현기증(Vertigo)
advertisement
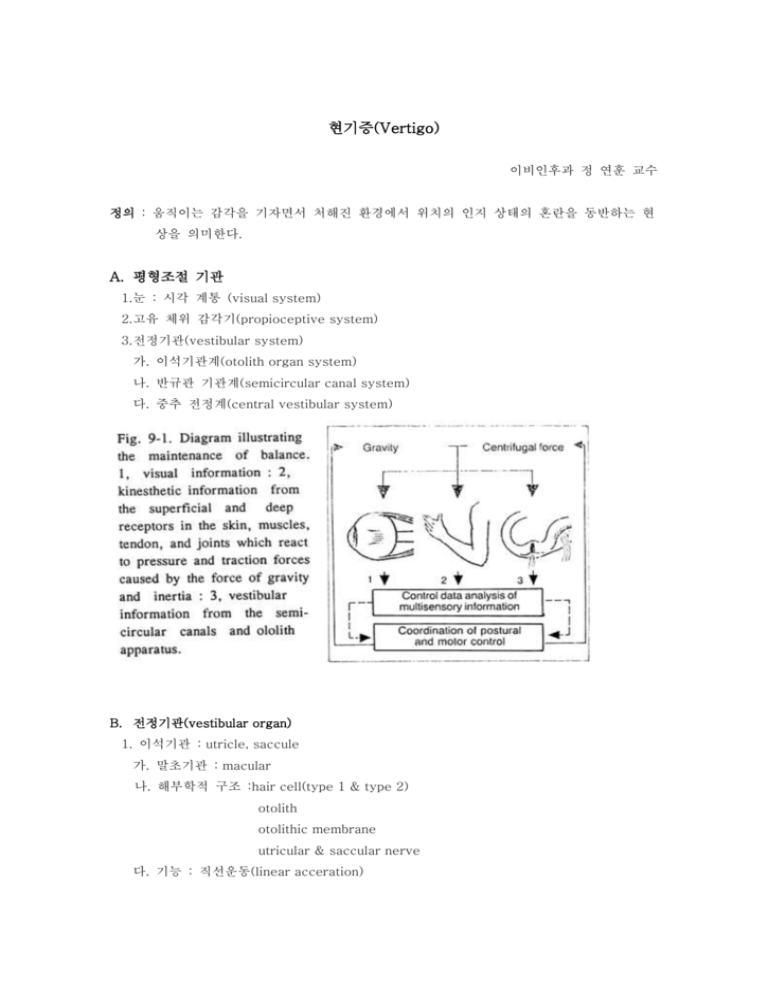
현기증(Vertigo) 이비인후과 정 연훈 교수 정의 : 움직이는 감각을 기자면서 처해진 환경에서 위치의 인지 상태의 혼란을 동반하는 현 상을 의미한다. A. 평형조절 기관 1.눈 : 시각 계통 (visual system) 2.고유 체위 감각기(propioceptive system) 3.전정기관(vestibular system) 가. 이석기관계(otolith organ system) 나. 반규관 기관계(semicircular canal system) 다. 중추 전정계(central vestibular system) B. 전정기관(vestibular organ) 1. 이석기관 : utricle, saccule 가. 말초기관 : macular 나. 해부학적 구조 :hair cell(type 1 & type 2) otolith otolithic membrane utricular & saccular nerve 다. 기능 : 직선운동(linear acceration) 2. 반규관 : superior semicircular canal horizontal semicircular canal posterior semicircular canal 가. 말초기관: crista ampularis 나. 해부학적구조 : hair cell(type 1 & type 2) capular semicircular nerves 다. 전정기관의 신경분포 a. afferent innervation superior vestibular nerve – superior semicircular nerve horizontal semicircular nerve utricular nerve inferior vestibular nerve – posterior semicircular nerve saccular nerve Scarpa’s ganglion 내이도 내의 전정신경의 위치 및 분포 b. efferent innervation group E : 전정 신경핵과 abducens nuclei사이에 존재하는 신경핵으로 전 정기관의 말초 hair cell에 분포한다. 라. 중추 전정핵 a. major vestibular nuclei – superior nuclei medial nuclei lateral nuclei descending nuclei b. minor vestibular nuclei – interstitial nuclei group L group Y group X group Z 마. 중추전정기 회로 a. vestibular-ocular reflex : nystagmus b. vestibular-spinal reflex c. vestibule-autonomic reflex : nausea, vomiting, pale etc 바. morphological polarization of the vestibular organ hair cell은 한 개의 kinocillium과 약 30-100개의 stereocillia를 가지고 있으며 endolymph의 움직임에 따른 hair의 운동이 세포의 electrical potential의 변화를 일 으켜 말초신경의 전기적 현상을 유발한다. a. resting discharge b. depolarization c. hyperpolarization C. 전정계의 병리기전. 1. postural system 2. relation between sources of vertigo & balance disorder 3. peripheral disorder 가. Tymapanogenic diseases(Oval or round window interferences) a. inflammatory – Otitis media b. Atmospheric – Tubal obstruction, aero-otitis 나. Labyrinthogenic a. inflammatory – Labyrinthitis –circumscribed, diffuse b. Vascular – Hemorrhage, Thrombosis, Ischemia c. Vasomotor – “Hydrops”, allergy 다. Systemic disease(Toxic effects upon neuroepithelium) a. Bacterial or viral b. Metabolic disorders c. Hematogenic diseases d. Chemical toxins(Drugs) 라. Neoplastic lesions a. Malignant tumors – primary of metastatic(Invasive) b. Histologically benign tumors – glomus jugulare(Erosive) 마. Trauma a. Morphological *Fracture of the temporal bone *Labyrinthine concussion b. Functional * Acoustic trauma(cochlear) * Motion sickness(vestibular) 4. central disorder 가. Inflammatory a. Meningitis b. Brain Abscess c. Encephalitis d. Vestibular neuronitis 나. Space occupying a. Neoplasms( Cerebello-pontine angle, hemispheric) b. Granulomas c. Arachnoid cysts 다. Vascular a. Internal auditory artery - apoplexy b. Inferior posterior cerebellar artery - Wallenberg syndrome c. Vertebral artery - benign paroxysmal postural vertigo 라. Systemic a. b. Toxins - Bacterial, viral, chemical Genetic or hereditary - Multiple sclerosis 마. Traumatic Brain concussion 바. Autonomic nervous a. Parasympathogenic (retrograde vagal effect) b. Sympathogenic 사. Neonatal a. Developmental anomalies b. RH Incompatibility c. Anoxia, neonatal jaundice, prematurity D. 현기증의 진단 안진(nystagmus)의 정의: 안구가 특정한 축을 중심으로 규칙적으로 되풀이되는 slow phase와 fast phase를 가지는 conjugated, cooperated한 운동을 하는 것을 말한다. 안진의 방향표기는 fast phase의 방향으로 표시한다. 1. 병력 조사 가. 