Chapter 12, section 3 – Water Underground
advertisement

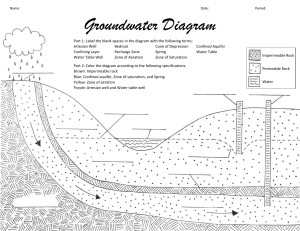
Chapter 12, section 3 – Water Underground Permeable 1. Rock and soil that allows water to pass through the ground. 2. The larger the pores, the easier it is for water to pass through, such as sand and gravel. Impermeable 1. Layers underground that water cannot pass through. 2. Examples are clay and granite. Saturated zone 1. The area of permeable rock that is totally filled or saturated with water. Water table 1. The top of the saturated zone. Unsaturated zone 1. The soil and rock layers above the water table. 2. The pores contain pockets of air as well as water. Springs 1. A location where the water table is close to the surface. 2. Water bubbles out of the ground or flows through cracks in the rock. Aquifer 1. An underground layer of rock or sediment that holds water. 2. Can range in size from a small area, to an area that covers several states. Wells 1. A method of getting groundwater by drilling below the water table. 2. Today, pumps are used to bring water to the surface. Artesian well 1. Water in an artesian well comes to the surface because of pressure in the aquifer. 2. Water is trapped between two layers of impermeable rock. Pressure from the rock pushing down on the water forces it to the surface.