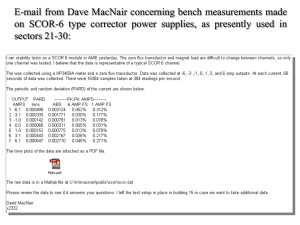
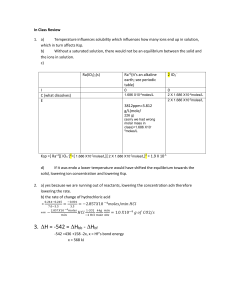
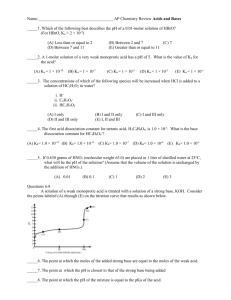
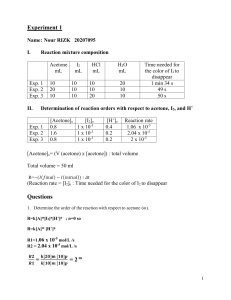
BIO-301 Optional 2004
advertisement

Bio301 Biochemistry Optional make-up exam, January 19, 2004 Question 1.(10 points) Why is an a-helix the preferred structure for transmembrane protein segments? (10 points) Question 2. (10 points) An understanding of the structure and function of membrane proteins has lagged behind that of other proteins. The primary reason is that membrane proteins are more difficult to purify and crystallize. Why might this be the case? Question 3. (10 points) Fill in the blanks: a) Solubilizing a protein by increasing the ionic strength of a solution is termed........................ Precipitating a protein at high ionic strength is termed.................. b) ..................... , .............................. and ........................ bonds are important in substrate binding. c) DEAE-cellulose is a(n) ............................exchanger. CM-cellulose is a(n) ............................ exchanger. d) Two general classes of enzymatic catalysis are ............................................. and .......................... . e) A protein with a net negative charge will bind strongly to an anion-exchange resin. A buffer, with a..............................pH or ............................... ionic strength than the original bufer will be needed to elute such a protein. Question 4. (15 points) What is the free-energy cost of pumping Ca+2 out of a cell when cytosolic concentration is 0.4 M, the extracellular concentration is 1.5 mM and the membrane potential is –60 mV? Question 5. (10 points) Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase A fail to cleave peptide bonds involving proline. Trypsin, for example, will not cleave a peptide at a Lys-Pro junction. Why do you think this is the case? Question 6. (10 points) After examining the structural formulas of the four lipids below, answer the following questions: a) Which are phosphoglycerides? b) Which is a glycolipid? c) Which contain sphingosine? d) Which contain choline? e) Which contain glycerol? Question 7. (20 points) List the four major regulatory mechanisms that control enzyme activity and give examples of each. Question 8 (15 points) : From the data below for a hypothetical enzyme-catalyzed reaction, determine KM and Vmax by inspection. Then plot the data using the EadieHofstee method and determine these constants graphically. Check your results with a calculation. Can you explain the discrepancy in your two determinations? [S] (moles/liter) v(moles/min) 5.0 x 10-4 125 2.0 x 10-4 125 6.0 x 10-5 121 4.0 x 10-5 111 3.0 x 10-5 96.5 2.0 x 10-5 62.5 1.6 x 10-5 42.7 1.0 x 10-5 13.9 8.0 x 10-6 7.50