cell webquest bio with answers 2010
advertisement

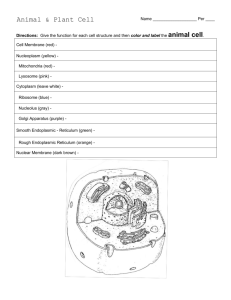
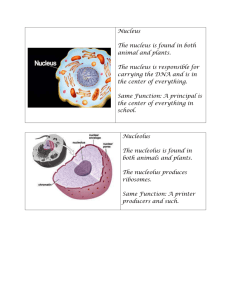
Name: _________________ date: ______________ Galoob /Biology Period: __ “Cells Alive” Web Quest Purpose: In this activity, you will discover different kinds of cells. You will learn about specific cell structures and their function. Procedure: 1. To begin go to www.cellsalive.com 2. Select “Cell Biology” from the left hand menu 3. Visit the “How Big is a…?” section of the site to get a better perspective on the variations of cell size. You should see an image of a person holding a pinhead. Part A. HOW BIG IS A...." Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart below and estimate the length of each (in nanometers, micrometers, or millimeters). The line in the bottom right corner of the screen is used to help you estimate. You do not need to record this information on this sheet. Part B. LABEL DIAGRAMS Next, under Cell Biology, click on Cell Models and select “Bacterial Cell”. In this section you will discover the significance of the bacterial cell and its parts! 5. 4. 6. 2. 1. Explain the function of the labeled parts # 1-6: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 3. Now select the “Plant and Animal Cell Animation” link from the top of the page. Once there, click on the Animal Cell and label the following parts below. 1. 12. 2. (the whole thing) = (stringy stuff inside) = 9a. 9b. 3. 7. 4. 11. 5 6. 5. . 8. 7. After looking at the bacteria cell and the animal cell, which is more complex? Circle. 8. Is the animal cell a prokaryote or a eukaryote? Circle. Part C: ANIMAL CELL MODEL For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there Animal Cell Model - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? Sketch each of the following. Mitochondria 2. How big are mitochondria? 3. What does the Golgi Apparatus do? Rough ER 4. What is the difference between smooth and rough ER? Plasma membrane 5. Where specifically is the nucleolus found? 7. What does the cytoskeleton do? 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Lysosome 9. What is the function of the cytosol? Golgi Apparatus 10. What is the function of the lysosome? 11. What is the main function of the plasma membrane Plant Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) . 5. 9 4. 1. . . 9. (outside membrane) 2. (the whole thing) = (stringy stuff inside)= 3. 6. 10. 12. . 8. 7. Plant Cell 1. What is the nucleus seen in both the animal and plant cell made of, what is so important about it? Sketch the following Nucleus 2. What is the specific function of the nucleolus? Chloroplast 3. What are ribosomes involved with? 4. What is the cell wall made of and what is its function? Vacuole 5. What makes the plant cells green? 6. What is the function of chloroplasts? 4. In plant cells, what does the vacuole do? Overview For the chart below, place a check in the box if the cell has that component. Plant Chloroplast Vacuole Ribosome Mitochondria DNA Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Cell membrane nucleus Animal Bacteria Web resources Cells Alive! http://www.cellsalive.com/index.htm Biology4kids: http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_main.html Virtual Cell biology: http://www.ibiblio.org/virtualcell/tour/cell/cell.htm Typical Animal and Plant cells: http://projects.edtech.sandi.net/miramesa/Organelles/animal.html Cellular Biology: Cell structures and functions: http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html#centrioles’ Inside a cell: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/units/basics/cell/ Cellular Organization: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/BioBookCELL2.html Interactive animations: http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.htm Online quizzes etc: http://www.zerobio.com/drag_gr11/organell.htm http://www.tvdsb.on.ca/westmin/science/sbi3a1/Cells/cellquiz.htm http://webinstituteforteachers.org/~halliepeskin/2003/activity3.html http://webinstituteforteachers.org/~halliepeskin/2003/activity4.html Name: _________________ Galoob /Biology date: ______________ Period: __ “Cells Alive” Web Quest Purpose: In this activity, you will discover different kinds of cells. You will learn about specific cell structures and their function. Procedure: 4. To begin go to www.cellsalive.com 5. Select “Cell Biology” from the left hand menu 6. Visit the “How Big is a…?” section of the site to get a better perspective on the variations of cell size. You should see an image of a person holding a pinhead. Part A. HOW BIG IS A...." Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart below and estimate the length of each (in nanometers, micrometers, or millimeters). The line in the bottom right corner of the screen is used to help you estimate. You do not need to record this information on this sheet. Part B. LABEL DIAGRAMS Next, under Cell Biology, click on Cell Models and select “Bacterial Cell”. In this section you will discover the significance of the bacterial cell and its parts! 5. Nucleiod (DNA) 4. 6. flagella 2. 1. Plasma membrane 3. Cell wall Explain the function of the labeled parts # 1-6: 1. plasma membrane: regulates transport of materials into or out of cell 2. capsule: protects the bacterial cell 3. cell wall: maintains the shape of the bacteria 4. ribosomes: translate messenger RNA into proteins 5. nucleoid: DNA not in a nuclear membrane 6. flagella: helps cell move. Capsule Ribosomes Now select the “Plant and Animal Cell Animation” link from the top of the page. Once there, click on the Animal Cell and label the following parts below. 1. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum 12. Lysosomes 2. the whole thing: Nucleus Stingy stuff inside: DNA, Chromatin 9a Microtubules 9b. Filaments 3. Cytosol (cytoplasm) 7. Mitochondria 5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum 11. Peroxisomes 10. Nucleolus 6. Vacuole 4. Cell membrane 8. Golgi 7. After looking at the bacteria cell and the animal cell, which is more complex? Circle. 8. Is the animal cell a prokaryote or a eukaryote? Circle. Part C: ANIMAL CELL MODEL For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there Animal Cell Model - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? Provides energy to the cell. Power center! 2. How big are mitochondria? They are about the size of a bacteria cell. 3. What does the Golgi Apparatus do? The golgi packages macromolecules for transport. 4. What is the difference between smooth and rough ER? The rough ER has ribosomes all around it. Sketch each of the following. Mitochondria 5. Where specifically is the nucleolus found and what does it do? The nucleolus is found in the nucleus and it produces ribosomes that are important part of making proteins. Rough ER 7. What does the cytoskeleton do? The cytoskeleton s made of microtubules microfilaments and helps the cell maintain shape and helps with cell movement. 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Cytoplasm Plasma membrane 9. What is the function of the cytosol? Cytoplasm is the fluid that fills the cell and where cellular metabolism happens 10. What is the function of the lysosome? Lysosomes have enzymes that help digest things like bacteria in white blood cells. 11. What is the main function of the plasma membrane? Lysosome The cell membrane is a double layer of lipids which is a protective barrier that regulates what goes into and out of the cell. Golgi Apparatus Plant Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) . 9. Cytoskeleton (microtubules and filaments) 5. Cell membrane 4. rough endoplasmic reticulum smooth endoplasmic reticulum . . 9. (outside membrane) Cell Wall 2. whole thing: nucleus Stringy stuff: Chromatin / DNA 3. Cytoplasm 6. Vacuole 10. Nucleolus 12. chloroplast . 7. mitochondria 8. golgi apparatus Plant Cell 1. What is the nucleus seen in both the animal and plant cell made of, what is so important about it? The nucleus is a membrane that contains chromatin and a nucleolus. It is important because it contains the DNA/chromatin which determines the cells characteristics. 2. What is the specific function of the nucleolus? The nucleolus is found in the nucleus and it produces ribosomes that are important part of making proteins. Sketch the following Nucleus 3. What are ribosomes involved with? Ribosomes are involved with translating messenger RNA into making proteins. 4. What is the cell wall made of and what is its function? The cell wall is made of cellulose and it maintains the cell shape and protects the cell. Chloroplast http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcSU8m94TkZgioMrbStPi_5o04THvP4it-lH-41Zs5x2ra6Bfc&t=1&usg=__Ty6GSpsaGN4wTIN2Klc8CIYRAI= Vacuole 5. What makes the plant cells green? chloroplasts 6. What is the function of chloroplasts? They are where photosynthesis takes place. 