Heat
advertisement
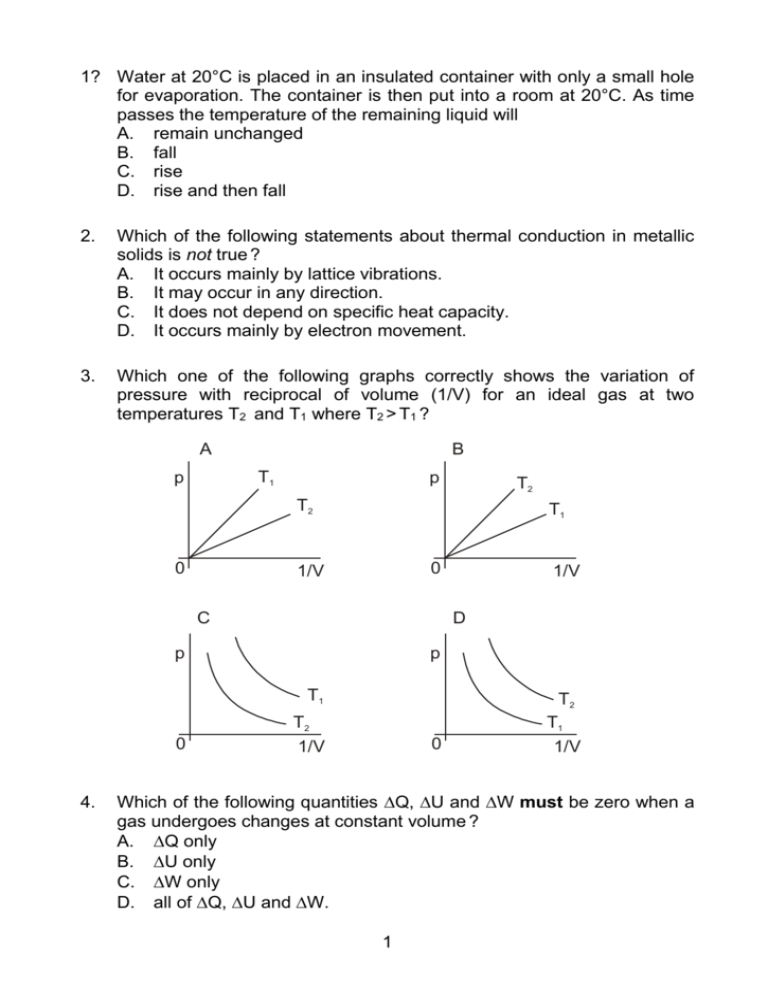
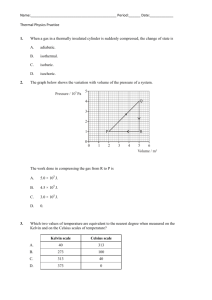
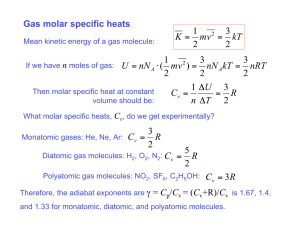
1? Water at 20°C is placed in an insulated container with only a small hole for evaporation. The container is then put into a room at 20°C. As time passes the temperature of the remaining liquid will A. remain unchanged B. fall C. rise D. rise and then fall 2. Which of the following statements about thermal conduction in metallic solids is not true ? A. It occurs mainly by lattice vibrations. B. It may occur in any direction. C. It does not depend on specific heat capacity. D. It occurs mainly by electron movement. 3. Which one of the following graphs correctly shows the variation of pressure with reciprocal of volume (1/V) for an ideal gas at two temperatures T2 and T1 where T2 > T1 ? A B T1 p p T2 T2 0 T1 0 1/V C D p p T1 0 4. 1/V T2 T1 T2 1/V 0 1/V Which of the following quantities Q, U and W must be zero when a gas undergoes changes at constant volume ? A. Q only B. U only C. W only D. all of Q, U and W. 1 5. When a substance changes phase from a solid to a liquid it does so at constant temperature. This can be understood from the fact that the energy transferred to the substance A. increases the kinetic energy of the molecules B. decreases the kinetic energy of the molecules C. increases the potential energy of the molecules D. decreases the potential energy of the molecules 6. When a heat engine operates in a Carnot cycle, an adiabatic expansion is followed by A. an adiabatic compression B. an isothermal compression C. an isothermal expansion D. none of the above 7. An engine operates between two reservoirs at temperatures 300 K and 500 K. The maximum possible efficiency of the engine is A. 0·4 B. 0·6 C. 1·0 D. 1·6 8. In order to determine experimentally the heat capacity of an object, one would need to measure A. The heat supplied to the object, the temperature rise, and the mass of the object. B. Only the heat supplied and the temperature rise. C. Only the heat supplied and the mass of the object. D. Only the temperature rise and the mass of the object. 9. Water at 20°C is mixed with twice the mass of water at 80°C. The final temperature of the mixture will be A. 40°C B. 50°C C. 60°C D. 80°C 10. A hot water tank has a double layered wall, an inner wall of copper and an outer layer of insulating material. The inside is at 80°C and the outside at 20°C. 2 Which option below correctly compares both the heat flow rates and the temperature gradients in the layers ? A. B. C. D. Heat flow rate Same for both Greater in copper Same for both Greater in copper Temperature gradient Same for both Greater in copper Greater in insulator Same for both 11. When a gas in a container increases in temperature, the pressure increases. Consider the following possible microscopic explanations of this pressure increase I. II. The gas molecules colliding with the container walls have greater speeds. There are more collisions of the gas molecules per unit time with the container walls. The best explanation of the pressure increase is provided by A. Only explanation I. B. Only explanation II. C. Both I and II in conjunction. D. Neither I nor II. 12 Two identical containers P and Q hold two different ideal gases at the same temperature. The number of moles of each gas is the same. The molecular weight of the gas in container P is twice that of the gas in Q. The ratio of the pressure in P to that of Q will be A. ½ B. 1 C. 2 D. 2 13 When the volume of a gas increases, it does work. The work done would be greatest for which one of the following processes ? A. Isobaric. B. Adiabatic. C. Isothermal. D. The work done would be the same for all of the above. 