Pelvic Orthopedic Tests
advertisement
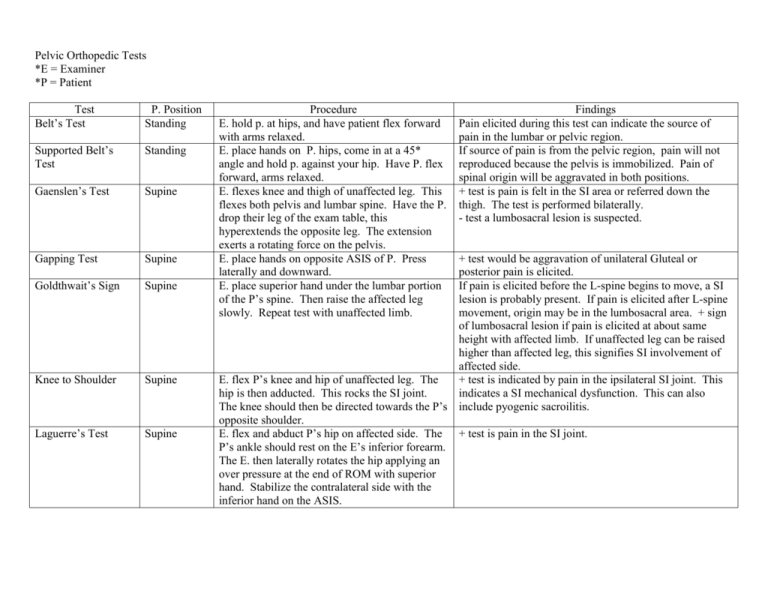
Pelvic Orthopedic Tests *E = Examiner *P = Patient Test Belt’s Test P. Position Standing Supported Belt’s Test Standing Gaenslen’s Test Supine Gapping Test Supine Goldthwait’s Sign Supine Knee to Shoulder Supine Laguerre’s Test Supine Procedure E. hold p. at hips, and have patient flex forward with arms relaxed. E. place hands on P. hips, come in at a 45* angle and hold p. against your hip. Have P. flex forward, arms relaxed. E. flexes knee and thigh of unaffected leg. This flexes both pelvis and lumbar spine. Have the P. drop their leg of the exam table, this hyperextends the opposite leg. The extension exerts a rotating force on the pelvis. E. place hands on opposite ASIS of P. Press laterally and downward. E. place superior hand under the lumbar portion of the P’s spine. Then raise the affected leg slowly. Repeat test with unaffected limb. Findings Pain elicited during this test can indicate the source of pain in the lumbar or pelvic region. If source of pain is from the pelvic region, pain will not reproduced because the pelvis is immobilized. Pain of spinal origin will be aggravated in both positions. + test is pain is felt in the SI area or referred down the thigh. The test is performed bilaterally. - test a lumbosacral lesion is suspected. + test would be aggravation of unilateral Gluteal or posterior pain is elicited. If pain is elicited before the L-spine begins to move, a SI lesion is probably present. If pain is elicited after L-spine movement, origin may be in the lumbosacral area. + sign of lumbosacral lesion if pain is elicited at about same height with affected limb. If unaffected leg can be raised higher than affected leg, this signifies SI involvement of affected side. E. flex P’s knee and hip of unaffected leg. The + test is indicated by pain in the ipsilateral SI joint. This hip is then adducted. This rocks the SI joint. indicates a SI mechanical dysfunction. This can also The knee should then be directed towards the P’s include pyogenic sacroilitis. opposite shoulder. E. flex and abduct P’s hip on affected side. The + test is pain in the SI joint. P’s ankle should rest on the E’s inferior forearm. The E. then laterally rotates the hip applying an over pressure at the end of ROM with superior hand. Stabilize the contralateral side with the inferior hand on the ASIS. Pelvic Orthopedic Tests Continued *E = Examiner *P = Patient Test Fabere-Patrick’s Test P. Position Supine Hibb’s Test Prone Yeoman’s Test Prone Iliac Compression Test Side Posture Lewin-Gaenslen’s Test Side Posture SI Resisted Abduction Test Side Posture * P = Patient * E = Examiner Procedure If P does not elicit pain from Laguerre’s Test, then place the P’s ankle of the flexed leg on their opposite knee. With your superior hand, push down on P’s bent knee. Support the P’s ASIS with inferior hand. E. place superior hand on P’s sacrum. Flex the P’s leg. Laterally rotate the P’s leg causing strong internal rotation of femoral head. Repeat on opposite leg. E. place superior hand on P’s sacrum. Place inferior hand on patients inner thigh and extend. E. place both hands, one on top of the other on the P’s superior ilium. Press towards the floor. P. lies on unaffected side. Have the P. pull their bottom knee toward their chest. E. puts pressure on the sacrum and hyperextends the affected thigh. P. lies on unaffected side. E. place superior hand on SI joint. Have the P. raise their leg and hold it. If this elicits pain, stop the test here. If not, have the P. resist downward pressure. Repeat test on opposite side. Results + sign is pain in the hip during the test, particularly abduction and external rotation, this is indicative of a coxapathologic condition. + test produces pelvic pain. This is significant for a sacroiliac lesion. Pain on extension on same side indicates SI joint stress. Pain at the opposite side indicates pelvic ligament sprain. Lumbar pain indicates lumbar involvement. Increases pressure on the SI joint suggests a SI lesion. It can also indicate a sprain of posterior SI ligament. + sign is pain produced in the SI joint. The test is indicative of SI lesions. + test will elicit pelvic pain near PSIS. This is specific for a SI sprain or subluxation.