4. In plant cells, what does the vacuole do? The vacuole stores nutrients and waste and water. Overview For the chart below, place a check in the box if the cell has that component. Plant Animal Chloroplast X Vacuole X X Ribosome X X Mitochondria X X DNA X X Endoplasmic Reticulum X X Cell Wall X Cell membrane X X nucleus X X Bacteria some X X X X OTHER EXAMPLE WEBQUEST: Name___________________________________________Block_______Date_____________ Cell WEBQUEST: An interactive journey into the cell! Answer the following questions. You do not have to answer these questions in complete sentences, but your answers should be complete with details and information! Go to: http://askabiologist.asu.edu/research/buildingblocks/cellparts.html 1) How many different kinds of cells are in your body? ________________ 2) What parts of our bodies are made of dead cells?_______________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ Go to: http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.h tm Click on “Animal Cell” Read the text and follow the directions. (Click on each organelle and read about what it does) 3) Name and define 3 of the organelles that we are learning about. a) b) c) Click “continue” and answer the “Pop-up Questions.” When you are finished, click on “Plant cell” and read the text. 4) Which organelle in the plant cell would mainly help the cell take in water or get rid of water, just like the potato did? This is also known as “osmosis.” How do you know that this organelle would help with that process? _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ 5) Which organelle, if empty, would cause the plant to wilt? Why is this? _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ 6) Name an organelle that you see in the plant cell that you did not see in the animal cell. _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ 7) Why do you think an animal cell does not have the part that you name in #6? _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm and go to “Plant Cell” first. Click around the plant cell and look/read about some other organelles. Then, click on the “Animal Cell.” Click on the different parts and read about them. 8) Why is the rough endoplasmic reticulum so “rough?” _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ 9) Think about your house, condo or apartment. What part of your home would be like the mitochondria of the cell? Why? _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ Go to the left column of the page and click on “Cell Biology” and go to “How big?…” and click on “Start the Animation” 10) How big is a blood cell? How does its size compare to Dust Mites, and then to the E. coli bacteria? _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ Go to the left column of the page and click on “Mitosis.” Watch this animation. 11) Which of the 8 characteristics of life is the cell doing here? _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ Go back to http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.ht m and click on “Construct a cell” First, construct an animal cell. 12) Name a part that does NOT BELONG in the animal cell (as you figured out during construction) _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ 13) Construct the plant cell next. Name a part that DOES BELONG here but didn’t belong in one of the other 2 cells. _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ Cell Disorders and Diseases… Go to http://www.umdf.org/site/c.otJVJ7MMIqE/b.5692879/k.3851/What_is_Mitochondrial_Disease.h tm 14) How is a person’s life affected by mitochondrial disease? _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ Go to http://www.pompe.com/patient/learning/pc_eng_pt_lsds.asp 15) What organelle does “Pompe Disease” affect in the cell, and how does this disease affect someone’s life? _________________________________________________________________________________ _____ Games and Activities… http://www.tvdsb.on.ca/westmin/science/sbi3a1/Cells/cellquiz.htm and try this quiz! http://www.cellsalive.com/puzzles/index.htm and try the word puzzles at the bottom of the page! http://webinstituteforteachers.org/~halliepeskin/2003/activity3.html plant cell labeling http://webinstituteforteachers.org/~halliepeskin/2003/activity4.html animal cell labeling http://darwin.nmsu.edu/~molbio/cellgame/cellpin.html animal cell labeling http://darwin.nmsu.edu/~molbio/cellgame/CellGamePlant.html plant cell labeling http://science.nhmccd.edu/BIOL/biolab/cell.htm animal cell labeling