Transformers - Ministry of Commerce and Industry
advertisement
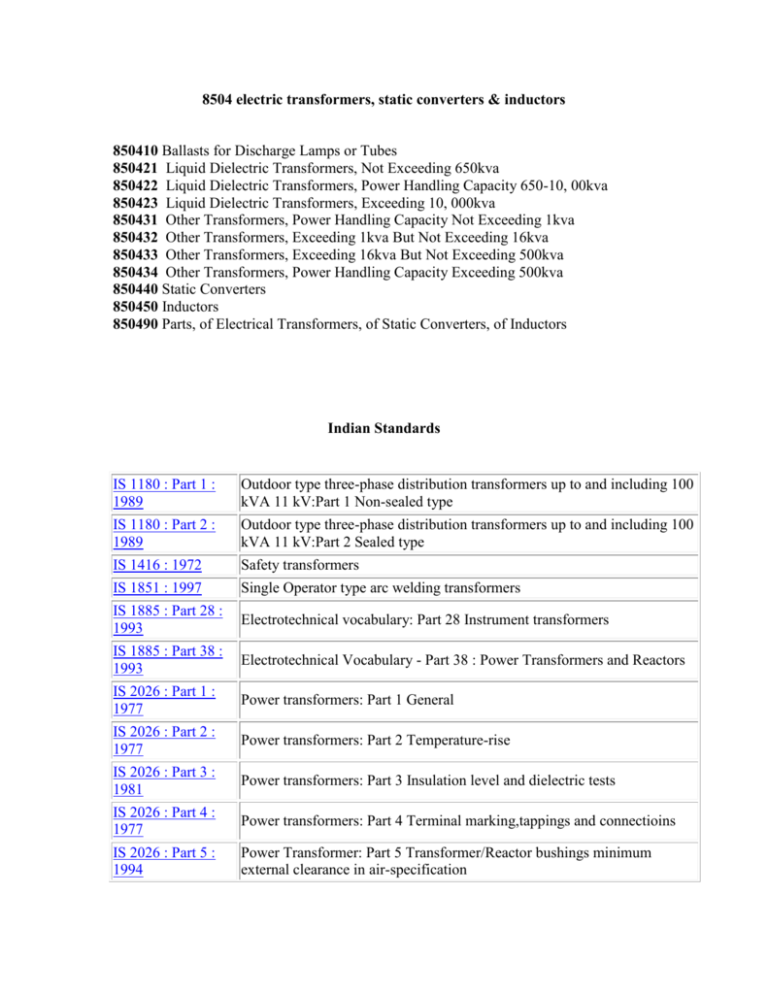
8504 electric transformers, static converters & inductors 850410 Ballasts for Discharge Lamps or Tubes 850421 Liquid Dielectric Transformers, Not Exceeding 650kva 850422 Liquid Dielectric Transformers, Power Handling Capacity 650-10, 00kva 850423 Liquid Dielectric Transformers, Exceeding 10, 000kva 850431 Other Transformers, Power Handling Capacity Not Exceeding 1kva 850432 Other Transformers, Exceeding 1kva But Not Exceeding 16kva 850433 Other Transformers, Exceeding 16kva But Not Exceeding 500kva 850434 Other Transformers, Power Handling Capacity Exceeding 500kva 850440 Static Converters 850450 Inductors 850490 Parts, of Electrical Transformers, of Static Converters, of Inductors Indian Standards IS 1180 : Part 1 : 1989 Outdoor type three-phase distribution transformers up to and including 100 kVA 11 kV:Part 1 Non-sealed type IS 1180 : Part 2 : 1989 Outdoor type three-phase distribution transformers up to and including 100 kVA 11 kV:Part 2 Sealed type IS 1416 : 1972 Safety transformers IS 1851 : 1997 Single Operator type arc welding transformers IS 1885 : Part 28 : 1993 Electrotechnical vocabulary: Part 28 Instrument transformers IS 1885 : Part 38 : 1993 Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Part 38 : Power Transformers and Reactors IS 2026 : Part 1 : 1977 Power transformers: Part 1 General IS 2026 : Part 2 : 1977 Power transformers: Part 2 Temperature-rise IS 2026 : Part 3 : 1981 Power transformers: Part 3 Insulation level and dielectric tests IS 2026 : Part 4 : 1977 Power transformers: Part 4 Terminal marking,tappings and connectioins IS 2026 : Part 5 : 1994 Power Transformer: Part 5 Transformer/Reactor bushings minimum external clearance in air-specification IS 2262 : 1963 Transformers for high voltage luminous discharge tubes IS 2705 : Part 1 : 1992 Current transformers: Part 1 General requirements IS 2705 : Part 2 : 1992 Current transformers: Part 2 Measuring current transformers IS 2705 : Part 3 : 1992 Current transformers: Part 3 Protective current transformers IS 2705 : Part 4 : 1992 Current transformers: Part 4 Protective current transformers for special purpose applications IS 2772 : 1982 Non-flameproof mining transformers for use below ground IS 3151 : 1982 Earthing transformers IS 3156 : Part 1 : 1992 Voltage transformers: Part 1 General requirements IS 3156 : Part 2 : 1992 Voltage transformers: Part 2 Measuring voltage transformers IS 3156 : Part 3 : 1992 Voltage transformers: Part 3 Protective voltage transformers IS 3156 : Part 4 : 1992 Voltage transformers: Part 4 Capacitor voltage transformers IS 3639 : 1966 Specification for Fittings and Accessories for Power Transformers IS 4146 : 1983 Application guide for voltage transformers IS 4201 : 1983 Application Guide for Current Transformer IS 4257 : Part I : 1981 Dimensions for Clamping Arrangements for Porcelain Transformer Bushings - Part I : For 12 kV to 36 kV Bushings IS 4257 : Part 2 : 1986 Dimensions for clamping arrangements for porcelain transformer bushings: Part 2 For 72.5 kV and 123 kV bushings IS 4804 : Part I : 1968 Specification for Resistance Welding Equipment - Part I : Single-phase Transformers IS 5142 : 1969 Continuously variable voltage auto transformers IS 5547 : 1983 Application guide for capacitor voltage transformers IS 5553 : Part 6 : 1990 Reactors: Part 6 Earthing transformers (Neutral couplers) IS 6088 : 1988 Specification for Oil-to-water Heat Exchangers for Transformers IS 8201 : 1976 Specification for High Frequency Wideband Matching Transformer IS 8322 : 1976 Guide for drafting of performance specifications for cores of transformers and inductors for telecommunication IS 9819 : Part I : 1981 Specification for Line Output Transformers (Eht) Used With Tv Picture Tubes - Part I : General Requirements and Tests IS 9819 : Part 2 : 1982 Specification for Line Output Transformers (EHT) Used with TV Picture Tubes - Part 2 : Type Lot 1S for 510mm, 590 mm and 610 mm TV Picture Tubes IS 9819 : Part 3 : 1982 Specification for Line Output Transformers (EHT) Used with TV Picture Tubes - Part 3 : Type Lot 1h for 470 mm, 510 mm, 590 mm and 610 mm TV Picture Tubes IS 9819 : Part 4 : 1984 Specification for Line Output Transformer (EHT) Used with TV Picture Tubes - Part 4 : Type Lot 2S for 310 mm and 340 mm TV Picture tubes IS 9819 : Part 5 : 1989 Specification for Line Output Transformers (Eht) Used with Tv Picture Tubes - Part 5 : Lot for Colour Picture Tubes Active IS 11171 : 1985 Specification for Dry-Type Power Transformers IS 11322 : 1985 Method for partial discharge measurement in instrument transformers IS 11333 : 1985 Specification for Flameproof Dry Type Transformers For Use in Mines IS QC 260000 : 2000 Transformers and Inductors for Use in Electronic and Telecommunication Equipment - Part 1 : Generic Specification IS QC 260100 : 1998 Transformers and Inductors for Use in Electronic and Telecommunication Equipment - Part 2 : Sectional Specification for Signal Transformers on the Basis of Capability Approval Procedure IS QC 260200 : 1999 Transformers and Inductors for Use in Electronic and Telecommunication Equipment - Part 3 : Sectional Specification for Power Transformers on the Basis of Capability Approval Procedure IS QC 260300 : 2000 Transformers and Inductors for Use in Electronic and Telecommunication Equipment - Part 4 : Sectional Specification for Power Transformers for Switched Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) on the Basis of Capability Approval Procedure IS QC 260400 : 2000 Transformers and Inductors for Use in Electronic and Telecommunication Equipment - Part 5 : Sectional Specification for Pulse Transformers on the Basis of Capability Approval Procedure IS QC 260500 : 2000 Transformers and Inductors for Use in Electronic and Telecommunication Equipment - Part 6 : Sectional Specification for Inductors on the Basis of Capability Approval Procedure IS 1534 : Part 1 : Ballasts for fluorescent lamps:Part 1 For switch start circuits 1977 IS 4242 : 1967 Methods of measurement of acoustical noise emitted by ballasts for gaseous discharge lamps IS 5991 : 1971 Specification for Ballast Rakes IS 6616 : 1982 Ballasts for high pressure mercury vapour lamps IS 13021 : Part 1 AC supplied electronic ballasts for tubular florescent lamps: Part 1 General : 1991 and safety requirements IS 13021 : Part 2 ac Supplied Electronic Ballasts for Tubular Fluorescent Lamps : 1991 Specification - Part 2 : Performance Requirements IS 9229 : 1979 Specification for Inductors for Electromagnetic Interference Suppression American Standards ANSI C57.12.10-1998, Transformers 230 kV and Below, 833/958 through 8333/10 417 kVA Single Phase, and 750/862 through 60 000/80 000/100 000 kVA Three Phase, Requirements for Covers certain electrical, dimensional and mechanical characteristics and takes into consideration certain safety features of 60-hz, two-winding liquid-immersed transformers used for step-down or step-up purposes rated 833/958 through 8333/10417 kVA, single phase; 750/862 through 60 000/80 000/100 000 kVA, three-phase without load tap changing; and 3750/4687 through 60 000/80 000/100 000 kVA with load tap changing. ANSI C57.12.20-1997, Transformers – Overhead-Type Distribution Transformers, 500 kVA and Smaller: High Voltage, 34 500 Volts and Below; Low Voltage, 7970/13 800Y Volts and Below Covers certain electrical, dimensional and mechanical characteristics. ANSI C57.12.24-2000, Transformers – Underground-Type Three-Phase Distribution Transformers, 2500 kVA and Smaller: High Voltage 34 500 Grd Y/19 920 Volts and Below; Low Voltage, 480 Volts and Below – Requirements Covers certain electrical and mechanical characteristics and takes into consideration certain safety features of three-phase, 60-Hz, liquid-immersed, self-cooled, underground-type transformers rated 2500 KVA abd smaller with high voltages of 34 500 GRdY/19 920 volts and below, and with low voltages of 480 volts and below. These transformers are generally used for step-down purposes from an underground primary cable supply and are suitable for occasional submerged operation. ANSI C57.12.29-1999, Switchgear and Transformers – Pad-Mounted Equipment – Enclosure Integrity for Coastal Environments Covers conformance tests and requirements for the intergrity of above-grade pad-mounted enclosures in coastal environments containing apparatus energized in excess of 600 volts that may be exposed to the public including but not limited to the following types of equipment enclosures: pad-mounted capacitors or inductors; pad-mounted distribution transformers; pad-mounted junction enclosures; pad-mounted metering equipment; and pad-mounted switchgear. ANSI C57.12.50-1981 (R1998), Distribution Transformers 1 to 500 kVA, Single-Phase; and 15 to 500 kVA, Three-Phase with High-Voltage 601–34 500 Volts, Low Voltage 120–600 Volt, Ventilated Dry-Type This standard is intended to set forth characteristics relating to performance, limited electrical and mechanical interchangeability, and saftey of the equipment described, and to assist in the proper selection of such equipment ANSI C57.12.51-1981 (R1998), Dry-Type Power Transformers 501 kVA and Larger, Three-Phase with High-Voltage 601 to 34 500 Volts, Low-Voltage 208Y/120 to 4160 Volts, Requirements for Ventilated This standard is intended to set forth characteristics relating to performance, limited electrical and mechanical interchangeability, and saftey of the equipment described, and to assist in the proper selection of such equipment. ANSI C57.12.52-1981 (R1998), Dry-Type Power Transformers, 501 kVA and Larger, Three-Phase with High-Voltage 601 to 34 500 Volts, Low-Voltage 208Y/120 to 4160 Volts, Requirements for Sealed This standard describes certain electrical and mechanical characteristics and takes into consideration certain saftey features of 60-Hz, two winding, three-phase, sealed dry-type transformers rate 501 kVA and larger. ANSI C57.12.55-1987 (R1998), Dry-Type Transformers in Unit Installations, Including Unit Substations – Conformance Standard This standard describes certain electrical, mechanical, and safety requirements and conformance tests for dry-type distribution and power transformers and for autotransformers. These transformers may either be single-phase or poly-phase, with ventilated, nonventilated or sealed enclosures IEEE 111-2000, Standard for Wide Band (Greater than 1 Decade) Transformers Pertains to electronic wide-band transformers transmitting power within a wide band of frequencies covering typically at least one decade in the frequency spectrum. Provision is made for including data for use in the design of feedback amplifiers and control networks or other circuits in which the knowledge of the transformer amplitude and phase-frequency response is needed by the system designer. These transformers are required to transform voltage within specified tolerances of amplitude and phase when operating between specified impedances. Guides to the application and test procedures are included. These appendixes contain certain precautions and recommended practices. The standard also pertains to hybrid transformers, primarily used in the telecommunications industry. The hybrid transformer is a wide-band transformer used in a manner which makes it part of a capacitance, IEEE 1276-2006, Guide for the Application of High-Temperature Insulation Materials in Liquid-Immersed Power Transformers Technical information is provided related to liquid-immersed power tranformers insulated with high-temperature materials. Guidelines for applying existing qualified high-temperature materials to certain insulation systems, recommendations for loading high-temperature liquid-immersed power transformers, and technical information on insulation-system temperature ratings and test procedures for qualifying new high-temperature materials are included. IEEE 1538-2000 (R2005), Guide for Determination of Maximum Winding Temperature Rise in Liquid Filled Transformers Provides guidance for determining the hottest-spot temperature in distribution and power transformers built in accordance with IEEE C57.12.00-2000. IEEE 259-1999 (R2004), Standard Test Procedure for Evaluation of Systems of Insulation for Dry-Type Specialty and General-Purpose Transformers Provides guidelines for preparing samples, conducting tests, and analyzing results of test procedures performed to evaluate insulation designed for dry-type specialty and general-purpose transformers. IEEE 295-1969 (R2000), Electronics Power Transformers Pertains to power transformers and inductors that are used in electronic equipment and supplied by power lines or generators of essentially sine wave or polyphase voltage. Guides to application and test procedures are included. IEEE 388-1992 (R1998), Transformers and Inductors in Electronic Power Conversion Equipment Pertains to transformers and inductors of both the saturating and nonsaturating type that are used in electronic power conversion equipment. Power conversion equipment includes items known as inverters, converters, power conditioners, switching power supplies, switched mode power supplies, and the like. These items are mostly devices used to change dc power from one voltage to another, to change dc power to ac, and to change ac power of one frequency to another frequency. This equipment is best described as utilizing transistors, silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRs), or other similar devices that switch power on and off at a high rate in order to achieve the power conversion or regulation desired. Therefore, this standard covers the various transformers and inductors that are used in any of the above mentioned equipment or devices, except for transformers operated directly from IEEE 389-1996, Recommended Practice for Testing Electronic Transformers and Inductors Presents a number of tests for use in determining the significant parameters and performance characteristics of electronic transformers and inductors. IEEE 436-1991 (R1998), Guide for Making Corona (Partial Discharge) Measurements on Electronics Transformers This guide covers the detection of corona (partial discharge) and the measurement of its magnitude in electronics transformers. Test conditions, test apparatus, and test requirements are included. IEEE 62-1995 (R2005), Guide for Diagnostic Field Testing of Electric Power Apparatus – Part 1: Oil Filled Power Transformers, Regulators, and Reactors This guide describes diagnostic tests and measurements which are performed in the field on oil-immersed power transformers and regulators. Whenever possible, shunt reactors are treated in a similar manner to transformers. IEEE 638-1992 (R2006), Standard for Qualification of Class 1E Transformers for Nuclear Power Generating Stations Procedures for demonstrating the adequacy of new Class 1E transformers, located in a mild environment of a nuclear power generating station, to perform their required safety functions under postulated service conditions are presented. Single and three phase transformers rated 601 V to 15 000 V for the highest voltage winding and up to 2500 kVA (self-cooled rating) are covered. IEEE C57.100-1999, Distribution Transformers, Test Procedure for Thermal Evaluation of Oil-Immersed The procedure is intended to provide a direct evaluation of the composite insulation system for either a power or distribution, liquid immersed transformer. IEEE C57.116-1990 (R2005), Guide for Transformers Directly Connected to Generators Describes selection and application considerations for the unit transformer and unit auxiliaries transformer. IEEE C57.117-1986 (R2005), Guide for Reporting Failure Data for Power Transformers and Shunt Reactors on Electric Utility Power Systems Addresses the reporting and statistical analysis of reliability of power transformers and shunt reactors used on electric utility power systems. IEEE C57.12.01-2005, Standard General Requirements for Dry-Type Distribution and Power Transformers Including Those with Solid-Cast and/or Resin Encapsulated Windings Electrical, mechanical, and safety requirements of ventilated, non-ventilated, and sealed dry-type distribution and power transformers or autotransformers (single and polyphase, with a voltage of 601 V or higher in the highest voltage winding) are described. IEEE C57.12.23-2002, Transformers Underground-Type, Self-Cooled, Single-Phase Distribution Transformers with Separable, Insulated, High-Voltage Connectors; High Voltage (24 940 GrdY/14 400 V and Below) and Low Voltage (240/120 V 167 kVA and Intended for use as a basis for determining performance, interchangeability, and safety of the equipment covered, and to assist in the proper selection of such equipment. Covers certain electrical, dimensional, and mechanical characteristics and takes IEEE C57.12.34-2004, Standard Requirements for Pad-Mounted, Compartmental-Type, Self-Cooled, Three-Phase Distribution Transformers, 2500 kVA and Smaller: High-Voltage, 34 500 GrdY/19 920 Volts and Below; Low Voltage 480 Volts and Below Intended for use as a basis for determining performance, interchangeability, and safety of the equipment covered, and to assist in the proper selection of such equipment. IEEE C57.12.35-1996 (R2004), Standard Bar Coding for Distribution Transformers Sets forth bar code label requirements for overhead, padmounted, and underground-type distribution transformers. Includes requirements for data content, symbology, label layout, print quality, and label life expectancy. IEEE C57.12.37-2006, Standard for the Electronic Reporting of Distribution Transformer Test Data Provides a basis for the electronic reporting of transformer test data on liquid immersed distribution transformers. IEEE C57.12.56-1994 (R1998), Test Procedure for Thermal Evaluation of Insulation Systems for Ventilated Dry-Type Power and Distribution Transformers (reinstatement of administratively withdrawn standard) Establishes a uniform method for determining the temperature classification of ventilated dry-type power and distribution transformer insulation systems by test rather than by chemical composition. IEEE C57.12.58-1991 (R2002), Guide for Conducting a Transient Voltage Analysis of a Dry Type Transformer Coil Covers general recommendations for measuring voltage transients in dry-type distribution and power transformers. IEEE C57.12.59-2002, Guide for Dry-Type Transformer Through-Fault Current Duration Sets forth recommendations believed essential for the application of overcurrent protective devices applied to limit the exposure time of dry-type transformers to short-circuit currents. IEEE C57.12.60-1998, Guide for Test Procedures for Thermal Evaluation of Insulation Systems for Solid Cast and Resin-Encapsulated Power and Distribution Transformers Modifies an existing standard to a Guide and expands its scope for improved application of the procedures for thermal evaluation of resin cast transformers. IEEE C57.12.70-2000 (R2006), Standard Terminal Markings and Connections for Distribution and Power Transformers Standard terminal markings and connections are described for single-phase and three-phase distribution, power, and regulating transformers. IEEE C57.12.80-2002, Terminology for Power and Distribution Transformers Is a compilation of terminology and definitions primarily related to electric power and distribution transformers and associated apparatus. Also includes similar data relating to power systems and insulation that is commonly involved in transformer technology. IEEE C57.12.90-1999, Test Code for Liquid-Immersed Distribution, Power and Regulating Transformers and Guide for Short-Circuit Testing of Distribution and Power Transformers Describe methods for performing tests specified in American National Standard General Requirements for Liquid-Immersed Distribution, Power and Regulating Transformers, ANSI/IEEE C57.12.00-1993, and other standards applicable to liquid-immersed distribution, power, and regulating transformers. It is intended for use as a basis for performance, safety, and proper testing of such transformers. This standard applies to all liquid-immersed transformers except instrument transformers, step-voltage and induction voltage regulators, arc furnace transformers, rectifier transformers, specialty transformers, grounding transformers, and mine transformers. When this standard is used on a mandatory basis, the words shall and must indicate mandatory requirements. The words should and may refer to matters that are recommended or permissive, but not IEEE C57.120-1991 (R2006), Loss Evaluation Guide for Power Transformers and Reactors A method for establishing the dollar value of the electric power needed to supply the losses of a transformer or reactor is provided. IEEE C57.124-1991 (R1996), Detection of Partial Discharges and the Measurement