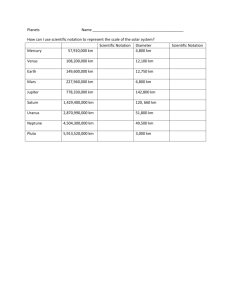
Astronomy Lecture 3c
advertisement

ASTRONOMY LECTURE TEST # 3 – FALL 2011 1. A ? spectrum is created where there is a thin gas in front of a hotter source of continuous radiation. A.continuous B.emission line C.absorption line D.all of these may be created where there is a thin gas in front of a hotter source of continuous radiation 2. The surface of ? is very complex, consisting of regions of scarps, faults, etc.; this messed-up appearance may be due to an early collision or prior orbital eccentricity. A.Ariel B.Oberon C.Titania D.Miranda E.Umbriel 3. Herbig-Haro Objects are created during the formation of A.comets B.asteroids C.dwarf planets D.centaurs E.stars 4. ? has the highest wind speeds of any planet. A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 5. The Great Red Spot is a characteristic feature of A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 6. ? is the most massive dwarf planet in the Solar System; it has one known moon, Dysnomia. A.Eris B.Ceres C.Pluto D.Makemake E.Haumea 7. Our Sun belongs to Luminosity Class A.I B.II C.III D.IV E.V 8. The axial tilt of ? is inclined at about 97.77°. A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 9. ? has a rotational period of over 6 days; its revolution period is about 248 years. A.Eris B.Ceres C.Pluto D.Makemake E.Haumea 10. The lineae on ? may indicate the presence of a layer of liquid water beneath. A.Ganymede B.Europa C.Io D.Enceladus E.Callisto 11. ?-Period Comets are believed to originate in the Kuiper Belt or the Scattered Disc. A.short B.long 12. Most meteorites are A.Chondrites B.Achondrites 13. ? is classified as either a “large asteroid” or a Dwarf Planet. A.Eris B.Ceres C.Pluto D.Makemake E.Haumea 14. In descending order of temperature, the spectral classification is A.O, B, A, F, G, M, K B.O, B, A, F, K, M, G C.O, B, A, F, G, K, M D.K, F, A, O, B, G, M E.F, A, B, O, K, M, G 15. The rings of Saturn are A.very thin B.very thick C.it depends upon where you are in the rings 16. The energy of PMS Stars is due to A.gravitational contraction B.fusion of hydrogen to helium C.both of these processes are important in production of energy for PMS Stars 17. It is believed that ? has more natural satellites than any other planet; about 56 of the moons are classified as “irregular”. A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 18. The ? is the relative direction in which the Sun is moving; this is an example of ? Motion. A.apex; Proper B.apex; Solar C.antapex; Proper D.antapex; Solar 19. Widmanstätten patterns are characteristic of ? Meteorites. A.Stony B.Stony-Iron C.Iron 20. The “Galilean Satellites” orbit A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 21. Solar neutrinos move ? through the Sun’s layers. A.slowly B.quickly 22. Limb Darkening of the Sun is due to A.radiative transfer B.convection C.temperature change D.granulation E.sunspots 23. The proton-proton chain is the way in which the Sun fuses A.helium to hydrogen B.hydrogen to helium C.both of these processes may occur 24. The atmosphere of Jupiter consists primarily of A.methane B.ammonia C.hydrogen D.helium E.all of these gases are equally important components in the atmosphere of Jupiter 25. The dark surface on Umbriel may be due to energetic particles “sputtering” ?-rich water ice. A.methane B.carbon dioxide C.carbon monoxide D.sulfur E.hydrogen 26. The darkest part of a sunspot is termed the A.Penumbra B.Umbra 27. Almost all of the Sun’s energy is produced within the A.core B.outer layers C.both of these regions produce the Sun’s energy 28. Jupiter rotates in about A.10 hours B.1 day C.2 days D.21 days E.12 years 29. ? formerly had a “Great Dark Spot”; although this spot has since disappeared other dark spots have appeared. A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 30. The higher the apparent magnitude number, the ? the astronomical object. A.dimmer B.brighter 31. Triton has a very similar composition to ? and is believed to have had similar origins. A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 