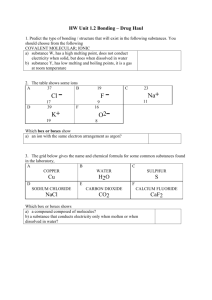
Chemical Bonding WS#1
advertisement

AP Chem Mr. Dehne Name: ________________________________________ Date: _________________ Per#:___ AP Chem Intramolecular (bonding) & Intermolecular Forces (s and l) Chemical Bonding WS#1 1. A molecule of which of the following compounds contains a double bond? (A) C3H8 (B) C2H6 (C) C2H4 (D) C2H6O (E) CH4 2. A compound that exhibits resonance is: (A) SO2 (B) N2 (C) CO2 (D) HCl (E) NH3 3. The best example of a nonpolar molecule containing polar bonds is: (A) F2 (B) SO2 (C) CS2 (D) PCl3 4. Which of the following is nonpolar? (A) F2O (B) HCN (C) SO2 (D) NO2 - (E) NO2+ 5. Which of the following compounds does not follow the Octet Rule? (A) H2O (B) PH3 (C) PCl3 (D) PCl5 (E) SO3 6. Which contains the shortest oxygen - oxygen bond? (A) O2 (B) O3 (C) O22- (D) HO27. Which species is a free radical? (A) N2O (B) NO2- (C) NO2+ (D) NO 8. Which of the following molecules has the shortest bond length? (A) N2 (B) O2 (C) Cl2 (D) Br2 (E) I2 9. (A) H2O (B) F2O (C) HCN (D) NH3 (E) CCl4 10. The best example of a nonpolar molecule containing polar bonds is: (A) CSe2 (B) H2O (C) CH4 (D) CCl4 11. Which of the following has zero dipole moment (i.e. is non- polar)? (A) H2O (B) NO2 (C) CCl4 (D) SO32- (E) HF Chemical Bonding WS#2 1. Draw the Lewis electron-dot structures for CO32-, CO2, and CO, including resonance structures where appropriate. Which of the three species has the shortest C-O bond length? Explain the reason for your answer. 2. There are three compounds with the formula C2H2Cl2. Draw Lewis structures for these three compounds. Which of the three are polar molecules? 3. Draw Lewis structures for H2CO, CNS- (C is the central atom), NO3-, and SO3. Include resonance structures where applicable, and using one of the above as an example, explain why resonance forms are necessary to represent the correct structure. 4. Draw Lewis structures for the following species: (A) CO2 (B) BeF2 (C) HN3 (D) SO42(E) N2O4 (F) NO 5. Draw reasonable Lewis structures for the following. (none obey the octet rule) (A) NO2 (B) SO2(C) BCl3 (D) CO+ Molecular Structure WS#3 1. Which molecule exhibits sp3d2 hybridization? A. SO2 B. SF6 C. CH4 2. When carbon undergoes sp2 hybridization, it forms: A. four sigma bonds. B. three sigma bonds and one pi bond. C. two sigma bonds and two pi bonds. D. one sigma bond and three pi bonds. E. four pi bonds. 3. Which molecule has a triangular bipyramidal geometry? A. PF5 B. H2O C. SF6 4. The approximate OSO angle in the SO2 molecule is: A. 90o B. 109o D. PCl5 E. NH3 D. ClF3 E. XeF2 C. 120o D. 180o 1 What is the probable shape of RnCl3+? A. Trigonal planar C. Trigonal bipyramidal B. T-shaped D. Square pyramidal 6. Which geometries are possible for compounds whose central atoms are sp 3 hybridized? A. Trigonal planar or bent. C. Square planar, tetrahedral, or trigonal planar. B. Tetrahedral, bent, or trigonal pyramidal. D. Trigonal bipyramidal or seesaw. 7. The geometries of the molecules BF3 and NF3 are trigonal planar and trigonal pyramidal respectively. Which statement best accounts for the difference? A. N is more electronegative than B. D. N has a non-bonding pair of valence electrons, while B. BF3 is ionic, while NF3 is covalent. B does not. C. B utilizes sp hybridization, while N does not. 8. The geometry of a molecule is best described in terms of the locations of the atomic nuclei. What geometries are possible for compounds whose bonding can be described using sp 2 hybrid orbitals? A. Trigonal planar or bent. C. Square planar, tetrahedral, or trigonal planar. B. Tetrahedral, bent, or trigonal pyramidal. D. Trigonal bipyramidal or seesaw. 9. In which of the following molecules or ions would the hybridization be sp 3d? A. CoCl63C. PCl6– E. BF4– B. PCl5 D. CO2 10. Which orbitals overlap to form a sigma bond between the carbon and nitrogen atoms in CH-CH=N-H? A. C sp3 and N sp2 C. C sp2 and N sp2 E. C sp3 and N sp3 B. C sp2 and N sp D. C sp2 and N sp3 Molecular Structure WS#4 1. Phosphorus reacts with chlorine to form two compounds PCl3 and PCl5 . What is the hybridization and shape for each molecule? 