of Apparent Charge in Dry Type Transformers Applies to the detection of partial discharges occurring in the insulation of dry-type transformers or their components, and to the measurement of the associated charge at the terminals when an alternating test voltage is applied. IEEE C57.13-2003, Standard Requirements for Instrument Transformers Electrical, dimensional, and mechanical characteristics are covered, taking into consideration certain safety features, for current and inductively coupled voltage transformers of types generally used in the measurement of electricity and the control of equipment associated with the generation, transmission, and distribution of alternating current. The aim is to provide a basis for performance, interchangeability, and safety of equipment covered, and to assist in the proper selection of such equipment. Accuracy classes for metering service are provided. The test code covers measurement and calculation of ratio and phase angle, demagnetization, impedance and excitation measurements, polarity determination, resistance measurements, short-time characteristics, temperature-rise tests, dielectric tests, and measurement of open-circuit voltage of current IEEE C57.13.1-1981 (R1999), Field Testing of Relaying Current Transformers Describe field test methods that will assure that the current transformers are connected properly, are of marked ratio and polarity, and are in condition to perform as designed both initially and after a period of service. IEEE C57.13.2-2005, Standard Conformance Test Procedure for Instrument Transformers Describes the tests and documentary requirements for conducting a conformance test on instrument transformers. Covers test requirements and control functions on 60 Hz primary systems with voltages from 600 volts through 38 kV. IEEE C57.13.3-2005, Guide for Grounding of Instrument Transformer Secondary Circuits and Cases Provides information on the grounding of: secondary circuits of electromagnetic current transformer (CT) and voltage transformer (VT) circuits; cases of relays, CTs and VTs; secondary circuits of opto-electronic CTs and VTs. The primary emphases of this guide are personnel safety and proper performance of relays at electric power frequencies. IEEE C57.13.6-2005, Standard for High Accuracy Instrument Transformers Defines one new 0.15 voltage transformer accuracy class, two new 0.15 current transformer accuracy classes, two new current transformer burdens, and two new current transformer routine accuracy test methods. IEEE C57.136-2000 (R2005), Guide for Sound Level Abatement and Determination for Liquid-Immersed Power Transformers and Shunt Reactors Rated Over 500 kVA Guidelines are provided for the selection of suitable sound reduction methods in oil-immersed power transformers and shunt reactors over 500 kVA. IEEE C57.138-1998 (R200x), Recommended Practice for Routine Impulse Test for Distribution Transformers General test procedures for performing routine quality control test that is suitable for high-volume production line testing. Transformer connections, test methods, circuit configurations, and failure detection methods are addressed. Covers liquid-immersed, singleand three-phase distribution transformers. IEEE C57.144-2004, Guide for Metric Conversion of Transformer Standards This guide assists IEEE Power Engineering Society/Transformer Committee Working Groups in the interpretation of IEEE/ASTM SI 10-2002 and other appropriate standards as they convert their document to the use of SI units. IEEE C57.146-2005, Guide for the Interpretation of Gases Generated in Silicone-Immersed Transformers Assists the transformer operator in evaluating Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA) data obtained for silicone-filled transformers. IEEE C57.18.10-1998 (R2003), Standard Practices and Requirements for Semiconductor Power Rectifier Transformers Includes practices and requirements for semiconductor power rectifier transformers for dedicated loads rated single-phase 300 kW and above and three-phase 500 kW and above IEEE C57.91-2004, Guide for Loading Mineral-Oil-Immersed Transformers General recommendations for loading 65 degree C rise mineral-oil-immersed distribution and power transformers are covered. IEEE C57.93-1995 (R2001), Guide for Installation of Liquid Immersed Power Transformers Applies to the shipping, handling, inspection, installation, and maintenance of liquid-immersed power transformers rated 501 kVA and above with secondary voltages of 1000 V and above. IEEE C57.96-1999 (R2004), Distribution and Power Transformers, Guide for Loading Dry-Type (appendix to ANSI C57.12 standards) General recommendations for the loading of dry-type distribution and power transformers that have 80 C, 115 C, and 150 C average winding rises and insulation systems limited to 150 C, 180 C, and 220 C maximum hottest-spot operating temperatures, respectively, are covered in this guide. IEEE C57.98-1993 (R1999), Impulse Tests, Guide for Transformer (appendix to ANSI/IEEE C57.12.90) Adds background information that will aid in the interpretation and application of standards for impulse tests for power transformers, distribution transformers, and instrument transformers. ANSI/NECA 409-2002, Recommended Practice for Installing and Maintaining Dry-Type Transformers Describes installation procedures for singleand three-phase distribution and power transformers and associated accessories rated 600 Volts AC or less, and 0.25 kVA or more, of the following types: 1) Ventilated, indoor and outdoor, self-cooled or forced air cooled. 2) Nonventilated, indoor and outdoor, self-cooled or forced air cooled. This publication applies to general purpose, dry-type, two-winding transformers used for supplying power, heating and lighting loads for commercial, institutional, and industrial use in nonhazardous locations both indoors and outdoors. lso covers periodic routine maintenance and troubleshooting procedures for transformers, and special procedures used after adverse operating conditions such as a short-circuit, ground-fault, or immersion in water. ANSI/NECA 410-2005, Standard for Installing and Maintaining Liquid-Filled Transformers This recommended practice describes installation procedures for pad-mounted, sealed, self-cooled, compartmental, single and three phase liquid filled distribution and power transformers. ANSI C82.7-1983 (R2003), Mercury Lamp Transformers, Constant Current (Series) Supply Type, Specifications for Concerns Mercury Lamp Transformers Constant-Current (Series) Supply Type ANSI C82.8-1988 (R2003), Lamp Transformers – Incandescent Filament Lamp Transformers – Constant-Current (Series) Supply Type IEEE C57.12.40-2006, Standard Requirements for Secondary Network Transformers, Subway and Vault Types (Liquid-Immersed) Covers certain electrical, dimensional, and mechanical characteristics and takes into consideration certain safety features of three-phase, 60 Hz, liquid-immersed, secondary network transformers with a three position grounding switch, subway and vault types, rated 2500 kVA and smaller; primary 34 400 volts and below; secondary 216Y/125 volts and 480Y/277 volts. ANSI/NETA MTS 7.2.1-2001, NETA Maintenance Testing Specifications for Dry-Type Transformers: Air-Cooled, 600 Volts and Below - Small (167 kV Single-Phase, 500 kVA Three-Phase, and Smaller) and Air-Cooled, All Above 600 Volts and 600 Volts and Below - Large Provises a specification for electrical maintenance testing of Dry-Type Transformers: Air-Cooled, 600 Volts and Below - Small (167 kV Single-Phase, 500 kVA Three-Phase, and Smaller) and Air-Cooled, All Above 600 Volts and 600 Volts and Below- Large (Greater than 167 kV Single-Phase and 500 kVA Three-Phase)Specification for electrical maintenance testing of Dry-Type Transformers: Air-Cooled, 600 Volts and Below - Small (167 kV Single-Phase, 500 kVA Three-Phase, and Smaller) and Air-Cooled, All Above 600 Volts and 600 Volts and Below- Large (Greater than 167 kV Single-Phase and 500 kVA Three-Phase) This standard was listed for public review in the 6/16/2000 issue of Standards Action. It is being resubmitted due to substantive changes to the text. This announcement concerns substantive changes made at the Committee level following the ANSI/NETA MTS 7.2.2-2001, Maintenance Testing Specifications for Liquid-Filled Transformers Provides a specification for electrical maintenance testing of liquid-filled transformers.Specification for electrical maintenance testing of liquid-filled transformers. This standard was listed for public review in the 6/16/2000 issue of Standards Action. It is being resubmitted due to substantive changes to the text. This announcement concerns substantive changes made at the Committee level following the Public Comment period previously published in ANSI Standards Action. No Public Comments were received during the initial announcement. Only the substantive changes are open for comment. ANSI/SCTE 120-2006, Test Method for Balance Ratio of 75-300 Ohm Matching Transformer This test procedure provides a method for measuring the balance ratio of broadband radio frequency (RF) devices whose primary purpose is to provide an impedance and connector match between 75 W, coaxial, type “F” and 300 W twin-lead open screw connectorized devices. UL 1561-2005, Dry-Type General Purpose and Power Transformers Resolve comments received in response to a proposal to revise the Definition of Type 3R Enclosures Provided in Table 5.3 of UL 1561. The original proposal was posted by UL on March 25, 2005. UL 1585-2006, Standard for Safety for Class 2 and Class 3 Transformers Propose the removal of all references to Fahrenheit from UL 1585 and a revision of the maximum allowable voltage potential of transformers specified in Table 21.2 of UL 1585 UL 506-2005, Specialty Transformers Resolve comments received in response to proposals to revise UL 506 by: 1) Adding New Requirements for Applying Insulation Between the Input and Output Windings of Concentrically Wound Transformers; 2) Revising the Procedure for Conducting the Heating Test; and 3) Adding Requirements for Specialty Step-Up Transformers. The original proposals were posted by UL on March 25, 2005. UL 5085-1-2006, Standard for Safety for Low Voltage Transformers - Part 1: General Requirements Resolve comments received by UL in response to the proposed new Standard UL 5085-1. The original proposal for the new standard was posted by UL on