CCNA2 module 8 Study guide
advertisement
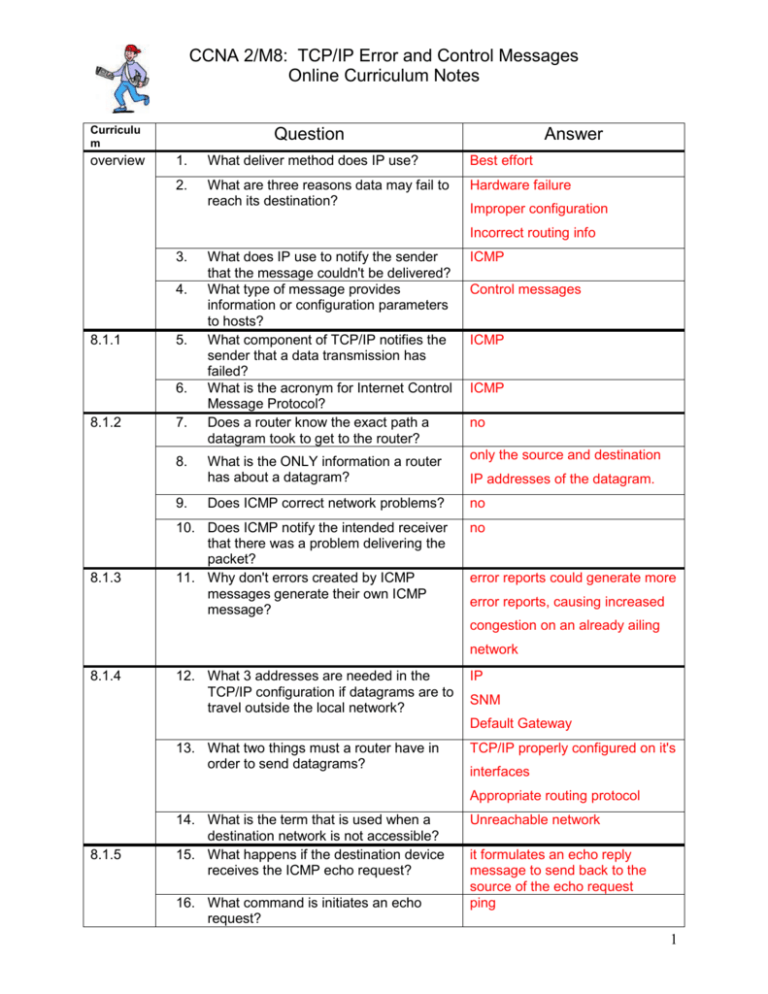
CCNA 2/M8: TCP/IP Error and Control Messages Online Curriculum Notes Curriculu m overview Question Answer 1. What deliver method does IP use? Best effort 2. What are three reasons data may fail to reach its destination? Hardware failure Improper configuration Incorrect routing info 3. What does IP use to notify the sender that the message couldn't be delivered? What type of message provides information or configuration parameters to hosts? What component of TCP/IP notifies the sender that a data transmission has failed? What is the acronym for Internet Control Message Protocol? Does a router know the exact path a datagram took to get to the router? ICMP What is the ONLY information a router has about a datagram? only the source and destination Does ICMP correct network problems? no 10. Does ICMP notify the intended receiver that there was a problem delivering the packet? 11. Why don't errors created by ICMP messages generate their own ICMP message? no 4. 8.1.1 5. 6. 8.1.2 7. 8. 9. 8.1.3 Control messages ICMP ICMP no IP addresses of the datagram. error reports could generate more error reports, causing increased congestion on an already ailing network 8.1.4 12. What 3 addresses are needed in the TCP/IP configuration if datagrams are to travel outside the local network? IP SNM Default Gateway 13. What two things must a router have in order to send datagrams? TCP/IP properly configured on it's interfaces Appropriate routing protocol 8.1.5 14. What is the term that is used when a destination network is not accessible? 15. What happens if the destination device receives the ICMP echo request? 16. What command is initiates an echo request? Unreachable network it formulates an echo reply message to send back to the source of the echo request ping 1 8.1.6 8.1.7 8.1.8 17. If a request is successful between the source and destination, what does it mean? 18. What would be created if two routers continually route a datgram back and forth? 19. What is the maximum hop count for RIP? 20. What is TTL? 21. What three fields are common to all ICMP messages? 22. What are four reasons datagrams may not make it to their destination? 23. If a "3" appears in the type field, what does that mean? 24. What does the "code value" indicate? 8.1.9 8.2.1 8.2.2 8.2.3 25. What is usually needed to forward a datagram from a token-ring to an Ethernet network? 26. If a datagram header has an error, what will a device like a router do? 27. When the code value of the problem message reaches 0, what will the pointer field indicate? 28. Why is a control message sent? 29. How are ICMP control messages sent? 30. What's another term for "gateway"? 31. What is the only device that can initiate a Redirect/Change request message? 32. How is a redirect/change configured on a Cisco router? 33. What allows a host to ask for the current time according to the remote host? 34. What are the 2 type fields on an ICMP timestamp message? 35. What 3 things are contained in the ICMP timestamp reply message? 36. What 2 things affects true transit time? 8.2.4 37. What 2 protocols are now used to allow a host to find it's network number? confirming IP connectivity between the two devices Loop - travels in circles 15 Time to live Type Code Checksum Hardware failures improper protocol configuration down interfaces incorrect routing information Destination unreachable The reason the packet could not be delivered Packet fragmentation It sends an ICMP type 12 parameter problem message to the source the octet of the datagram that produced the error To inform hosts of conditions such as network congestion or a better gateway Inside IP dtagrams router router It's the default The ICMP timestamp request message 13 (timestamp request) or 14 (timestamp reply). The code field value is always set to 0 because there are no additional parameters available the originate, receive and transmit timestamps Traffic and congestion on the network BOOTP DHCP 2 8.2.5 8.2.6 8.2.7 8.2.8 38. What type of message is sent out when a host doesn't know the network address? 39. What is the multicast address for router discovery? Address mask request 40. What happens if a router receives the multicast but isn't configured for multicasting? 41. If the default gateway is missing, what is the message generated by the host? 42. What happens when there is too much congestion on a network? 43. Why don't Cisco routers send sourcequench messages (by default)? It doesn't answer the request 44. What type of office might use sourcequench messages? small office home office (SOHO) 224.0.0.2 router solicitation Packets are dropped because the source-quench message may itself add to the network congestion. 3