26. Organisational behaviour and human
advertisement
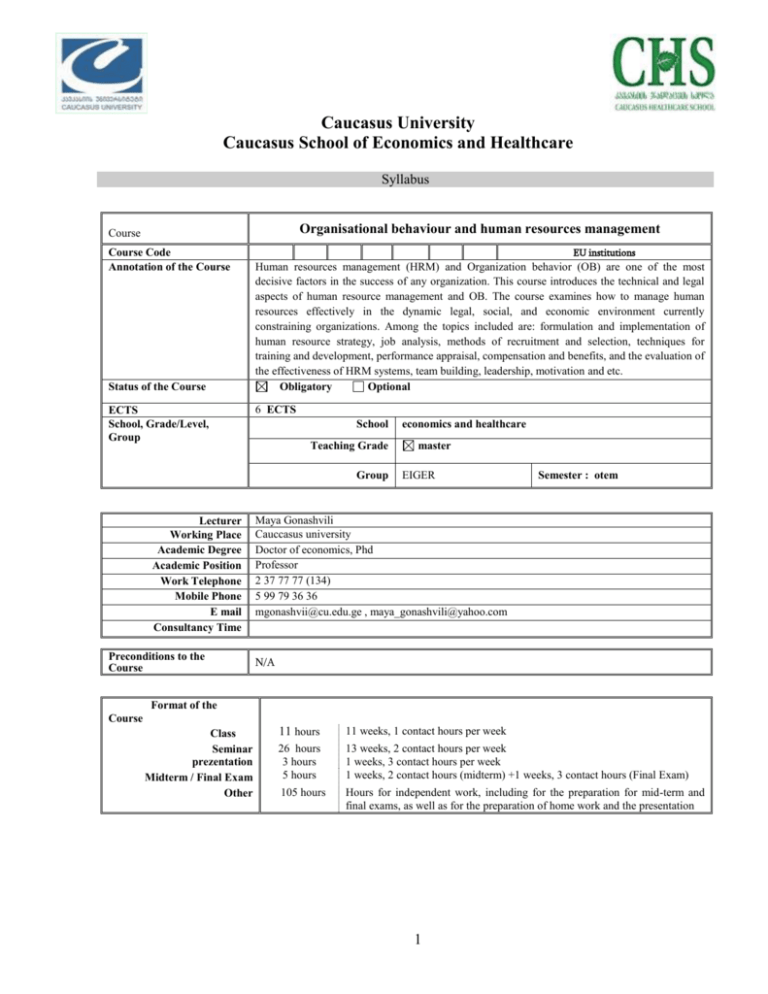
Caucasus University Caucasus School of Economics and Healthcare Syllabus Organisational behaviour and human resources management Course Course Code Annotation of the Course Status of the Course ECTS School, Grade/Level, Group EU institutions Human resources management (HRM) and Organization behavior (OB) are one of the most decisive factors in the success of any organization. This course introduces the technical and legal aspects of human resource management and OB. The course examines how to manage human resources effectively in the dynamic legal, social, and economic environment currently constraining organizations. Among the topics included are: formulation and implementation of human resource strategy, job analysis, methods of recruitment and selection, techniques for training and development, performance appraisal, compensation and benefits, and the evaluation of the effectiveness of HRM systems, team building, leadership, motivation and etc. Obligatory Optional 6 ECTS School Teaching Grade Group Lecturer Working Place Academic Degree Academic Position Work Telephone Mobile Phone E mail Consultancy Time Preconditions to the Course economics and healthcare master EIGER Semester : otem Maya Gonashvili Cauccasus university Doctor of economics, Phd Professor 2 37 77 77 (134) 5 99 79 36 36 mgonashvii@cu.edu.ge , maya_gonashvili@yahoo.com N/A Format of the Course Class Seminar prezentation Midterm / Final Exam Other 11 hours 26 hours 3 hours 5 hours 11 weeks, 1 contact hours per week 105 hours Hours for independent work, including for the preparation for mid-term and final exams, as well as for the preparation of home work and the presentation 13 weeks, 2 contact hours per week 1 weeks, 3 contact hours per week 1 weeks, 2 contact hours (midterm) +1 weeks, 3 contact hours (Final Exam) 1 The course goal is to teach students: Objectives of the Course Outcome of the teaching learning of issues provided by this course students should have developed the following skills: attitudes towards knowledge and critical approach,new and/or different ideas; the capacity for close reading and analysis of a range of sources; the capacity for critical and independent thought and reflection; the capacity to plan and manage time; the capacity to work effectively in a team Compulsory Reading Supplementary Literature and Other Sources of Information Teaching Methods Requirements for the Students The Changing Nature of Human Resource Management and modern concepts OB; Human Resource Planning Equal Employment Opportunity and Diversity The Nature of Jobs Staffing the Organization :Recruitment; Selection HR Training, Development, & Talent Management Performance Management Motivation; Compensation Strategies and Practices Managing Employee Benefits; Employee Rights and Responsibilities; Health and Safety; Comunicaton, Design making; Conflict management, stress management, chaing management; Team building, lidership; Etc. - Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 Gerard H. Seijts, Cases in Organizational Behavior (The Ivey Casebook Series) , 2010 www.labourline.org www.europa.eu www.geostatistics.ge Explanation method Inductive and deductive teaching method Method of Analysis and synthesis Discussions/debates Group work /Collaborative Case study, Demonstrative method, Presentation method Simulation and role playing Problem bases teaching (PBL) Brain storming Students must attend lectures. There shall not be justification for missing classes without solid reason. Non-attendance will be reflected in the final grade. Students must attentively follow the lecture and participate actively in the discussions around the topics considered during the class. No other activities are allowed during the classes (talking to each other, using mobiles or other electronic devices for purposes other than class related, etc.) No talking of students with each other during the written or oral examination is allowed. No copying of material from books or each other is allowed either. A student disregarding this rule will leave the class and the task or the exam will be considered as failed. 