April 22, 2005. UL 5085-2-2006, Standard for Safety for Low Voltage Transformers - Part 2: General Purpose Transformers Resolve comments received by UL in response to the proposed new Standard UL 5085-2. The original proposal for the new standard was posted by UL on April 22, 2005. UL 5085-3-2006, Standard for Safety for Low Voltage Transformers - Part 3: Class 2 and Class 3 Transformers Resolve comments received by UL in response to the proposed new Standard UL 5085-3. The original proposal for the new standard was posted by UL on April 22, 2005. International Standards IEC IEC 60044-1 Amd.1 Ed. 1.0 b:2000 Amendment 1 - Instrument transformers - Part 1: Current transformers IEC 60044-1 Amd.2 Ed. 1.0 b:2002 Amendment 2 - Instrument transformers - Part 1: Current transformers IEC 60044-1 Ed. 1.2 b:2003 Instrument transformers - Part 1: Current transformers "Applies to newly manufactured current transformers for use with electrical measuring instruments and electrical protective devices at frequencies from 15 Hz to 100 Hz. Applies basically to transformers with separate windings, but also to autotransformers. IEC 60044-2 Amd.1 Ed. 1.0 b:2000 Amendment 1 - Instrument transformers - Part 2: Inductive voltage transformers IEC 60044-2 Amd.2 Ed. 1.0 b:2002 Amendment 2 - Instrument transformers - Part 2: Inductive voltage transformers IEC 60044-2 Ed. 1.2 b:2003 Instrument transformers - Part 2 : Inductive voltage transformers IEC 60044-3 Ed. 2.0 b:2002 Instrument transformers - Part 3: Combined transformers "This part of IEC 60044 applies to newly manufactured combined transformers for use with electrical measuring instruments and electrical protective devices at frequencies from 15 Hz to 100 Hz. The requirements and tests of this standard, in addition to the requirements and tests of IEC 60044-1, IEC 60044-2 and IEC 60044-5 cover current, voltage and capacitor voltage transformers, that are necessary for combined instrument transformers. This standard shall be used in conjunction with IEC 60044-1 and IEC 60044-2. " IEC 60044-5 Ed. 1.0 b:2004 Instrument transformers - Part 5: Capacitor voltage transformers "This part of IEC 60044 applies to new single-phase capacitor voltage transformers connected between line and ground for system voltages Um 72,5 kV at power frequencies from 15 Hz to 100 Hz. They are intended to supply a low voltage for measurement, control and protective functions. The capacitor voltage transformer can be equipped with or without carrier-frequency accessories for power line carrier-frequency (PLC) application at carrier frequencies from 30 kHz to 500 kHz. " IEC 60044-6 Ed. 1.0 b:1992 Instrument transformers - Part 6: Requirements for protective current transformers for transient performance "Concerns requirements and tests, in addition to those given in chapter 1 of IEC 60185, that are necessary when inductive current transformers are used with electrical protective schemes in which the prime requirement is the maintenance of a defined performance up to several times the rated current when the current contains an exponentially decaying d.c. component of defined time constant. " IEC 60044-7 Ed. 1.0 b:1999 Instrument transformers - Part 7: Electronic voltage transformers "Applies to newly manufactured electronic voltage transformers with analogue output, for use with electrical measuring instruments and electrical protective devices at frequencies from 15 Hz to 100 Hz. The standard covers optical arrangements with electronic components. Three-phase voltage transformers are not included, but some of the requirements apply." IEC 60044-8 Ed. 1.0 en:2002 Instrument transformers - Part 8: Electronic current transformers "This part of IEC 60044 applies to newly manufactured electronic current transformers having an analogue voltage output or a digital output, for use with electrical measuring instruments and electrical protective devices at nominal frequencies from 15 Hz to 100 Hz." IEC 60050-321 Ed. 1.0 b:1986 International Electrotechnical Vocabulary. Chapter 321: Instrument transformers IEC 60050-421 Ed. 1.0 b:1990 International Electrotechnical Vocabulary. Chapter 421: Power transformers and reactors IEC 60076-1 Amd.1 Ed. 2.0 b:1999 Amendment 1 - Power transformers - Part 1: General IEC 60076-1 Ed. 2.1 b:2000 Power transformers - Part 1: General Applies to three-phase and single-phase transformers including autotransformers. Defines the rating and connection symbols. Gives certain specifications for transformers having a tapped winding. Defines information which shall be marked on the rating plate and the tests to be conducted. Supersedes IEC 60076-1(1976) and IEC 60076-4 (1976). IEC 60076-10 Ed. 1.0 b:2005 Power transformers - Part 10: Determination of sound levels "Defines sound pressure and sound intensity measurement methods by which sound power levels of transformers, reactors and their associated cooling auxiliaries may be determined. Is applicable to transformers and reactors covered by the IEC 60076 series, IEC 60289, and the IEC 61378 series, without limitation as regards size or voltage and when fitted with their normal cooling auxiliaries. " IEC 60076-10-1 Ed. 1.0 b:2005 Power transformers - Part 10-1: Determination of sound levels - Application guide "Provides supporting information to help both manufacturers and purchasers apply the measurement techniques described in IEC 60076-10. Describes the sources and characteristics of transformer and reactor sound, provides practical guidance on making measurements, and discusses factors that may influence the accuracy of the methods. Is applicable to transformers and reactors together with their associated cooling auxiliaries." IEC 60076-11 Ed. 1.0 b:2004 Power transformers - Part 11: Dry-type transformers "Applies to dry-type power transformers (including auto-transformers) having values of highest voltage for equipment up to and including 36 kV and at least one winding operating at greater than 1,1 kV. Applies to all construction technologies." IEC 60076-13 Ed. 1.0 b:2006 Power transformers - Part 13: Self-protected liquid-filled transformers "Applies to high-voltage/low-voltage self-protected liquid-filled and naturally cooled transformers for rated power 50 kVA to 1 000 kVA for indoor or outdoor use having a primary winding (high-voltage) with highest voltage for equipment up to 24 kV; a secondary winding (low-voltage) with highest voltage for equipment of 1,1 kV." IEC 60076-2 Ed. 2.0 b:1993 Power transformers - Part 2: Temperature rise "Includes clauses on identification according to cooling method, temperature-rise limits and type tests of temperature rise. " IEC 60076-3 Ed. 2.0 b:2000 "Power transformers - Part 3: Insulation levels, dielectric tests and external clearances in air " Gives insulation requirements for power transformers and the corresponding insulation tests for specific windings. Applies to single-phase and three-phase oil-immersed power transformers as defined in the IEC 60076-1. It Includes appendices on: partial discharge measurements during induced a.c. withstand voltage test on transformers; overvoltage transferred from a high-voltage winding to a low-voltage winding; information to be supplied with enquiries and orders. IEC 60076-4 Ed. 1.0 b:2002 Power transformers - Part 4: Guide to the lightning impulse and switching impulse testing - Power transformers and reactors "Gives guidance and explanatory comments on the existing procedures for lightning and switching impulse testing of power transformers to supplement the requirements of IEC 60076-3. Also generally applicable to the testing of reactors (see IEC 60289), modifications to power transformer procedures being indicated where required. Information is given on waveshapes, test circuits including test connections, earthing practices, failure detection methods, test procedures, measuring techniques and interpretation of results." IEC 60076-5 Ed. 3.0 b:2006 Power transformers - Part 5: Ability to withstand short circuit Identifies the requirements for power transformers to sustain without damage the effects of overcurrents originated by external short circuits. Describes the calculation procedures used to demonstrate the thermal ability of a power transformer to withstand such overcurrents and both the special test and the theoretical evaluation method used to demonstrate the ability to withstand the relevant dynamic effects. IEC 60076-7 Ed. 1.0 b:2005 Power transformers - Part 7: Loading guide for oil-immersed power transformers Is applicable to oil-immersed transformers and describes the effect of operation under various ambient temperatures and load conditions on transformer life. IEC 60076-8 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 Power transformers - Part 8: Application guide "Provides information to users about certain fundamental service characteristics of different transformer connections and magnetic circuit designs; system fault currents; parallel operation of transformers, calculation of voltage drop or rise under load; selection of rated quantities and tapping quantities; application of transformers of conventional design to convertor loading; measuring techniques etc.... Cancels and replaces IEC 60606" IEC 60076-SER Ed. 1.0 b:2006 Power transformers - ALL PARTS This pack contains all parts to IEC 60076 IEC 60092-303 Amd.1 Ed. 3.0 b:1997 Amendment 1 - Electrical installations in ships. Part 303: Equipment - Transformers for power and lighting IEC 60092-303 Ed. 3.0 b:1980 Electrical installations in ships. Part 303: Equipment - Transformers for power and lighting "Applies to all transformers used for power lighting and static convertors and, where appropriate, starting transformers, static balancers, saturable reactors and transductors. " IEC 60146-1-3 Ed. 3.0 b:1991 Semiconductor convertors - General requirements and line commutated convertors - Part 1-3: Transformers and reactors "Specifies characteristics wherein convertor transformers differ from ordinary power transformers. In all other respects, the rules specified in IEC 60076 shall apply. " IEC 60588-1 Ed. 1.0 b:1977 Askarels for transformers and capacitors. Part 1: General "Describes the electrical applications of askarels, the benefits and risks arising from their use as well as various aspects related to safety, disposal, packaging and labelling. " IEC 60588-2 Ed. 1.0 b:1978 Askarels for transformers and capacitors. Part 2: Test methods Describes the test