Biology 11
advertisement
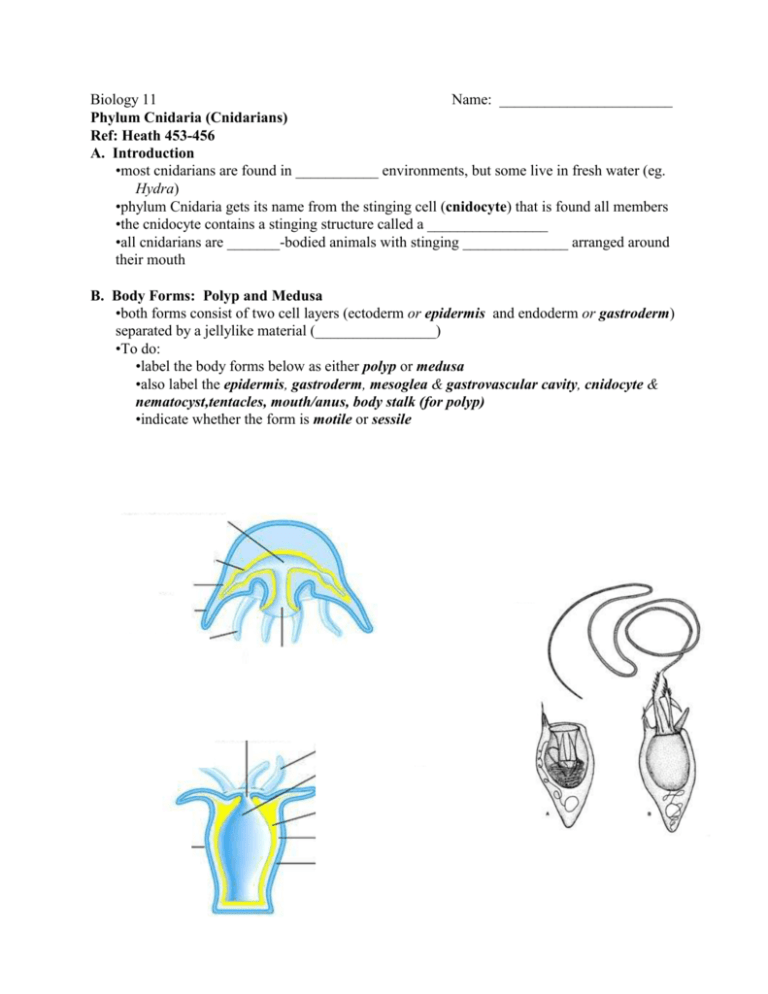
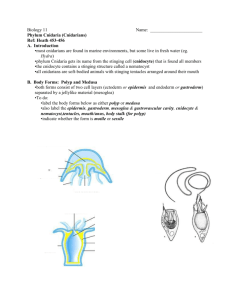
Biology 11 Name: _______________________ Phylum Cnidaria (Cnidarians) Ref: Heath 453-456 A. Introduction •most cnidarians are found in ___________ environments, but some live in fresh water (eg. Hydra) •phylum Cnidaria gets its name from the stinging cell (cnidocyte) that is found all members •the cnidocyte contains a stinging structure called a ________________ •all cnidarians are _______-bodied animals with stinging ______________ arranged around their mouth B. Body Forms: Polyp and Medusa •both forms consist of two cell layers (ectoderm or epidermis and endoderm or gastroderm) separated by a jellylike material (________________) •To do: •label the body forms below as either polyp or medusa •also label the epidermis, gastroderm, mesoglea & gastrovascular cavity, cnidocyte & nematocyst,tentacles, mouth/anus, body stalk (for polyp) •indicate whether the form is motile or sessile •cnidarians are classified according to which stage (polyp or medusa) predominates in the life cycle (some cnidarians have an alternation of generations type of life cycle where a polyp stage alternates with a ____________ stage) •examples of cnidarians in which polyp stage predominates: •examples of cnidarians in which medusa stage predominates: C. Reproduction: Life Cycle of Jellyfish Aurelia (simplified version) Label the following structures: medusa, polyp, egg, sperm, blastula, planula 1. What is the planula? _________________________________________________________ 2. What are the two body forms of the jellyfish shown in the diagram? __________________________________________________________________________ 3. What kind of symmetry does Aurelia have? _______________________________________ 4. Where does meiosis occur in the jellyfish life cycle? ________________________________ 5. What happens between fertilization and the planula stage of the jellyfish? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 6. Is the production of medusae from the polyp shown in the life cycle an example of sexual or asexual reproduction? Explain your answer. ______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 7. What are the structures that aid mobility of the planula called? _________________________ 8. Describe how a medusa moves through the water. __________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 9. How is the planula like the larva of a sponge? ______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ D. Structure of Hydra •Label the following structures: Gastrovascular cavity,Tentacle,Cnidocyte,Ectoderm, Endoderm,Mesoglea,Ovary/Teste,Bud,Nematocyst,Mouth,Basal Disk E. Form and Function in Cnidarians 1. Feeding and Digestion •____________ located on tentacles release barbs containing ___________ to paralyze or kill prely •_____________ push food through ___________ & into ____________________________ •specialized cells in the gastroderm (endoderm) release _____________ that partially digest food •food fragments taken up by gastroderm cells (via ____________________) & further digestion takes place inside cells (________cellular digestion) •nutrients transported throughout body by __________________ •undigested wastes are expelled through _______________ (therefore _______________ body plant) Symbiotic Relationships (describe how many cnidarians are dependent on photosynthetic symbionts) 2. Gas Exchange, Excretion, Internal Transport •no specialized systems are necessary because 3. Nervous System •cnidarians lack a _______________ nervous system & _____________ •have simple nerve _______ that coordinates movement of ______________ & body •nerve ______ is concentrated around the ____________ & is found throughout ___________ •specialized _____________ cells in epidermis detect ______________ in food & _________ •movement is accomplished by ______________ cells that contract under ______________ stimulation 4. Reproduction •most cnidarians reproduce ____________ & ________________ •asexual is via ________________ (describe process) •sexual (describe usual process) •some exhibit ________________ of generations between ________ & __________ stages (although both are ____ n ...ie. _______________)