Name
advertisement

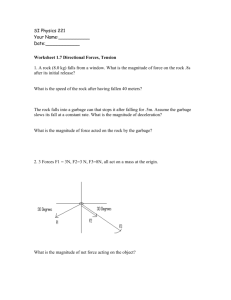
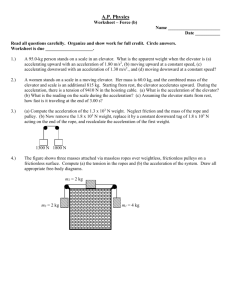
Name __________________________________ Date _________________ Partners _________________________________________________________________ Apparent Weight in Elevators (and Newton's Laws of Motion): Lab #6 By M. Derengowski-Stein, M.L. West Objective: to experience and understand the various accelerations in an elevator Equipment: a working elevator, a scales or spring, a mass such as a person. Background: a) Define weight: A person of mass 60 kg has a weight of ____________ A box of weight 110 Newtons has a mass of ____________ On the moon (g = 1.62 m/s2 ) this box would have a weight of _________________________ and a mass of __________ b) Draw a free-body diagram of a 60 kg person standing on the floor. Label each of the forces acting on her. Label the object causing each force. Label the magnitude of each of these forces. c) Draw a free-body diagram of a 60 kg person standing on a bathroom scale on the floor. Label each of the forces acting on her. Label the object causing each force. Label the magnitude of each of these forces. d) Draw a free-body diagram of the bathroom scale (1 kg) on the floor with the 60 kg person standing on the scale. Label each of the forces acting on it. Label the object causing each force. Label the magnitude of each of these forces. Which force produces the reading on the scale? e) Draw a free-body diagram of an elevator of mass 200 kg suspended from a cable Label each of the forces acting on it. Label the object causing each force. Label the magnitude of each of these forces. 2 f) If the elevator is traveling upwards at a velocity of 2 m/s, what are the magnitudes of the forces on it? g) If the elevator accelerates upwards, then will the forces acting on it add up to zero? ______ Explain: Which force will change? Which force remains the same? If the upwards acceleration is 3 m/s2, then what is the magnitude of each force? h) If the elevator accelerates downward at 3 m/s2, then what is the magnitude of each force? i) Now a 60 kg woman enters the elevator. When the elevator is stationary what are the forces and their magnitudes acting on her? j) If the elevator is moving downward with a constant velocity of 2.5 m/s, then what is the magnitude of each force acting on her? k) If she is standing on a scale in the elevator moving downward with a constant velocity of 2.5 m/s, then what is the magnitude of each force acting on the scale? l) If she is standing on a scale in the elevator then what is the magnitude of each force acting on the scale if the upwards acceleration is 3 m/s2? m) If she is standing on a scale in the elevator then what is the magnitude of each force acting on the scale if the acceleration is 3 m/s2 downwards? 3 Procedure: Each team will have one bathroom scale and one spring scale with a mass. Do three trials of each situation and average the results. The acceleration will take place quickly, so try to read the scale quickly. Situation Scale Scale Scale Spring reading, reading, reading, scale, trial 1 trial 2 trial 3 trial 1 Spring scale, trial 2 Spring scale, trial 3 Scale, Spring ave scale, ave Stationary Scale/ Spring statio scale/ nary station ary 1.0 1.0 Moving up, increasing speed Moving up, constant speed Moving up, decreasing speed Moving down, increasing speed Moving down, constant speed Moving down, decreasing speed If a person on the bathroom scales suddenly jumps upward off the scales, what happens to the reading on the scales? (Please don't break the scales. Jump to land on the floor.) Conclusions: Summarize your observations in 100 words or less. How can you use Newton's laws of motion to explain your results? Further Research: Make several suggestions as to further use for this equipment. a