methods which are to be employed to test properties of used and unused askarels. IEC 60588-3 Ed. 1.0 b:1977 Askarels for transformers and capacitors. Part 3: Specifications for new askarels "Contains the requirements relating to the physical, chemical and electrical properties of two types of askarel for capacitors and four types of askarel for transformers. " IEC 60588-4 Ed. 1.0 b:1979 Askarels for transformers and capacitors. Part 4: Guide for maintenance of transformer askarels in equipment "The purpose of this guide is to assist the power equipment operator in evaluating askarels in transformers, reactors and accessory equipment operated at power frequencies and in his efforts to maintain askarels in serviceable condition. It recommends standardized tests and evaluation procedures. Methods are outlined for reconditioning and reclaiming askarels whenever necessary. Precautions are also outlined for the disposal of unserviceable askarels in order to prevent environmental pollution. Local regulations should be followed. " IEC 60588-5 Ed. 1.0 b:1979 Askarels for transformers and capacitors. Part 5: Screening test for compatibility of materials and transformer askarels "The method described uses the changes of electrical and/or chemical characteristics of askarels, as well as various physical tests on materials exposed to askarels, in order to eliminate those materials which are not suitable owing to their contaminating effect on askarels. " IEC 60588-6 Ed. 1.0 b:1979 Askarels for transformers and capacitors. Part 6: Screening test for effects of materials on capacitor askarels The method described uses the change of electrical characteristics of askarels to eliminate those materials which are not suitable owing to their contaminating effect on the askarels. IEC 60740-1 Ed. 1.0 en:2005 Laminations for transformers and inductors - Part 1: Mechanical and electrical characteristics "Specifies the characteristics of laminations normally used as cores for transformers and inductors. The laminations are made of sheets and strips of magnetic materials, specified in IEC 60404-8-4 and IEC 60404-8-7." IEC 60740-2 Ed. 1.0 b:1993 Laminations for transformers and inductors for use in telecommunication and electronic equipment Part 2: Specification for the minimum permeabilities of laminations made of soft magnetic metallic materials "Specifies requirements for the minimum permeabilities of laminations made of silicon-iron and nickel-iron alloys as defined by the alloy classes C2, E1, E3 and E4 of IEC 60404-1. " IEC 60787 Ed. 1.0 b:1983 Application guide for the selection of fuse-links of high-voltage fuses for transformer circuit application "Applies to the use, for transformer circuit applications, of fuse-links of fuses complying with the requirements of IEC 60282-1. Specifies criteria for co-ordination of high-voltage fuse-links with other circuit components in transformer applications and gives guidance for the selection of such fuse-!inks with particular reference to their time/current characteristics and ratings. " IEC 60852-1 Ed. 1.0 b:1986 Outline dimensions of transformers and inductors for use in telecommunication and electronic equipment. Part 1: Transformers and inductors using YEI-1 laminations "Specifies the outline dimensions of transformers and inductors, using E and I laminations, built for the three most commonly used forms of mounting style, namely bracket mounting, U-clamp mounting and printed wiring board mounting. " IEC 60852-2 Ed. 1.0 b:1992 Outline dimensions of transformers and inductors for use in telecommunication and electronic equipment - Part 2: Transformers and inductors using YEx-2 laminations for printed wiring board mounting IEC 60852-3 Ed. 1.0 b:1992 Outline dimensions of transformers and inductors for use in telecommunication and electronic equipment - Part 3: Transformers and inductors using YUI-1 laminations "Specifies the outline dimensions of transformers and inductors, using U and I laminations, built for the most commonly used forms of mounting style, namely vertical mounting and level mounting. " IEC 60852-4 Ed. 1.0 b:1996 Outline dimensions of transformers and inductors for use in telecommunication and electronic equipment - Part 4: Transformers and inductors using YUI-2 laminations "Specifies the outline dimensions of transformers and inductors, using YUI-2 laminations, built for the most commonly used forms of mounting style. " IEC 60852-5 Ed. 1.0 b:1994 Outline dimensions of transformers and inductors for use in telecommunication and electronic equipment - Part 5: Transformers and inductors using the series Q of C-cores "Specifies the outline dimensions of transformers and inductors, using the series Q of C-cores in accordance with IEC 60329 for assembly forms H, J and U. " IEC 61007 Ed. 2.0 b:1994 Transformers and inductors for use in electronic and telecommunication equipment - Measuring methods and test procedures "Describes measuring methods and test procedures for inductors and transformers for use in electronic and telecommunication equipment that may be involved in any specifications for such components, in particular those forming part of the IEC Quality Assessment System for Electronic Components (IECQ). IEC 61021-1 Ed. 1.0 b:1990 Laminated core packages for transformers and inductors used in telecommunication and electronic equipment - Part 1: Dimensions "Specifies the dimensions, with their associated tolerances, of a range of laminated core packages using YEE 2 laminations, both in their standard configuration and for assemblies using two larger E parts. " IEC 61021-2 Ed. 1.0 b:1995 Laminated core packages for transformers and inductors for use in telecommunication and electronic equipment - Part 2: Electrical characteristics for cores using YEE2 laminations Specifies the electrical characteristics of laminated core packages using YEE 2 laminations according to IEC 60740. It also gives the marking and packaging requirements. IEC 61248-1 Ed. 1.0 b:1996 Transformers and inductors for use in electronic and telecommunication equipment - Part 1: Generic specification Prescribes the compliance requirements for manufacturers of transformers and inductors for use in electronic equipment in order to obtain capability approval and the component test schedules to be used for the assessment of that capability. IEC 61248-2 Ed. 1.0 b:1996 Transformers and inductors for use in electronic and telecommunication equipment - Part 2: Sectional specification for signal transformers on the basis of the capability approval procedure "Specifies how to prepare detail specifications for signal transforme rs. Includes a blank detail specification, which shows the format, a nd indicates which tests are considered to be appropriate to this type of component. " IEC 61248-3 Ed. 1.0 b:1996 Transformers and inductors for use in electronic and telecommunication equipment - Part 3: Sectional specification for power transformers on the basis of the capability approval procedure "Specifies how to prepare detail specifications for power transformers. Includes a blank detail specification, which shows the format, and indicates which tests are considered to be appropriate to this type of component. " IEC 61248-4 Ed. 1.0 b:1996 Transformers and inductors for use in electronic and telecommunication equipment - Part 4: Sectional specification for power transformers for switched mode power supplies (SMPS) on the basis of the capability approval procedure "Specifies how to prepare detail specifications for SMPS power transformers. Includes a blank detail specification, which shows the format, and indicates which tests are considered to be appropriate to this type of component. " IEC 61248-5 Ed. 1.0 b:1996 Transformers and inductors for use in electronic and telecommunication equipment - Part 5: Sectional specification for pulse transformers on the basis of the capability approval procedure "Specifies how to prepare detail specifications for pulse transformers. Includes a blank detail specification, which shows the format, and indicates which tests are considered to be appropriate to this type of component. " IEC 61248-6 Ed. 1.0 b:1996 Transformers and inductors for use in electronic and telecommunication equipment - Part 6: Sectional specification for inductors on the basis of the capability approval procedure "Specifies how to prepare detail specifications for inductors. Includes a blank detail specification, which shows the format, and indicates which tests are considered to be appropriate to this type of component. " IEC 61248-7 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 Transformers and inductors for use in electronic and telecommunication equipment - Part 7: Sectional specification for high-frequency inductors and intermediate frequency transformers on the basis of the capability approval procedure "Specifies how to prepare detail specifications for high-frequency inductors and intermediate frequency transformers between 10 kHz and 2 GHz.Includes a blank detail specification, which shows the format and indicates which tests are considered to be appropriate to this type of component. " IEC 61378-1 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 Convertor transformers - Part 1: Transformers for industrial applications "Deals with specifications, design and testing of power transformers and reactors which are intended for integration within semiconductor convertor plants. It is limited to applications of power convertors of any power rating for local distribution and for equipment not exceeding 36kV. It is not applicable to transformers for HVDC power transmission." IEC 61378-2 Ed. 1.0 b:2001 Convertor transformers - Part 2: Transformers for HVDC applications " This part of IEC 61378 applies to oil-immersed three-phase and -single-phase convertor transformers for use in HVDC power transmission. It applies to transformers having two, three or multiple windings. This standard does not apply to convertor transformers for industrial applications (see IEC 61378-1) and to convertor transformers for traction applications (see IEC 60310). " IEC 61378-3 Ed. 1.0 b:2006 Converter transformers - Part 3: Application guide "Provides information to users about specific topics related to industrial and HVDC converter transformers with design, construction, testing and operating conditions differing from conventional transformers used in power systems. Also provides manufacturers with the technical background that forms the basis for the principles used within IEC 61378-1 and IEC 61378-2. Supplements the information provided in IEC 60076-8." IEC 61558-2-1 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 "Safety of power transformers, power suply units and similar - Part 2: Particular requirements for separating transformers for general use " "This part 2 of IEC 61558 applies to stationary or portable, single-phase or polyphase, air-cooled separating transformers, associated or not. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104. This part 2 supplements or modifies the corresponding clauses in IEC 61558-1 This Standard replaces Chapter I of IEC 60989 " IEC 61558-2-12 Ed. 1.0 b:2001 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar devices - Part 2-12: Particular requirements for constant voltage transformers" "This part 2 of IEC 61558 is intended to be used in conjunction with IEC 61558-1. This international standard deals with all aspects of safety such as electrical, thermal and mechanical. This part of IEC 61558 applies to stationary or portable, single-phase or polyphase, air-cooled (natural or forced), associated or independent: - constant voltage auto-transformers; - constant voltage separating transformers; - constant voltage isolating transformers; - constant voltage safety isolating transformers; having a rated supply voltage not exceeding 1 000 V a.c., a rated frequency not exceeding 500 Hz, an internal operational frequency not exceeding 30 kHz and no limitation of the rated output. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104 " IEC 61558-2-13 Ed. 1.0 b:1999 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar devices - Part 2-13: Particular requirements for auto-transformers for general use" "Deals with all aspects of safety such as electrical, thermal and mechanical. This part 2-13 of IEC 61558 applies to stationary or portable, single-phase or polyphase, air-cooled (natural or forced), independent or associated auto-transformers, having a rated supply voltage not exceeding 1000 V a.c., a rated frequency not exceeding 500 Hz. This part 2-13 is intended to be used in conjunction with IEC 61558-1. This standard replaces Chapter III of IEC 60989. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104." IEC 61558-2-15 Ed. 1.0 b:1999 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar - Part 2-15: Particular requirements for isolating transformers for the supply of medical locations" "This part 2-15 of IEC 61558 applies to stationary, single-phase or polyphase, air-cooled (natural or forced) isolating transformers for the supply of group II medical locations, designed to be permanently connected to the fixed wiring of IT supply system. This standard also applies to transformers incorporating electronic circuits. This standard does not apply to external circuits and their components intended to be connected to the input and output terminals or socket-outlets of the transformer. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104. This part 2 is intended to be used in conjunction with IEC 61558-1." IEC 61558-2-17 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar - Part 2: Particular requirements for transformers for switch mode power supplies " "This part 2 of IEC 61558 applies to associated power transformers for switch mode power supplies, single-phase or polyphase, air-cooled: separating transformers; isolating transformers; safety isolating transformers, 10 kVA for single-phase transformers; 16 kVA for polyphase transformers. This standard is applicable to dry type transformers. The windings may be encapsulated or non-encapsulated. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104 This part 2 supplements or modifies the corresponding clauses in IEC 61558-1 " IEC 61558-2-19 Ed. 1.0 b:2000 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar devices - Part 2-19: Particular requirements for perturbation attenuation transformers " "This International Standard deals with all aspects of safety such as electrical, thermal and mechanical. This part 2-19 of IEC 61558 applies to stationary or portable, single-phase or poly-phase, air-cooled (natural or forced), independent or associated, isolating or safety isolating transformers, having a rated supply voltage not exceeding 1 000 V a.c., a rated frequency not exceeding 500 Hz, a rated output not exceeding 10 kVA. Perturbation attenuation transformers are intended to the supply of office machines and the like and have a mid-point lead out in the output circuit in order to attenuate mains borne disturbances. In addition, double or reinforced insulation between circuits required by the installation rules or by the appliance specification is fulfilled by using this transformer. This part 2-19 is intended to be used in conjunction with IEC 61558-1 It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104. " IEC 61558-2-2 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar - Part 2-2: Particular requirements for control transformers " "This part of IEC 61558 applies to stationary or portable, single-phase or poly-phases, air-cooled control transformers associated or otherwise. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104. This part 2-2 supplements or modifies the corresponding clauses in IEC 61558-1. This standard replaces chapter II, section 1 of IEC 60989." IEC 61558-2-20 Ed. 1.0 b:2000 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar devices - Part 2-20: Particular requirements for small reactors " "This part of IEC 61558 applies to stationary or portable, single-phase or poly-phase, air-cooled (natural or forced) general purpose small reactors, including alternating current, premagnetised and current compensated reactors, independent or associated, having a rated supply voltage not exceeding 1000 V a.c. or d.c. and rated frequency not exceeding 1 MHz, the rated power not exceeding - 2 kVAR a.c. (2 kW d.c.) for single-phase reactors; - 10 kVAR a.c. (10 kW d.c.) for poly-phase reactors. This part 2-20 is intended to be used in conjunction with IEC 61558-1. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104. " IEC 61558-2-23 Ed. 1.0 b:2000 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar devices - Part 2-23: Particular requirements for transformers for construction sites" "Applies to stationary or portable single-phase or poly-phase air-cooled (natural or forced) independent or associated, isolating or safety isolating transformers intended for use on construction sites, having a rated supply voltage not exceeding 1 000 V a.c., and a rated frequency not exceeding 500 Hz. This part 2-23 is intended to be used in conjunction with IEC 61558-1. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104." IEC 61558-2-3 Ed. 1.0 b:1999 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar devices - Part 2-3: Particular requirements for ignition transformers for gas and oil burners" "Deals with all aspects of safety such as electrical, thermal and mechanical aspects. This part of IEC 61558 applies to fixed single-phase air-cooled (natural or forced) associated transformers (incorporated or not) used in the ignition system of gas and oil burners, having a rated supply voltage not exceeding 1 000 V a.c. and a rated frequency not exceeding 500 Hz. The rated output current does not exceed 500 mA a.c. This part 2-3 is intended to be used in conjunction with IEC 61558-1. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104." IEC 61558-2-4 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar - Part 2: Particular requirements for isolating transformers for general use " "This part 2 of IEC 61558 applies to stationary or portable, single-phase or polyphase, air-cooled isolating transformers, associated or otherwise. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104. This part 2 supplements or modifies the corresponding clauses in IEC 61558-1, This Standard replaces Chapter I of IEC 742. " IEC 61558-2-5 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar - Part 2-5: Particular requirements for shaver transformers and shaver supply units " "This part 2-5 of IEC 61558 applies to shaver supply units, embodying one or more socket-outlets and a single phase air cooled isolating transformer. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104. This part 2-5 supplements or modifies the corresponding clauses in IEC 61558-1. This standard replaces chapter II, section 1, of IEC 60742." IEC 61558-2-6 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar - Part 2: Particular requirements for safety isolating transformers for general use " "This part 2 of IEC 61558 applies to stationary or portable, single-phase or polyphase, air-cooled safety isolating transformers, associated or otherwise. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104 This part 2 supplements or modifies the corresponding clauses in IEC 61558-1, This Standard replaces Chapter III, Section 1 of IEC 60742. " IEC 61558-2-7 Ed. 1.0 b:1997 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar - Part 2: Particular requirements for transformers for toys " "This part 2 of IEC 61558 applies to transformers for toys having a rated supply voltage not exceeding 250 V a.c., a rated frequency of 50/60 Hz, a rated output voltage not exceeding 24 V a.c. or 33 V ripple-free d.c. and a rated output not exceeding 200 VA and a rated output current not exceeding 10 A. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104 This part 2 supplements or modifies the corresponding clauses in IEC 61558-1 This standard replaces Chapter III, Section 2 of IEC 60742. " IEC 61558-2-8 Ed. 1.0 b:1998 "Safety of small power transformers, power supply units and similar - Part 2-8: Particular requirements for bell and chime transformers " "Applies to fixed, single-phase, air-cooled independant or associated safety isolating transformers. This part 2 supplements or modifies the corresponding clauses in IEC 61558-1. