Óbuda University
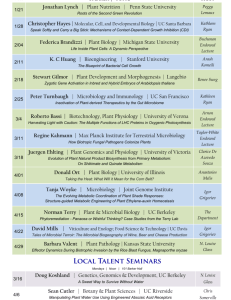
advertisement
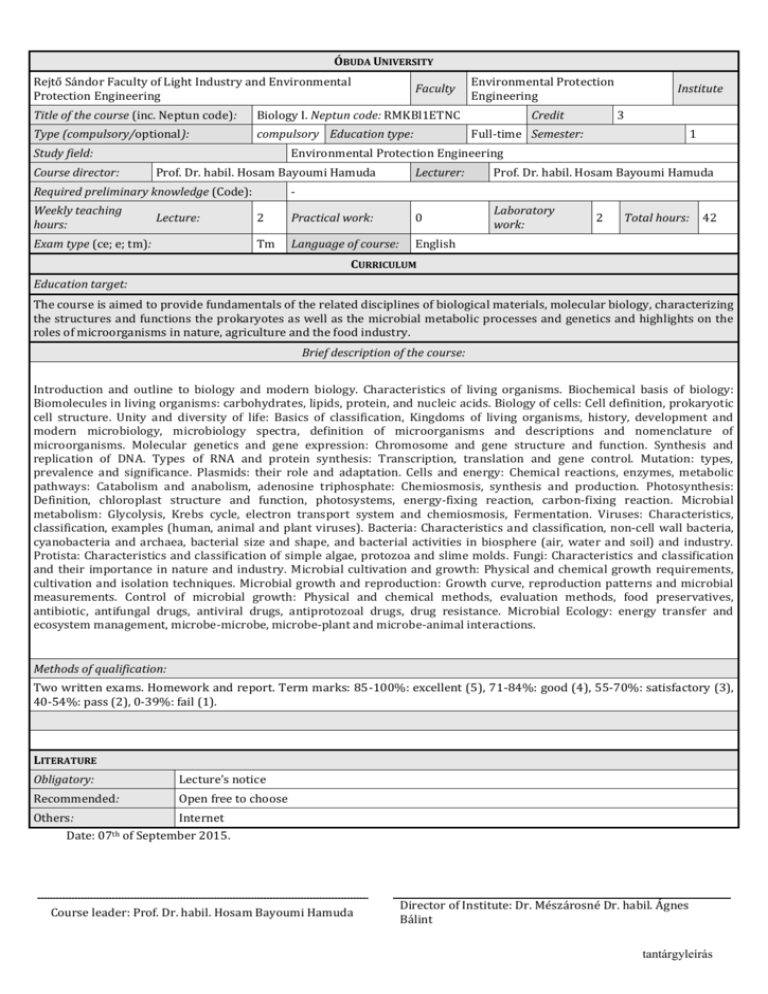
ÓBUDA UNIVERSITY Rejtő Sándor Faculty of Light Industry and Environmental Protection Engineering Faculty Title of the course (inc. Neptun code): Biology I. Neptun code: RMKBl1ETNC Type (compulsory/optional): compulsory Education type: Study field: Course director: Credit Institute 3 Full-time Semester: 1 Environmental Protection Engineering Prof. Dr. habil. Hosam Bayoumi Hamuda Required preliminary knowledge (Code): Weekly teaching hours: Environmental Protection Engineering Lecture: Exam type (ce; e; tm): Lecturer: Prof. Dr. habil. Hosam Bayoumi Hamuda Laboratory work: 2 Practical work: 0 Tm Language of course: English 2 Total hours: 42 CURRICULUM Education target: The course is aimed to provide fundamentals of the related disciplines of biological materials, molecular biology, characterizing the structures and functions the prokaryotes as well as the microbial metabolic processes and genetics and highlights on the roles of microorganisms in nature, agriculture and the food industry. Brief description of the course: Introduction and outline to biology and modern biology. Characteristics of living organisms. Biochemical basis of biology: Biomolecules in living organisms: carbohydrates, lipids, protein, and nucleic acids. Biology of cells: Cell definition, prokaryotic cell structure. Unity and diversity of life: Basics of classification, Kingdoms of living organisms, history, development and modern microbiology, microbiology spectra, definition of microorganisms and descriptions and nomenclature of microorganisms. Molecular genetics and gene expression: Chromosome and gene structure and function. Synthesis and replication of DNA. Types of RNA and protein synthesis: Transcription, translation and gene control. Mutation: types, prevalence and significance. Plasmids: their role and adaptation. Cells and energy: Chemical reactions, enzymes, metabolic pathways: Catabolism and anabolism, adenosine triphosphate: Chemiosmosis, synthesis and production. Photosynthesis: Definition, chloroplast structure and function, photosystems, energy-fixing reaction, carbon-fixing reaction. Microbial metabolism: Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport system and chemiosmosis, Fermentation. Viruses: Characteristics, classification, examples (human, animal and plant viruses). Bacteria: Characteristics and classification, non-cell wall bacteria, cyanobacteria and archaea, bacterial size and shape, and bacterial activities in biosphere (air, water and soil) and industry. Protista: Characteristics and classification of simple algae, protozoa and slime molds. Fungi: Characteristics and classification and their importance in nature and industry. Microbial cultivation and growth: Physical and chemical growth requirements, cultivation and isolation techniques. Microbial growth and reproduction: Growth curve, reproduction patterns and microbial measurements. Control of microbial growth: Physical and chemical methods, evaluation methods, food preservatives, antibiotic, antifungal drugs, antiviral drugs, antiprotozoal drugs, drug resistance. Microbial Ecology: energy transfer and ecosystem management, microbe-microbe, microbe-plant and microbe-animal interactions. Methods of qualification: Two written exams. Homework and report. Term marks: 85-100%: excellent (5), 71-84%: good (4), 55-70%: satisfactory (3), 40-54%: pass (2), 0-39%: fail (1). LITERATURE Obligatory: Lecture’s notice Recommended: Open free to choose Others: Internet Date: 07th of September 2015. Course leader: Prof. Dr. habil. Hosam Bayoumi Hamuda Director of Institute: Dr. Mészárosné Dr. habil. Ágnes Bálint tantárgyleírás