2 Any attempt of plagiarism will be revealed and controlled to the maximum degree possible. At the point of handing over the work, a student will confirm by signing a short statement that the work handed over, prepared for the purposes of the course is original, individual, drafted by him/her and excludes plagiarism. If this requirement is neglected, the work/component of the course will get an automatic “0” grade. Knowledge Assessment Forms and Criteria Form of the Exam Written tasks/quizzes Oral, casy Presentation/ research Midterm Exam Final Exam Quantity 5 2 Assessment 2 5 Total Points 10 points 10 points 5 1 1 1 1 2 10 10 20 30 10 points 20 points 20 points 30 points 100 points Evaluation System The course requires the active participation of students and is based on the permanent assessment of the knowledge acquired during the course. The course will be assessed with the 100 point system, broken down to the different methods used during the course. The assessment of students will encompass the following: • The assessment of the independent work • The assessment throughout the term • The final exam The oral, as well as written methods shall be used for the assessment of students. The mid-term exam shall be held in the 8th week. The 7th week shall be devoted to the preparation for the mid-term exam. The mid-term exam shall cover all the material covered during the first 6 weeks of the course. For the mid-term exam a student shall provide the answer to a case and questions. The mid-term exam shall be evaluated with 20 maximum points. The test will include open ended, as well as, closed questions. NOTE: A student shall get at least 21 points during the term (via seminars, interim exams) to be allowed to pass the final exam. The final written exam will be held at the end of the course. There shall be a case and questions to be answered by a student during the final exam. The test will include open ended, as well as, closed questions. The final-term exam shall be assessed with 30 maximum points. Essay/Presentation: Each student has to prepare a final essay of about 2,500-3,000 words (excluding bibliography). Any topic is acceptable as far as it is related to the subject of the course. A proposal for the final paper should be submitted by week 11.The proposal should be not longer than 2 pages, and it should include the proposed topic with the main questions or hypotheses, the methods of inquiry, and a rough bibliography. The proposals will be discussed in class on the 11 th week Students will receive individual feedback on their proposals and will be expected to submit the final paper on the 17th week. Note: all papers should be in Times New Roman font, space-1.5, and font size - 12. /Also PPT/. Indexed System of Evaluation and Indicators Excellent Very Good Good Satisfactory Passed Could not Pass Failed Evaluation Scale A (91%-100) B (81%-90%) C (71%-80%) D (61%-70%) E (51%-60%) FX (41%-50%) F (40%-0) 3 Points 91-100 81-90 71-80 61-70 51-60 41-50 0-40 Academic Calendar I week Class/lecture 2 hours V week Class/lecture/ Seminar – 2 hours 1. written task/ quiz #1 – 5 points X week Class/lecture – 2 hours XIV week Class/lecture/ Seminar – 3 hours 1. written task/ quiz #2– 5 points II week Class/lecture/Seminar –- 2 hours 1. written task – 2 points VI week Class/lecture/ Seminar –3 hours 1. Group oral present. – 2 points XI week Class/lecture/ Seminar – 3 hours 1.oral/proposal present.-2 points 2.written task – 2 points XV week Class/lecture/ Seminar – 3 hours 1. oral present/case study. – 2 XVIII- XIX week Final exam – 3 hours- 30 points III week Class/lecture/ Seminar –- 3 hours 1. written task – 2 points IV week Class/lecture/ Seminar –3 hours 1. oral present. – 2points VII week Lecture / Seminar / Discussion 2 hours preparation for midterm VIII-IX week Mid-term exam–2 hours -20 points XII week Class/lecture/ Seminar – 3 hours 1. written task – 2 points 2.oral present/case study. – 2 points XIII week Class/lecture/ Seminar – 3 hours 1. written task – 2 points XVI week Lecture / Seminar / Discussion 2 hours preparation for final exam XVII week oral presentation/research – 3 hours-20 points (10+10) XXI week Retake of FX XX week Renewal Final exam Calendar Plan for Classes Time, place and date N 1st Week Day - Start Date Finish Auditorium Topic for discussion, home work, reading Introduction to the class, the content of the course, methods and assessment system, the mandatory and supplementary readings Class 1. INTRODUCTION: The Changing Nature of Human Resource Management and organization behavior. Issues to consider: What is HRM and What is OB? Individual Behavior: Personality & Values . Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: 2nd Week A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 Class 2. Human Resource Planning. Equal Employment Opportunity and Diversity Issues to consider: 4 Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 written task – 2 points 3rd Week Class 3. The Nature of Jobs Issues to consider: Jobs description, Carier management, models of carier s , etc. Mandatory Reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary Reading: written task – 2 points 4th Week Class 4. Staffing the Organization I:-Recruitment Issues to consider: A CASE STUDY: Staffing the Organization , what is recruitment, principals, goals and policy of recruitments, etc. Obligatory Reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary Reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 oral present. – 2points 5th Week Class 5 –. Staffing the Organization II---Selection Issues to consider: Staffing the Organization, what is Selection, principals selection, selection in successful people management , selection policies and procedures, criteria of professionalism including reliability, validity and fairness appreciate. A CASE STUDY: Mandatory Reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary Reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 written task/ quiz #1 – 5 points 6th Week Class 6. HR Training, Development, & Talent Management Issues to consider: . Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 5 Supplementary reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 Group oral present. – 2 points 7th Week Class 7.: HR Training, Development, & Talent Management (continued) Issues to consider: HR Training aims, goals, principals, etc Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: preparation for midterm Mid-term exam – 2 hours 8-th Week 9th Week 10th Week Class 8. Motivation and organization behavior. Compensation Strategies and Practices Issues to consider: Motivation and Rewards, Introduction , Need-Based Theories of Motivation, etc. Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 11th Week Class 9. Performance Management. Managing Employee Benefits. Employee Rights and Responsibilities. Health and Safety Issues to consider: Performance Management. Managing Responsibilities. Health and Safety Employee Benefits. Employee Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 oral/proposal present.-2 points 2.written task – 2 points 12th Week Class 10. Comunication. Team building and lidership Issues to consider: Communication in Teams and Organizations Leadership & Organizational Culture Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles 6 Rights and Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 1. written task – 2 points 2.oral present/case study. – 2 points 13th Week Class 11. Power, Persuasion, & Influence . Issues to consider:. Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 written task – 2 points 14th Week Class 12. Conflict management. Negotiations Issues to consider: Introduction, What Is confict? Managing conflict proceies, conflict at the work, printipals of negotiations Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 . written task/ quiz #2– 5 points 15th Week Class 13. Stress management. Chaing management Issues to consider: Introduction, What Is Stress? Avoiding and Managing Stress, What Are Emotions? Emotions at Work Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014 oral present/case study. – 2 16th Week Class 14. Decision Making & Ethics Issues to consider: Organizational Design; The Role of Ethics and National Culture Summary all course materials. Course wrap-up & summary Preparation for the final exam. Mandatory reading: Gary Dessler, Human Resource Management, 14 E, 2014; Stephan P. Robbins, Timothy A. Judge, Organizational Behavior, 16 /E, 2014 Supplementary reading: 7 A reader will be available to the students with additional papers and articles , Amstrong, A Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice: 16 /E ,2014, Gerard H. Seijts, Cases in Organizational Behavior (The Ivey Casebook Series) , 2010, and etc. th 17 Week Presentation 3 hours- 20 points 18th -19th Weeks 20th Week Final exam – 3 hours- 30 points 21th Renewal Final exam Week Retake of FX 8