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104. This standard replaces section 3 of chapter III of IEC 60742." IEC 61558-2-9 Ed. 1.0 b:2002 "Safety of power transformers, power supply units and similar products - Part 2-9: Particular requirements for transformers for class III handlamps for tungsten filament lamps" "This Part 2-9 of IEC 61558 applies to stationary or portable single-phase air-cooled (natural or forced) associated safety isolating transformers for class III handlamps for tungsten filament lamps, having a rated supply voltage not exceeding 1 000 V a.c., a rated frequency not exceeding 500 Hz and a rated output not exceeding 10 kVA. It has the status of a group safety publication in accordance with IEC Guide 104 " IEC 61797-1 Ed. 1.0 b:1996 Transformers and inductors for use in telecommunication and electronic equipment Main dimensions of coil formers - Part 1: Coil formers for laminated cores "Specifies the main dimensions of coil formers for transformers and inductors, using a square stack of the laminations inserted in the coil formers." IEC 62032 Ed. 1.0 en:2005 "Guide for the application, specification, and testing of phase-shifting transformers " "Covers the application, specification, theory of operation, and factory and field testing of single phase and three-phase oil-immersed phase-shifting transformers (PSTs). Provides guidance to those specifying, designing, and using PSTs. IEC 62041 Ed. 1.0 b:2003 "Power transformers, power supply units, reactors and similar products - EMC requirements " "This international product family standard applies to independent transformers, reactors and power supply units covered by IEC 60989 and the IEC 61558 series of standards. It prescribes the electromagnetic compatibility requirements for emission and immunity in the frequency range 0 Hz to 1 000 MHz." IEC/TR 60616 Ed. 1.0 b:1978 Terminal and tapping markings for power transformers Gives guidance in accordance with the rules given in IEC 60445. Has the status of a technical report. IEC/TS 60076-14 Ed. 1.0 b:2004 Power transformers - Part 14: Design and application of liquid-immersed power transformers using high-temperature insulation materials "Provides design, testing and loading information for use by both the manufacturer and user of liquid-immersed power transformers using either high-temperature insulation or combinations of high-temperature and conventional insulation." IEC/TS 61639 Ed. 1.0 b:1996 "Direct connection between power transformers and gas-insulated metal-enclosed switchgear for rated voltages of 72,5 kV and above " "Applicable to the single-phase connection assemblies between gas-insulated metal-enclosed switchgear for rated voltages of 72,5 kV and above satisfying the requirements of IEC 60517 and power transformers satisfying the requirements of IEC 60076 and fitted with completely immersed bushings satisfying the requirements of IEC 60137, one end of which is immersed in the transformer oil, and the other end in the insulating gas of the switchgear. Its purpose is to establish electrical and mechanical interchangeability in the interface arrangement of these connection assemblies and to determine the limits of supply. " ISO Standards ISO 10656:1996 Electric resistance welding - Integrated transformers for welding guns ISO 12166:1997 Resistance welding equipment - Particular specifications applicable to transformers with one secondary winding for multi-spot welding, as used in the automobile industry ISO 5826:1999 Resistance welding equipment - Transformers - General specifications applicable to all transformers ISO 7284:1993 Resistance welding equipment - Particular specifications applicable to transformers with two separate secondary windings for multi-spot welding, as used in the automobile industry Additional requirements Transformers & inductors US Code – Title 42, Chapter 77 – Energy Conservation http://fatty.law.cornell.edu/uscode/html/uscode42/usc_sup_01_42_10_77.html http://fatty.law.cornell.edu/uscode/search/display.html?terms=testing%20and%20labeling %20requirements%20for%20air%20pumps&url=/uscode/html/uscode42/usc_sup_01_42 _10_77notes.html US Code 6315 A labelling rule prescribed in accordance with this section shall require the product discloses by label, the energy efficiency of such article, determined in accordance with test procedures under section 6314…. http://fatty.law.cornell.edu/uscode/search/display.html?terms=testing%20and%20labeling %20requirements%20for%20air%20pumps&url=/uscode/html/uscode42/usc_sec_42_00 006315----000-.html Distribution Transformers Energy Conservation Requirements for Distribution Transformers Lamp ballasts Federal Standards Standards for dishwashers; clothes washers; clothes dryers; fluorescent lamp ballasts Each fluorescent lamp ballast— (A) (i) manufactured on or after January 1, 1990; (ii) sold by the manufacturer on or after April 1, 1990; or (iii) incorporated into a luminaire by a luminaire manufacturer on or after April 1, 1991; and (B) designed— (i) to operate at nominal input voltages of 120 or 277 volts; (ii) to operate with an input current frequency of 60 Hertz; and (iii) for use in connection with an F40T12, F96T12, or F96T12HO lamps; shall have a power factor of 0.90 or greater and shall have a ballast efficacy factor not less than the following: Application for Operation of Ballast Input Voltage Watts Total Nominal Ballast Efficacy Lamp Factor one F40T12 lamp 120 277 120 277 120 277 120 277 40 40 80 80 150 150 220 220 two F40T12 lamps two F96T12 lamps two F96T12HO lamps 1.805 1.805 1.060 1.050 0.570 0.570 0.390 0.390 The standards described in paragraph (5) do not apply to (A) a ballast which is designed for dimming or for use in ambient temperatures of 0° F or less, or (B) a ballast which has a power factor of less than 0.90 and is designed for use only in residential building applications. (7) (A) The Secretary shall publish a final rule no later than January 1, 1992, to determine if the standards established under paragraph (5) should be amended, including whether such standards should be amended so that they would be applicable to ballasts described in paragraph (6) and other fluorescent lamp ballasts. Such rule shall contain such amendment, if any, and provide that the amendment shall apply to products manufactured on or after January 1, 1995. (B) After January 1, 1992, the Secretary shall publish a final rule no later than five years after the date of publication of a previous final rule. The Secretary shall determine in such rule whether to amend the standards in effect for fluorescent lamp ballasts, including whether such standards should be amended so that they would be applicable to additional fluorescent lamp ballasts. (C) Any amendment prescribed under subparagraph (B) shall apply to products manufactured after a date which is five years after— (i) the effective date of the previous amendment; or (ii) if the previous final rule did not amend the standards, the earliest date by which a previous amendment could have been effective; except that in no case may any amended standard apply to products manufactured within three years after publication of the final rule establishing such amended standard. General service fluorescent lamps and incandescent reflector lamps (1) (A) Each of the following general service fluorescent lamps and incandescent reflector lamps manufactured after the effective date specified in the tables listed in this paragraph shall meet or exceed the following lamp efficacy and CRI standards: FLUORESCENT LAMPS Lamp Type Nominal Lamp Minimum Minimum Average Effective Date Wattage CRI Lamp Efficacy (LPW) (Months) 4-foot medium bipin 2-foot Ushaped 8-foot slimline 8-foot high output 35 W 69 75.0 36 35 W 35 W 45 69 75.0 68.0 36 36 35 W 65 W 45 69 64.0 80.0 36 18 65 W 100 W 45 69 80.0 80.0 18 18 100 W 45 80.0 18 Nominal Lamp Wattage 40–50 51–66 67–85 86–115 116–155 156–205 INCANDESCENT REFLECTOR LAMPS Minimum Average Lamp Efficacy Effective Date (LPW) (Months) 10.5 11.0 12.5 14.0 14.5 15.0 36 36 36 36 36 36 (B) For the purposes of the tables set forth in subparagraph (A), the term “effective date” means the last day of the month set forth in the table which follows October 24, 1992. (2) Notwithstanding section 6302 (a)(5) of this title and section 6302 (b) of this title, it shall not be unlawful for a manufacturer to sell a lamp which is in compliance with the law at the time such lamp was manufactured. (3) Not less than 36 months after October 24, 1992, the Secretary shall initiate a rulemaking procedure and shall publish a final rule not later than the end of the 54-month period beginning on October 24, 1992, to determine if the standards established under paragraph (1) should be amended. Such rule shall contain such amendment, if any, and provide that the amendment shall apply to products manufactured on or after the 36month period beginning on the date such final rule is published. (4) Not less than eight years after October 24, 1992, the Secretary shall initiate a rulemaking procedure and shall publish a final rule not later than nine years and six months after October 24, 1992, to determine if the standards in effect for fluorescent lamps and incandescent lamps should be amended. Such rule shall contain such amendment, if any, and provide that the amendment shall apply to products manufactured on or after the 36-month period beginning on the date such final rule is published. (5) Not later than the end of the 24-month period beginning on the date labeling requirements under section 6294 (a)(2)(C) of this title become effective, the Secretary shall initiate a rulemaking procedure to determine if the standards in effect for fluorescent lamps and incandescent lamps should be amended so that they would be applicable to additional general service fluorescent and general service incandescent lamps and shall publish, not later than 18 months after initiating such rulemaking, a final rule including such amended standards, if any. Such rule shall provide that the amendment shall apply to products manufactured after a date which is 36 months after the date such rule is published. (6) (A) With respect to any lamp to which standards are applicable under this subsection or any lamp specified in section 6317 of this title, the Secretary shall inform any Federal entity proposing actions which would adversely impact the energy consumption or energy efficiency of such lamp of the energy conservation consequences of such action. It shall be the responsibility of such Federal entity to carefully consider the Secretary’s comments. (B) Notwithstanding subsection (n)(1) of this section, the Secretary shall not be prohibited from amending any standard, by rule, to permit increased energy use or to decrease the minimum required energy efficiency of any lamp to which standards are applicable under this subsection if such action is warranted as a result of other Federal action (including restrictions on materials or processes) which would have the effect of either increasing the energy use or decreasing the energy efficiency of such product. (7) Not later than the date on which standards established pursuant to this subsection become effective, or, with respect to high-intensity discharge lamps covered under section 6317 of this title, the effective date of standards established pursuant to such section, each manufacturer of a product to which such standards are applicable shall file with the Secretary a laboratory report certifying compliance with the applicable standard for each lamp type. Such report shall include the lumen output and wattage consumption for each lamp type as an average of measurements taken over the preceding 12-month period. With respect to lamp types which are not manufactured during the 12-month period preceding the date such standards become effective, such report shall be filed with the Secretary not later than the date which is 12 months after the date manufacturing is commenced and shall include the lumen output and wattage consumption for each such lamp type as an average of measurements taken during such 12-month period. Appendix Q to Subpart B of Part 430—Uniform Test Method for Measuring the Energy Consumption of Fluorescent Lamp Ballasts 1. Definitions 1.1ANSI Standard means a standard developed by a committee accredited by the American National Standards Institute. 