현기증의 기술 a. character b. pattern & progression c. provoking factor d. accompanying symptom 나. personal & past history 2. 이신경학 검사 가. general ENT examination 나. cranial nerve examination 다. cerebellar fuction examination 3. metabolic examination 4. 방사선 검사 5. 청각검사 6. 전정기능 검사 가. righting reflex test 나. deviation test 다. positioning test 라. positional test 마. vestibule ocular test - sccadic test slow persuit test optokinetic test 바. vestibular organ test - caloric test rotation test 7. 말초성 및 중추성 안진의 감별 Peripheral Origin CNS Origin Always bilateral and conjugate May be disjugate or unilateral Horizontal or hoorizontorotary, Any direction including vertical(vertical Occasionally almost pure rotary nystagmus with eyes open is Direction of the fast phase is constant pathognomonic of CNS disease Voluntary fixation in the direction of the Direction of the fast phase changes with fast phase has no effect or may increase the direction of gaze nystagmus; voluntary fixation in the Fast phase is in the direction of gaze direction of the slow phase decreases nystagmus Supressed by ocular fixation Not suppressed; may even be enhanced Most pronounced at the onset and Continues or increases in intensity gradually subsides May be associated with other signs or May be associated with other symptoms or symptoms of auditory or vestibular disease signs of CNS disease E. 현기증을 동반하는 귀 질환 1. Endolymphatic hydrops 가. fluid of the inner ear Perilymph : High sodium, low potassium Between bony and membranous labyrinth May be communicated with CSF through cochlear aqueduct Production : Ultrafiltration from plasma Diffusion of CSF via conchlear aqueduct Endolymph : High potassium, low sodium Within membranous labyrinth Circulation : Longitudinal flow : stria vascularis-cochlear duct-ductus reunions -saccule-utriculosaccular duct-endolymphatic sac (rugose portion) Radial flow : From stria vascularis to stria vascularis * Blood-labyrinthine barrier . Examined by injection of test substance(Glycerol, urea, mannitol, furosemide etc)into the systemic circulation and recovering them in the perilymph. . The levels of substances in perilymph lagged behind serum concentrations, with transport inversely related to the molecular weight of the substance. . Freely permeable to water but less permeable to other substances. . The concentration and differences between serum and inner ear fluids slow,incomplete equilibration over prolonged periods implicate a blood-labyrinth barrier. 가. Classification a. Symptomatic - Embryopathic : developmental hypoplasia Acquired : inflammation, trauma, etc. Idiopathic : Meniere's disease 나. Concept of pathophysiology a. Developmental hypoplasia, trauma, or viral labyrinthitis cause decreased function of the endolymphatic sac(due to subepithelial fibrosis of sac) b. A slow over accumulation of endolymph causing and distortion of the membranous labyrinth c. As the volume of endolymph increases - ruptures of the endolymphatic system(saccular wall & Reissner's membrane) and contamination the of perilymphatic fluid with neurotoxic endolymph, causing episodes of and/or fluctuating d. The ruptures heal and the entire repeats itself. e. With progression of the disease - permanent the membranous labyrinth and persistent dysequilibrium and/ or hearing loss. 