14 A system absorbs 70 J of thermal energy and in the process does 40 J of work. The internal energy change is A. 30 J. 3 B. C. D. 40 J. 70 J. 110 J. 15 A vacuum flask (or Dewar flask) is an insulated container useful for storing hot or cold liquids (coffee, tea, liquid nitrogen, etc.). In its construction a vacuum is used to minimise energy transfer with the environment. vacuum between walls The vacuum reduces A. radiation, convection and conduction losses. B. convection and conduction losses. C. convection losses only. D. radiation losses only. 16 A small object of mass m at 100°C is placed into an equal mass of water at 0°C in a calorimeter. The specific heat capacity of the object is half that of the water. Assuming there are no energy transfers to the environment or to the calorimeter, the final equilibrium temperature of the object plus water will be A. 67°C B. 50°C C. 33°C D. 25°C 17 The temperature of an ideal gas is a measure of the gas molecules’ A. average velocity. B. maximum velocity. C. average kinetic energy. D. total kinetic energy. 18 It is proposed to build a heat engine that would operate between a hot reservoir at a temperature of 400 K and a cold reservoir at 300 K. See the diagram below. In each cycle it would take 100 J from the hot reservoir, lose 25 J to the cold reservoir and do 75 J of work. 4 This proposed heat engine would violate A. both the first and the second laws of thermodynamics. B. the first but not the second law of thermodynamics. C. the second but not the first law of thermodynamics. D. neither the first nor the second law of thermodynamics. 19. The specific latent heat of vaporisation of a substance is the quantity of energy required to A. raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree centigrade. B. convert a unit mass of liquid to vapour at constant temperature and pressure. C. convert a unit mass of solid to vapour at constant temperature and pressure. D. convert a unit mass of liquid to vapour at a temperature of 100°C and a pressure of one atmosphere. 20. When a gas in a cylinder is compressed at constant temperature by a piston, the pressure of the gas increases. Consider the following three statements. I. The rate at which the molecules collide with the piston increases. II. The average speed of the molecules increases. III. The molecules collide with each other more often. Which statement(s) correctly explain the increase in pressure ? A. I only B. II only C. I and II only D. I and III only 21. When a gas in a thermally insulated cylinder is suddenly compressed, the change of state is A. adiabatic. B. isothermal. 5 C. D. isobaric. isochoric. 22. Which one of the following diagrams correctly represents the directions of the energy transfers that take place in a heat pump ? A. B. hot hot Qh Qh pump W pump W Qc Qc cold cold C. D. hot hot Qh Qh pump W pump W Qc Qc cold cold 23. The graph below shows the variation with volume of the pressure of a system. 5 Q 4 5 Pressure /10 Pa 3 2 0 R P 1 0 2 1 3 4 5 6 3 Volume / m The work done in compressing the gas from R to P is A. 5·0 ×105 J B. 4·5×105 J C. 3·0 ×105 J 6 D. 0 7 ANSWERS: March 2005 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. B A B C C 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. B A B C C 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. C D D A B 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. C C C D A 21. 22. 23. A B C 8