2. When nitrogen reacts with chlorine only ONE compound (NCl 3 ) is formed. Explain why nitrogen is different from phosphorus in this reaction. 3. What are the approximate bond angles in each of the following? Justify your answers. A. ONO in NO3– B. HPH in PH3 C. FSF in SF6 4. What is the shape and hybridization of the central atom for each of the following? A. SO3 C. IF5 E. ICl4– B. XeF2 D. SeF6 F. I3– 5. Draw a Lewis electron-dot structure for each of the molecules below and identify the shape of each. CF4 XeF4 ClF3 i. Identify the hybridization of each central atom. ii. Use the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model to explain the geometry of each of these molecules. 6. The bond angles for H-N-H in the ammonia molecule is 107°, whereas the bond angle for H-P-H in the molecule PH3 is 93°. Explain: A. Why the H-N-H bond angle is 107°. C. Since N and P are in the same group in the periodic B. Why the H-P-H bond angle is 93°. table, why are their bond angles different? 7. Draw a Lewis structure and predict the molecular geometry of each of the following: A. SiF4 B. SeF4 C. KrF4 Explain why these three molecules have different shapes and which, if any, are polar? Molecular Structure WS#5 1. In each of the following: A. Draw a Lewis structure D. Identify the bond angles B. Label any formal charges E. Indicate whether the molecule is polar or non-polar C. Give the shape or geometry F. Identify the hybridization of all atoms i. CH2Cl2 v. SO42ii. COCl2 vi. SF2 iii. SO2 vii. CH3COOH (don't give the shape) iv. HCN viii. NH2OH 2. SiF4 can react with F- to give SiF62- but CF4 does not react with F- to form CF62-. Explain this observation in terms of structural and bonding considerations. Draw Lewis structures for SiF4, SiF62-, and CF4 and explain their shapes to reinforce your answer. 3. What is the geometry of each of the following compounds? A. XeF2 C. ClF3 E. CIF5 B. SF6 D. XeF4 4. Use simple structure and bonding models to account for each of the following: A. The bond angle in H2O is 104.5°. C. SF4 is not tetrahedral with 109.5o B. Each of the NO bonds in NO3 are of equivalent length and strength. 2 5. The N2O molecule is linear and polar. A. On the basis of this experimental evidence, which arrangement, NNO or NON, is correct? B. Explain your answer. C. On the basis of your answer in (a) above, write the Lewis structure of N 2O (including resonance forms). Give the formal charge on each atom and the hybridization of the central atom. D. How would the multiple bonding in N N - O be described in terms of orbitals? 6. Using Lewis structures: A. Predict the geometry of the following species. B. Give the hybridization of the central atom. i. BrF5 ii. CS2 iii. SiF4 iv. NO3– v. AlF63Intermolecular Forces WS#6 1. In which of the following processes are covalent bonds broken? A. melting benzene C. boiling C2H5OH E. dissolving bromine in B. melting quartz D. evaporating water water 2. Which of the following is insoluble in water? A. KI C. NaBr E. Mg(OH)2 B. CO2 D. CHCl3 3. Which of these solids is the best conductor of electricity? A. tungsten C. sodium chloride E. quartz B. carbon dioxide, “dry ice” D. ice 4. Which of the following will be highest melting? A. naphthalene, C8H10 C. Hg E. C2H5OH B. methane CH4 D. SiO2 5. Which of the following is an example of a substance held together by dispersion forces that melts far below room T? A. sodium C. neon E. water B. germanium D. calcium chloride 6. Which of the following will be most soluble in water? A. C8H10 C. NaI E. Cr B. Br2 D. SiC 7. Which of the following choices is an example of a high melting, network solid consisting of covalently bonded atoms? A. sodium C. neon E. water B. germanium D. calcium chloride 8. Which of the following would have the lowest melting point? A. iron C. Cl2 E. I2 B. BaCl2 D. water 9. Which of the following molecules is not capable of hydrogen bonding? A. H2NCN C. H2F+ E. [NH3F]+ B. H2O2 D. HCN 10. A student is given a sample of a solid to test in the lab. He tests solubility of the sample in H2O and then in CCl4. Both tests are negative. He then tests the volatility of the sample and discovers it to be very volatile. The solid vaporizes as soon as it touches the hot spatula. What can the student conclude? A. The sample must be metallic. D. The sample is ionic. B. The sample is a covalent network solid. E. None of the above. The results of the tests are C. The sample is a molecular compound. contradictory. 