다. Diagnosis a. History : The most important(four cardinal symptoms) 1) Intermitent attacks of often associated with nausea, and with vomiting 2) A fluctuating type 3) Roaring 4) A sensation of fullness or pressure on the affected side b. Audiometric evaluation(Glycerol or Urea test, EchoG) c. Vestibular function test 라. Differential diagnosis a. Acoustic neurinoma b. Basilar artery insufficiency c. Labyrinthitis d. Postural vertigo e. Cerebellar and brainstem lesions f. Vestibular neuronitis 마. Treatment a. Medical treatment 1) Correction of endolymphatic hydrops (가) Reduction of the hy drops (나) Inner car blood supply in severe cases 2) Vestibular suppression 3) Correction of associated medical abnormalities b. 1) Surgical treatment Conservative surgery for hearing -shunt operation 2) Vestibular ablative technique -labyrinthectomy 2. Cupulolithiasis(Positional Nystagmus of the Benign Paroxysmal type) 가. Concept : The disorder is caused by an inorganic deposit the posterior semicircular canal which renders this organ on the cupula sensitive of to gravitational force. 나. Etiology a. Age(over 65 years) b. Post head injury c. Middle ear pathology d. Surgical manupulation of stapes of round window 다. Temporal bone histopathology a. the b. Degeneration of superior division sense organ & nerves with preservation of sensorienural element of inferior vestibular division Notable deposit of basophilic material on the cupula of posterior semicircular canal 라. Diagnosis a. Dizziness is precipitated not by head movement but head position due to disorder of the otoliths. b. Characteristic symptom & sign(1952: Dix & Hallpike) 1) Critical provocative position 2) Characteristic Nystagmus 3) Latency 4) Limited duration 5) Reversal 6) Fatigability * Hallpike maneuver 마. Differential diagnosis 1) Convergent paroxysmal positional nystagmus 2) Vertebro-basilar insufficiency 3) Astrocytoma of cerebellar inferior vermis 사. Treatment 1) Avoidance of the provocative position 2) Adaptive exercise(Cawthorne's exercise) 3) Singular nerve neurectomy 4) Labyrinthectomy 3. Vestibular neuronitis(viral) Some form of organic disease confined to the vestibular apparatus localized probability to peripheral nervous pathway up to and including the in vestibular all nuclei in the brain stem(Dohlman 1929) 가. Clinical data a. No sex difference b. Age : middle(mean 39) c. Rapid onset(over 70%) and complete absence of auditory signs & symptoms d. Role of infection Frequently occurs after a systemic or localized infection (Upper respiratory tract infection, maxillary sinusitis) 나. Pathology Degeneration of Scarpa's ganglion and of the nerve supplying the utricle & horizontal canal (Lindsay & Hemenway 1956) 다. Symptom & sign . Nausea & vomiting . Vertigo . Spontaneus Nystagmus(about 70%) occasionally positional Nystagmus & upper Diminished galvanic & caloric response 라. Differential diagnosis a. Vertebrobasilar insufficiency b. Cervical vertigo c. Epilepsy 마. Treatment Supportive care 4. Acoustic Neuroma 가. Incidence . 