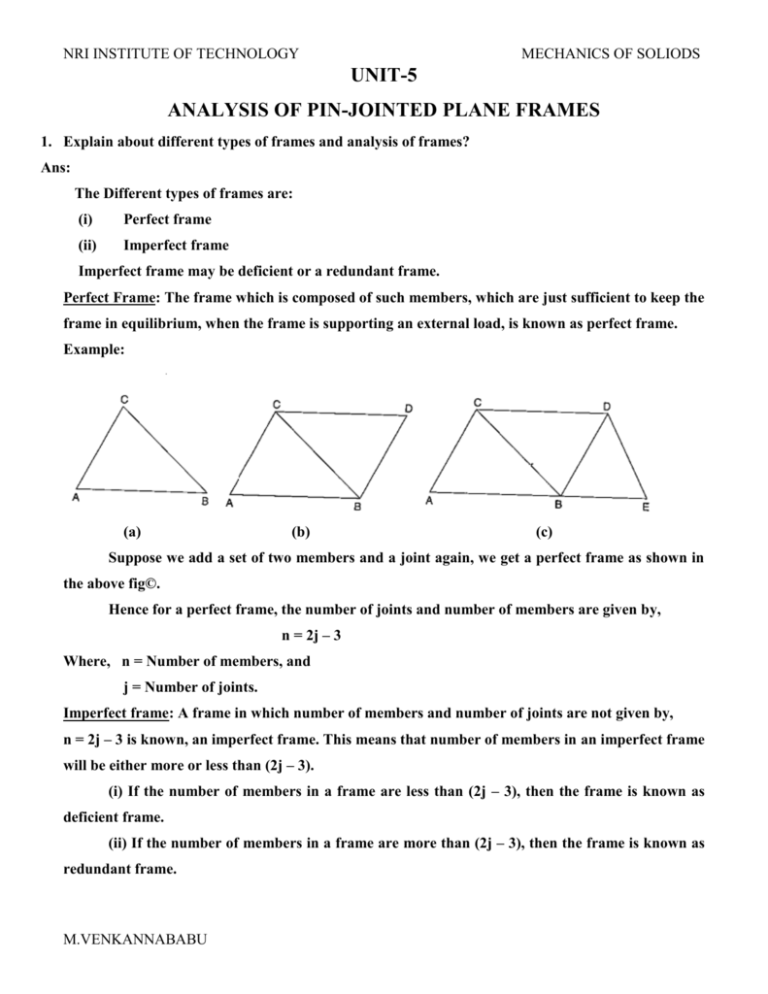
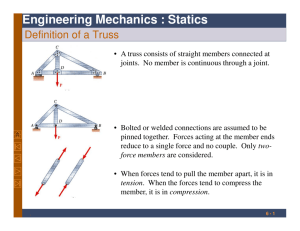
NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICS OF SOLIODS UNIT-5 ANALYSIS OF PIN-JOINTED PLANE FRAMES 1. Explain about different types of frames and analysis of frames? Ans: The Different types of frames are: (i) Perfect frame (ii) Imperfect frame Imperfect frame may be deficient or a redundant frame. Perfect Frame: The frame which is composed of such members, which are just sufficient to keep the frame in equilibrium, when the frame is supporting an external load, is known as perfect frame. Example: (a) (b) (c) Suppose we add a set of two members and a joint again, we get a perfect frame as shown in the above fig©. Hence for a perfect frame, the number of joints and number of members are given by, n = 2j – 3 Where, n = Number of members, and j = Number of joints. Imperfect frame: A frame in which number of members and number of joints are not given by, n = 2j – 3 is known, an imperfect frame. This means that number of members in an imperfect frame will be either more or less than (2j – 3). (i) If the number of members in a frame are less than (2j – 3), then the frame is known as deficient frame. (ii) If the number of members in a frame are more than (2j – 3), then the frame is known as redundant frame. M.VENKANNABABU NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICS OF SOLIODS The assumptions made in finding out the forces in a frame are: (i) The frame is a perfect frame (ii) The frame carries load at the joints (iii) All the members are pin-joined. Reactions of supports of a frame: (i) On roller support or (ii) On a hinged Analysis of a frame consists of: (i) Determinations of the reactions at the supports and (ii) Determinations of the forces in the members of the frame. A frame is analysed by the following methods: (i) Method of joints, (ii) Method of sections, and (iii) Graphical method. ========================================================================== 2. Find the forces in the members AB, AC and BC of the truss as shown in the below figure? Ans: M.VENKANNABABU NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICS OF SOLIODS Now let us consider the equilibrium of the various joints. Joint B: Resolving the forces acting on the joint B, vertically Joint C: 3. A truss of span 7.5m carries a point load of 1 KN at joint D as shown in the below figure. Find the reactions and forces in the members of the truss? Ans: Moments about A, & M.VENKANNABABU NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Now let us consider the equilibrium of the various joints. Joint A: Joint B: M.VENKANNABABU MECHANICS OF SOLIODS NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICS OF SOLIODS Joint D: Let the direction of F3 is assumed as shown in the below figure. 4. Determine the forces in the truss shown in the below figure. Which is subjected to inclined loads? Ans: M.VENKANNABABU NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Joint A: Joint C: Joint E: M.VENKANNABABU MECHANICS OF SOLIODS NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICS OF SOLIODS Joint F: Joint B: Joint G: MEMBER M.VENKANNABABU FORCE IN THE MEMBER NATURE OF FORCE NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICS OF SOLIODS 5. Find the forces in the members AB and AC of the truss as shown in the below figure using method of section? Ans: 6. A truss of span 9m is loaded as shown in the below figure. Find the reactions and foreces in the members marked 1, 2 and 3. Ans: M.VENKANNABABU NRI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MECHANICS OF SOLIODS Now draw a section line (1-1), cutting the members 1, 2 and 3 in which forces are to be determined. Consider the equilibrium of the left part of the truss because it is smaller than the right part. Moments about D: Moments about G: Moments about C: M.VENKANNABABU