11. Which of these solvents will dissolve salt, NaCl? A. carbon tetrachloride C. benzene, C6H6 E. bromine B. acetone, (CH3)2CO D. carbon disulfide, CS2 12. Which of these tests would best distinguish between sodium chloride and diamond dust, both of which are finely divided clear crystals? A. volatility-—NaCl is volatile while diamond is not. C. conductivity—NaCl is ionic and will conduct B. solubility in benzene—NaCl will dissolve in a electricity in the solid form. nonpolar solvent. D. solubility in water—only NaCl will dissolve. E. heat samples—NaCl will decompose. Intermolecular Forces WS#7 1. Which of the following will have the highest melting point? A. benzene, C6H6 C. Hg E. C2H5OH B. CF4 D. silicon 2. Which of the following substances melts far below room temperature and is held together by dispersion forces? A. potassium C. magnesium oxide E. water B. quartz D. argon 3 3. Which of the following would be lowest melting? A. gold C. Br2 E. I2 B. BaO D. ice 4. Which of the following is a polar molecular compound? A. CH4 C. SiO2 E. BH3 B. SO2 D. hydrogen 5. Which of the following processes would require the most energy? A. melting iodine C. dissolving Br2 in CCl4 melting KMnO4 E. B. boiling SiH4 D. vaporizing H2O2 6. Out of the following molecules, which would you expect to have the largest lattice energy: A. NaCl C. RbCl E. CaO B. KCl D. KBr 7. Salts dissolve in water to give solutions that boil at a higher temperature than pure water. Alcohol dissolves in water to give solutions that boil at a lower temperature than pure water. Explain these facts in terms of vapor pressure and intermolecular forces. 8. The normal freezing and boiling points of oxygen are 54.75 K and 90.19 K, respectively. The triple point is at 54.3 K. A. Use these data to draw a phase diagram for oxygen. Label the axes and label the regions in which the solid, liquid, and gas phases are stable. On the phase diagram, show the position of the normal boiling point. B. What changes will be observed in a sample of oxygen when the temperature is increased from 40 K to 150 K at a constant pressure of 1.00 atm. Intermolecular Forces WS#8 1. Select the highest boiling member of each pair and indicate which intermolecular forces are involved. A. K2CrO4 or HNO3 C. H2O2 or H2S B. NH3 or CH4 D. PH3 or SbH3 2. Indicate the strongest attractive forces that must be overcome to A. Vaporize Hg C. Boil C3H7OH B. Melt NaNO3 D. Dissolve (CH3)2CO in H2O 3. State TRUE or FALSE accordingly and provide an explanation if false. A. KBr is higher melting than IF. C. Dry Ice (solid CO2) melts readily at room B. C2H5OH is higher boiling than C2H5Cl. temperature. D. Iodine is more volatile than bromine 4. A 10.0 g sample of napthalene (C10H8 ) is added to 50.0 ml of benzene (C6H6 ) of density 0.879 g/ml. What is the boiling point of the solution? (Kb for benzene = 2.53 °C/m and the normal boiling point of benzene is 80°C) 5. Use the principles of intermolecular forces and/or chemical bonding to explain each of the following. A. Neon has a lower boiling point than krypton. B. Solid silver chloride is not a good conductor of electricity though solid silver metal is an excellent conductor of electricity. C. At room temperature silicon dioxide, SiO2 , is a solid. If you move up in group IV to carbon and look at the analogous molecule, carbon dioxide, CO2 , you will see that it is a gas at room temperature. Explain how oxides of members of the same family can have widely varying physical properties. D. Molecules of BF3 are nonpolar while PF3 is polar. 