32. ? Binaries are recognized by their large Doppler shifts. A.Visual B.Spectroscopic C.Eclipsing 33. A ? is found in space. A.meteor B.meteorite C.meteoroid 34. The volcanoes on ? spew molten and gaseous sulfur; it is probably the most geologically-active object in the Solar System. A.Ganymede B.Europa C.Io D.Enceladus E.Callisto 35. The surface coloration and brightness of ? varies greatly; it also appears to have extreme changes in its atmosphere. A.Eris B.Ceres C.Pluto D.Makemake E.Haumea 36. Dark coronal holes ? found within “active regions”. A.are B.are not 37. All absorptions that begin with the electron in the first energy level or emissions that end with the electron in the first energy level are called ? Lines. A.Balmer B.Paschen C.Brackett D.Lyman 38. Enceladus is a moon of A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 39. The ? the mass, the greater the luminosity of stars. A.less B.greater 40. The “asteroid belt” is between A.Mercury and Venus B.Venus and Earth C.Earth and Mars D.Mars and Jupiter E.Jupiter and Saturn 41. One parsec is about ? light years. A.3.26 C.9.46 D.11.2 D.13.7 E.18.2 42. The formation of Sunspots can best be explained by Sun A.fission B.fusion C.prominences D.CME’s E.magnetism 43. Tektites are associated with A.asteroids B.Dwarf Planets C.comets D.centaurs E.meteorites 44. There is a strange hexagonal-shaped wave pattern developed around the North Polar Vortex of A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 45. ? asteroids cross Earth’s orbit. A.Trojan B.Amor C.Apollo D.all of these asteroids cross Earth’s orbit 46. M stars are A.blue B.white C.yellow D.red 47. Most stars in the H-R Diagram occur in the A.White Dwarf Region B.Supergiant Region C.Giant Region D.Main Sequence 48. The layer that we see in visible images of the Sun is the A.chromosphere B.corona C.photosphere 49. Parallax and Standard Candles are used to determine the ? of astronomical objects. A.movement B.mass C.composition D.distance E.Parallax and Standard Candles may be used to determine characteristics of all of these 50. A ? Comet Tail is created by the pressure of the solar wind pushing ionized gas away from the comet head. A.Type I B.Type II 51. The largest satellite in the Solar System is ?; it is larger than Mercury. A.Ganymede B.Europa C.Io D.Enceladus E.Callisto 52. The equatorial region of the Sun rotates ? versus the poles. A.slower B.faster 53. ? names of stars often begin with “al”. A.Greek B.Latin C.Arabic 54. Luminosity is measured A.only in the visible light portion of the electromagnetic spectrum B.is summed over the entire electromagnetic spectrum 55. Pluto is considered to be part of the A.Asteroid Belt B.Scattered Disc C.Kuiper Belt D.Pluto has been classified in all of these 56. The most common meteorites are ? Meteorites. A.Stony B.Stony-Iron C.Iron 57. ? is the only moon in the Solar System with a significant atmosphere; it seems to have wind, liquid methane rain, as well as lakes and seas of liquid methane and ethane. A.Enceladus B.Mimas C.Titan D.Tethys E.Dione 58. The average density of ? is about 0.7 grams per cubic centimeter; the cloud belts on this planet are relatively faint, probably due to ammonia crystals hiding the deeper layers. A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 59. CME’s ? associated with Solar Flares and Prominences. A.are B.are not 60. ?-Type Asteroids are the darkest asteroids; they include most known asteroids. A.X or M B.S C.C 61. “Kirkwood Gaps” are found in A.ring systems B.the asteroid belt C.“Kirkwood Gaps” are found in both ring systems and the asteroid belt 62. The Sun probably began as a ? Star. A.T Tauri B.Herbig Ae/Be 63. The rings of Saturn are primarily made of A.ice B.rock debris C.dust D.the rings of Saturn are made of approximately equal portions of ice, rock debris and dust 64. ? has the coldest planetary atmosphere in the solar System; there are “extreme seasons” on this planet. A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 65. Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 fragmented and impacted ? in 1994. A.Saturn B.Uranus C.Mars D.Neptune E.Jupiter 66. The farthest planet from the Sun is A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 67. ? has about 13 narrow rings; the inner rings are gray and the outer rings are blue. A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 68. The “Late Heavy Bombardment” was probably due to gravitational attraction of A.the Sun B.Terrestrial Planets C.Jovian Planets D.the Oort Cloud E.the Kuiper Belt 69. ? primarily consist of frozen gases, water ice, rock, dust, with minor amounts of organic compounds and possibly amino acids. A.asteroids B.Dwarf Planets C.comets D.centaurs E.meteorites 70. The presence of ? in the upper atmosphere gives Uranus and Neptune their blue coloration. A.oxygen B.hydrogen C.helium D.ammonia E.methane 71. Granulation is due to Solar A.radiation B.conduction C.convection 72. Titania, Ariel and Oberon are moons of A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 73. Asteroids in the outer part of the Asteroid Belt tend to have more ? than those in the inner part of the Asteroid Belt. A.silica versus carbon B.carbon versus silica 74. Spicules are formed within the Sun’s A.core B.photosphere C.corona D.chromosphere 75. Charon may be a moon (or dwarf companion) of A.Eris B.Ceres C.Pluto D.Makemake E.Haumea 76. Most meteors consist of pieces of A.comets B.asteroids C.comets and asteroids both provide abundant parent material for creating meteors 77. The Barringer Crater and Odessa Meteor Crater were created by ? Meteorites. A.Stony B.Stony-Iron C.Iron 78. A “coma” is a feature seen on A.asteroids B.Dwarf Planets C.comets D.centaurs E.meteorites 79. Cepheid Variables are often used to determine the ? of astronomical bodies. A.movement B.mass C.composition D.distance E.all of these may be determined by Cepheid Variables 80. Dione, Tethys and Rhea are moons of A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 81. The Oort Cloud is a hypothetical portion of the Solar System that is believed to contain abundant A.asteroids B.comets C.centaurs D.the Oort Cloud probably contains all of these objects 82. Triton and Nereid are ? satellites of Neptune. A.regular B.irregular 83. The largest planet in the Solar System is A.Saturn B.Uranus C.Neptune D.Jupiter 84. ? has an ellipsoidal shape that is probably due to its very rapid rotation. A.Eris B.Ceres C.Pluto D.Makemake E.Haumea 85. The gases and ices that form the Jovian Planets consitute about ? percent of the material surrounding the Sun. A.71 B.75 C.88 D.92 E.99 86. The Amalthea Group are the inner regular satellites of A.Uranus B.Pluto C.Saturn D.Neptune E.Jupiter 87. Deimos and Phobos may be captured ? asteroids. A.Trojan B.Amor C.Apollo D.Deimos and Phobos are probably remnant centaurs, not asteroids 88. Saturn’s moon Phoebe may be a “captured” A.comet B.dwarf planet C.asteroid D.centaur 89. ? stars belong to binary or multiple star systems. A.few B.many 90. Bok Globules seem to be important in the formation of many A.comets B.asteroids C.dwarf planets D.centaurs E.stars 91. The metallic hydrogen layer is ? well-developed in Saturn versus Jupiter. A.less B.more C.the metallic hydrogen layer is equally well-developed in Saturn and Jupiter 92. ? probably has the most reflective surface of any Solar System object; this is probably due to its “water volcanism”. A.Enceladus B.Mimas C.Titan D.Tethys E.Dione 93. The “iridium layer” and presence of “shocked quartz” has been hypothesized to be due to impact by a massive asteroid at the end of the ? Period. A.Cambrian B.Devonian C.Jurassic D.Cretaceous E.Pleistocene 94. In the Sun’s ? temperature rises to 1 to 2 million degrees Kelvin, probably due to heating by waves. A.core B.photosphere C.chromosphere D.corona 95. Which of the following would not be classified as a Minor Planet? A.Dwarf Planet B.asteroid C.comet D.centaur E.all of these are types of Minor Planets 96. Solar prominences are relatively ? gases. A.cool B.hot 97. This is test “A”. Please answer “A” for question # 97.