1.2Ballast input voltage means the rated input voltage of a fluorescent lamp ballast. 1.3F4OT12 lamp means a nominal 40 watt tubular fluorescent lamp which is 48 inches in length and one and a half inches in diameter, and conforms to ANSI standard C78.1– 1978(R1984). 1.4F96T12 lamp means a nominal 75 watt tubular fluorescent lamp which is 96 inches in length and one and one-half inches in diameter, and conforms to ANSI Standard C78.1–1978 (R1984). 1.5F96T12HO lamp means a nominal 110 watt tubular fluorescent lamp which is 96 inches in length and one and a half inches in diameter, andto operate. 1.6Input current means the root-mean-square (RMS) current in amperes delivered to a fluorescent lamp ballast. 1.7Luminaire means a complete lighting unit consisting of a fluorescent lamp or lamps, together with parts designed to distribute the light, to position and protect such lamps, and to connect such lamps to the power supply through the ballast. 1.8Nominal lamp watts means the wattage at which a fluorescent lamp is designed to operate. 1.9Power factor means the power input divided by the product of ballast input voltage and input current of a fluorescent lamp ballast, as measured under test conditions specified in ANSI Standard C–82.2–1984. 1.10Power input means the power consumption in watts of a ballast and fluorescent lamp or lamps, as determined in accordance with the test procedures specified in ANSI Standard C82.2–1984. 1.11Relative light output means the light output delivered through the use of a ballast divided by the light output delivered through the use of a reference ballast, expressed as a percent, as determined in accordance with the test procedures specified in ANSI Standard C82.2–1984. 1.12Residential building means a structure or portion of a structure which provides facilities or shelter for human residency, except that such term does not include any multifamily residential structure of more than three stores above grade. 1.13ANSI Standard C82.2–1984 means the test standard published by the American National Standard Institute (ANSI), titled “American National Standard for Fluorescent Lamp Ballasts—Method of Measurement, 1984”, and designated as ANSI C82.2–1984. 2. Test conditions. The test conditions for testing fluorescent lamp ballasts shall be done in accordance with the American National Standard Institute (ANIS) Standard C82.2– 1984, “American National Standard for Fluorescent Lamp Ballasts—Methods of Measurement,” approved October 21, 1983. This incorporation by reference was approved by the Director of the Federal Register in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR, part 51. Copies may be obtained from ANSI Publication Sales, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10068. Copies may be inspected at the Department of Energy, Freedom of Information Reading Room, Room 1E–190, Fluorescent Lamp Ballasts, Docket No. CE–RM–89–102, 1000 Independence Avenue, SW, Washington DC 20585, or at the Office of the Federal Register, 800 North Capitol Street, NW., suite 700, Washington, DC 20001. Any subsequent amendment to this standard by the standard-setting organization will not affect the DOE test procedures unless and until amended by DOE. The test conditions are described in sections 4, 5, 6, 7, and 21 of ANSI Standard C82.2– 1984. 3.Test Method and Measurements. The test method for testing fluorescent lamp ballasts shall be with ANSI Standard C82.2–1984. 3.1. done in accordance 3.2Instrumentation. The instrumentation shall be as specified by sections 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 19.1, and 23.2 of ANSI Standard C82.2–1984. 3.3Electric Supply. 3.3.1.Input Power. Measure the input power (watts) to the ballast in accordance with ANSI Standard C82.2–1984, section 3.2.1(3) and section 4. 3.3.2Input Voltage. Measure the input voltage (volts) (RMS) to the ballast in accordance with ANSI Standard C82.2–1984, section 3.2.1(1) and section 4. 3.3.3Input Current. Measure the input current (amps) (RMS) to the ballast in accordance with ANSI Standard C82.2–1984, section 3.2.1(2) and section 4. 3.4Light Output. Measure the light output of the reference lamp with the 3.4.1 reference ballast in accordance with ANSI Standard C82.2–1984, section 16. Measure the light output of the reference lamp with the test with ANSI Standard C82.2–1984, section 16. 3.4.2 ballast in accordance 4.Calculations. Calculate relative light output: 4.1 ec14no91.053 Where: photocell output of lamp on test ballast is determined in accordance with section 3.4.2, expressed in watts, and photocell output of lamp on ref. ballast is determined in accordance with section 3.4.1, expressed in watts. Determine the Ballast Efficacy Factor (BEF) using the following 4.2. equations: (a) Single lamp ballast ec14no91.054 (b) Multiple lamp ballast ec14no91.055 Where: input power is determined in accordance with section 3.3.1, relative light output as defined in section 4.1, and average relative light output is the relative light output, as defined in section 4.1, for all lamps, divided by the total number of lamps. Determine Ballast Power Factor (PF): 4.3 ec14no91.056 Where: Input power is as defined in section 3.3.1, Input voltage is determined in accordance with section 3.3.2, expressed in volts, and Input current is determined in accordance with section 3.3.3, expressed in amps. [54 FR 6076, Feb. 7, 1989, as amended at 56 FR 18682, April 24, 1991] Energy & Water Conservation Standards: (m) Fluorescent lamp ballasts. (1) Except as provided in paragraph (m)(2) of this section, each fluorescent lamp ballast— (i)(A) Manufactured on or after January 1, 1990; (B) Sold by the manufacturer on or after April 1, 1990; or (C) Incorporated into a luminarie by a luminarie manufacturer on or after April 1, 1991; and (ii) Designed— (A) To operate at nominal input voltages of 120 or 277 volts; (B) To operate with an input current frequency of 60 Hertz; and (C) For use in connection with F40T12, F96T12, or F96T12HO lamps; shall have a power factor of 0.90 or greater and shall have a ballast efficacy factor not less than the following: -----------------------------------------------------------------------Total Ballast nominal Ballast Application for operation of input lamp efficacy voltage watts factor -----------------------------------------------------------------------One F40T12 lamp........................... 120 40 1.805 277 40 1.805 Two F40T12 lamps.......................... 120 80 1.060 277 80 1.050 Two F9T12 lamps........................... 120 150 0.570 277 150 0.570 Two F96T12HO lamps........................ 120 220 0.390 277 220 0.390 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ (2) The standards described in paragraph (m)(1) of this section do not apply to (i) a ballast which is designed for dimming or for use in ambient temperatures of 0 °F or less, or (ii) a ballast which has a power factor of less than 0.90 and is designed for use only in residential building applications. (n) General service fluorescent lamps and incandescent reflector lamps. (1) Each of the following general service fluorescent lamps manufactured after the effective dates specified in the table shall meet or exceed the lamp efficacy and CRI standards shown in the table below: Fluorescent Lamps --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Minimum average Lamp type Nominal lamp wattage Minimum lamp Effective date CRI efficacy (LPW) --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-foot medium bi-pin.................. gt;35W 69 75.0 Nov. 1, 1995. [le]35W 45 75.0 Nov. 1, 1995. 2-foot U-shaped....................... gt;35W 69 68.0 Nov. 1, 1995. [le]35W 45 64.0 Nov. 1, 1995. 8-foot slimline....................... gt;65W 69 80.0 May 1, 1994. [le]65W 45 80.0 May 1, 1994. 8-foot high output.................... gt;100W 69 80.0 May 1, 1994. [le]100W 45 80.0 May 1, 1994. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- (2) Each of the following incandescent reflector lamps manufactured after November 1, 1995, shall meet or exceed the lamp efficacy standards shown in the table in this paragraph: Incandescent Reflector Lamps -----------------------------------------------------------------------Minimum average Nominal lamp wattage lamp efficacy (LPW) -----------------------------------------------------------------------40-50....................................................... 10.5 51-66....................................................... 11.0 67-85....................................................... 12.5 86-115...................................................... 14.0 116-155..................................................... 14.5 156-205..................................................... 15.0 -----------------------------------------------------------------------For more information on test procedures please visit: http://a257.g.akamaitech.net/7/257/2422/14mar20010800/edocket.access.gpo.gov/cfr_20 01/janqtr/pdf/10cfr430.22.pdf