6. Within the group I metals, the boiling points decrease from Lithium to Cesium. In contrast, the boiling points of the halogens increase as you go down the family. A. Account for the decrease in the boiling points of the group I metals in terms of bonding principles. B. Account for the increase in the boiling points of the halogens in terms of bonding principles. C. What trend is expected in the boiling points of the compounds LiF, NaCl, KBr and CsI? Use bonding principles to explain. Intermolecular Forces WS#9 1. Classify each of the following as ionic, molecular (polar or non-polar), network covalent, or metallic. A. sodium C. C10H8 E. titanium B. SiO2 D. CaCO3 F. fluorine 2. Of the four general types of solids, which one(s) A. melt below 100oC to give a non-conducting D. conduct electricity as a solid? liquid? E. are very hard solids but dissolve readily in H2O? B. melt at moderate (l00 – 600oC) temperatures to F. are very hard solids that do not dissolve in give a conducting liquid? common solvents? C. melt at very high temperatures to give a G. dissolve in non- polar solvents? conducting liquid? 4 3. For each pair below choose the compound with stronger intermolecular forces and identify the forces involved. A. ICl or NaCl D. H2S or H2O G. GeH4 or AsH3 B. Kr or Ar E. SiC or LiCl H. CCl4 or CH4 C. H2Te or H2S F. CO2 or SiO2 4. Substance Melting Point, K Substance Melting Point, K N2 63.3 Kl 854.15 C2H6 89.85 NaF 1266.15 HCl 158.4 SiC > 2,273 A. In terms of the types of attractive forces and/or bonds in the above substances, explain the trend in the melting points. B. For pairs of substances with the same predominate attractive forces and/or bonds, discuss the factors that cause variations in the strengths of the forces and/or bonds. 5. The molecular weights of butane, chloroethane, acetone, and 1-propanol are approximately the same. Boiling point and solubility in water data are listed in the table below. Compound Formula Boiling Point, K Solubility in Water Propane CH3-CH2-CH3 231 Insoluble Fluoroethane CH3CH2-F 235 Insoluble Dimethyl ether CH3OCH3 248 Completely miscible Ethanol CH3-CH2OH 352 Completely miscible In terms of molecular polarities (dipole moments) and/or hydrogen bonding, explain in a qualitative way the differences in the A. boiling points of propane and fluoroethane C. water solubilities of propane and ethanol B. water solubilities of fluoroethane and dimethyl D. boiling points of dimethyl ether and ethanol ether Intermolecular Forces WS#10 1. Classify each of the following characteristics as belonging to an ionic, covalent network, metallic, or molecular solid. A. melts below 100°C to give a non-conducting C. dissolves in H2O to give a conducting solution liquid D. is a non-conductor but conducts when melted B. conducts electricity as a solid E. melts below 100°C and reacts violently with H2O 2. Describe the nature of the structural units that would be in each of the following: A. Fe C. Cl2 E. K2O B. FeCl2 D. C F. BN 3. Of the following substances, which would interact primarily through dispersions forces and which would interact with dipole forces? A. CH4 C. CH2Cl2 E. H2S B. CH3Cl D. CO2 4. A 1.00 molal aqueous solution of an acid, HB, has an apparent percent dissociation of 62.0%. Calculate the freezing point of the solution. (the freezing point depression constant for water is (K f = 1.86 °C/m) 5. Explain the following statements in terms of intermolecular forces. A. C2H6 has a higher boiling point than CH4 D. O2 has a higher boiling point than N2 B. C2H5OH has a higher boiling point than C2H6 E. CO has a higher boiling point that N2 C. C2H5OH has a lower boiling point than NaF 6. Out of the following pairs, select the member that you would expect to have a lower boiling point. A. F2 or Cl2 C. HCl or HBr E. NH3 or PH3 B. ClO2 or SiO2 D. LiCl or C3H8 F. PH3 or AsH3 7. Classify which of the following substances as I. Molecular (polar) II. Molecular (nonpolar) III. Metallic IV. Ionic V. Covalent Network A. NH4NO3 ___ B. CCl4 ___ C. BeH2 ___ D. Al ___ E. Si ___ 5 F. BrF ___ E. SF6 ___ F. K2CO3 ___