Shoulder Exam
advertisement
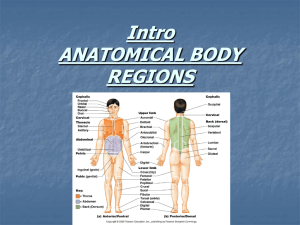
LHUP PA Shoulder Exam 04 Shoulder Exam Student’s Name __________________________________ Evaluators’ Name ____________________________________ Grading Criteria 1) The item must be performed correctly, completely, and accurately. 2) The item must be performed with regard to patient’s comfort, safety or feelings. 3) Student, when requested by faculty, must be able to explain the technique or the reason (DiffDx) for the exam. 4) You must tell the examiner everything you are inspecting for or you will not receive credit. 5) You must initiate all exams and continue unless instructor tells you to proceed to the next exam. You will NOT get credit for saying “I would do …” 6) As a student patient you are required to appropriately attired as to enable the examiner to correctly complete the examination with appropriate exposure 7) The examiner may notify you immediately of a failure should you: Fail to adequately expose the body part being examined Auscultate through clothing Any exam performed without concern for patient safety (i.e. palpating the abdomen before percussing, improperly using otoscope etc)\ Any technique that may significantly decrease the accuracy of an exam (not auscultating the abdomen before palpation etc) Faculty Comments: Today’s Date: _____________________________ Evaluation Criteria Unsatisfactory Satisfactory Exceeds Expectations Communication Student politely greets patient and explains to patient technique to be performed History Student acquires appropriate detail of symptoms and pertinent ROS, PMH,FHX,SOCHx,Meds,Alle rgies N/A Exam Technique Student performs examinations using a techniques that assure accuracy Thoroughness Student completes greater than 90% of required examinations Organization Student completes the exam in an organized fashion Diff Diagnosis Student aware of primary and competing Diagnosis Labs/Studies Student orders cost effective, appropriate labs and studies and is able to interpret results Management Student able to state basic management principles including pt education, meds/surg treatments,Health Promotion/Disease Prevention Strategies, Disposition and follow up Overall Evaluation N/A N/A N/A Neuro_Exam-Complete-04 LHUP PA Shoulder Exam 04 Shoulder Exam Diff Dx Stated Test 1. deformity 2. swelling 3. atrophy Inspect Test Done N/A States inspecting & comparing bilaterally Stand behind pt., palpate and name: 1) Suprasternal notch & SC (sternoclavicular) joint 2) Clavical 3) Coracoid process 4) AC (acromioclavicular) joint. (bilat. using “crossover test”) 5) Acromion 1). Greater Tuberosity of the Humerus 2). Biciptal Grove (bicipital tendon) Palpation Differential Considerations & Notes 1. scoliosis may cause elevation of one shoulder.; dislocation; 3. atrophy may be cervical nerve lesions 1) Spine of scapula 2) Body of scapula Rotator Cuff (SITS) (palpate general area, name muscles if you can) 1. Supraspinatus 2. Infraspinatus 3. Teres minor (4. Subscapularis) Subacromial & Subdeltoid bursa (passively extend shoulder post) Axilla (clearly use a pyramidal-shaped searching style) Major Muscles 1. Sternocleidomastoid 4. Deltoid 2. Pectoralis Major 5. Trapezius 3. Biceps 6. Rhomboid 7. Latissimus Dorsi 1. dislocation SC joint 2. fx clavical 3. 4. AC separation (crepitus, elevated clavicle, tender), arthritis Bicipital Tendinitis Fractures Tender sprains & tears Bursitis lymph node enlargement Bicep rupture Exam Shoulder 3-11.doc last updated 03-11, sj LHUP PA Shoulder Exam 04 Test Done DiffDx Stated N/A Special Tests ROM N/A Sensory Vascular n/a n/a Active & Passive ROM 1. Flexion (180) & Ext (60) 2. ABduct (180) & ADduct (45) 3. External rotation (90) & Internal rotation ( 90) Apley “scratch” test (active ROM with rotation): 1) touch opposite superior medial angle of scapula 2) touch opposite A/C joint 3) touch opposite inferior angle of scapula “Drop-arm” sign: The examiner abducts the pt’s shoulder to 90 and then asks pt to slowly lower it to the side in the same arc of movement. If pt. is unable to return arm slowly or without severe pain then this is positive for rotator cuff tear. Yergason Test Pt flex elbow 90 and hand in pronation. Examiner grasps base of elbow and wrist resisting pt.’s attempt tosupinate and externally rotate the shoulder. Bicept tendon, if unstable. will slip out causing pain. Allen Test Examiner locates the radial pulse, flexes pt’s elbow to 90 while shoulder is extended horizontally and rotated laterally. The patient then rotates the head AWAY from the test side. If the pulse disappears when patient rotates head AWAY then it is positive for Thoracic Outlet syndrome. Apprehension Test for chronic Shoulder Dislocation Examiner ABducts and Ext. rotates shoulder. Pt. will look apprehensive if positive. The Impingement Test The pt’s arm is forcibly elevated through forward flexion by the examiner. If pt.’s face shows pain, this is positive. Pain is caused by “jamming” of the greater tuberosity against the anteroinferior acromial surface. States C5 patch over lateral arm. o/w gross exam Rotator cuff will drop. (especially in the supraspinatus muscle) long head of the biceps tendon instability Thoracic Outlet syndrome Chronic Shoulder dislocation Glenohumeral Impingement. Overuse injury of the supraspinatus muscle or biceps tendon Checks radial pulse. Cursory exam neck Others Cursory exam same side elbow Cursory exam opposite shoulder Exam Shoulder 3-11.doc last updated 03-11, sj