80-90% of all tumors of cerebellopontine angle . Age : 30-40 years . No sex difference 나. Pathology a. Site of origin Vestibular portion of the nerve in the region of Scarpa's ganglion b. Type 1) Antoni type A 2) Antoni type B 다. Symptom & sign a. Early symptom Tinnitus, hearing loss, dizzindess b. Late symptom Numbness of face(5th cranial nerve) Weakness of facial musculature(7th cranial nerve) Ataxia of gait, slurring of the speech (cerrbellum) Internal hydrocephalus c. Sign 1) Audiometric evaluation . P.T.A. & speech audio . SISI, ABLB(Recruitment) . Tone decay(Adaptation) . Acoustic reflex & reflex decay . BERA 2) Vestibular evaluation Diminished or absent response to caloric test 3) Neurological evaluations 4) Radiologic evaluation 5) . Stenver's Towne's & Submentovertex projection . Tomography . Posterior fossa myelography . Computerized axial tomography(gas cysternography) Laboratory evaluation . C.S.F. & perilymph(protein & pressure) 라. Differential diagnosis a. Meningioma b. Congenital cholesteatoma c. Arachnoid cyst d. Hemangioma e. Aneurysm 마. Treatment a. Middle fossa approach b. Translabyrinthin approach c. Suboccipital approach 5. Vestibular toxicity Caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, quinine, barbiturate, streptomycin, gentamycin, Chloroform, Guanidine, Arsenicals . The earliest and best indication of ototoxicity for is the SM toxicity - onset SM of imbalance . dose dependant . contributing factor : renal insufficiency & GM . Route : perilymph & endolymph . Target : type I hair cell Ampulla crista > utricular macular > saccular macular 6. Glomus Tumor (Nonchromaffm Paraganglioma) Neuroectoderm에서 기원하는 종양으로서 middleear에 호발하며 조직학적으로 carotidbody의 chemoreceptor tissue와 유사하며 매우 왕성한 혈관분포를 특징으로 한다. 가. 증상 증상은 종물의 기원한 부위와 그 침윤상태에 의해서 나타나며, 일반적으로 혈관의 박동과 일치하는 이명, 편측성 청력소실과 귀의 압박감, 평행감의 소실, 안면신경마비를 포함한 9,10,11 뇌신경 마비. 나. 호발부위 경정맥구 (jugular bulb) tympanic plexus, lesser superficial petrosal nerve 다. 분류 Glomus Tympanicum – 종물이 중이강 내에 국한된 경우 Glomus Jugular Tumor – 중이강과 경정맥구에 국한되어 있으며 골조직과의 파괴가 없는경우 Glomus Jugular Tumor – 유양동전체와 petros apex를 침윤한 종물 Glomus Jugular Tumor – 종물이 intracranial로 침윤된 경우 라. 진단 Octoscopy – 혈관의 분포가 왕성한 붉은 색깔을 띠는 종물이 고막의 내측에서 관찰된다. 청각검사 소견 및 복합 뇌신경의 마비- 초기에는 전음성난청이나 종물이 자라 내이를 침윤한 경우 감각신경성 난청을 동반하게 되며 종물의 침윤상태에 따라 7,8,9,10,11,12뇌신경마비가 나타난다. 전정기능검사 – Caloric 검사를 포함하여 모든 Electrony stagmographic test battery가 상태의 평가에 도움을 주며, Caloric 검사상 감소된 경우는 lavyrinthininvasion을 고려해야 한다. Polytomography Angiography Jugular Venogram Temporal bone CT scanning MRI 마. 치료 방사선치료 수술적 제거 – Embolization G. 현기증을 동반하는 귀 질환의 치료 Optimal therapeutic strategy . Successful thorough . management & of dizzy patient depends on objective neuro-otologic survey Use medications to relieve the vegetative symptoms 1. Support & reassurance 2. Elimination of treatable causes 가. Otologic : Chronic otitis meida, cholesteatoma, acoustic neurinoma, etc. 나. Neurologic : Demyelinating disease, brainstem tumors, etc. 다. Metabolic : Diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, hyperlipidemia, etc. 라. Infections : Syphilis, etc. 3. Symptomatic treatment 가. Antivertigenous medication a. Pure symptomatic treatment b. Affect the basic pathophysiology 나. Vestibular exercise 다. Surgical therapy a. Vestibular ablative technique b. Conservative technique 4. * Rehabilitation Drug groups for the symptomatic relief of vertigo Primary : 1. Sedative hypnotics Others : * 2. Antihistamine 3. Anticholinergics 4. Phenothiazines 1. Vasodilators 2. Vitamines 3. Allergy medicines Surgical procedure of vertigo 1. Decompression & drainage procedure a. Endolymphatic sac shunts & decompression b. Sacculotomy c. Cochleosacculotomy 2. Partially destructive procedure a. Vestibular neurectomy b. Singular neurectomy a c. Ultrasonic irradiation d. Cryosurgery 3. Totally destructive procedure a. Labyrinthectomy b. Chemical labyrinthectomy






