Router
advertisement

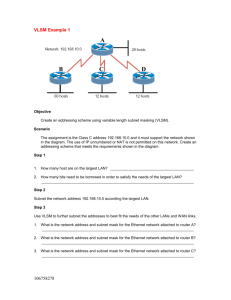
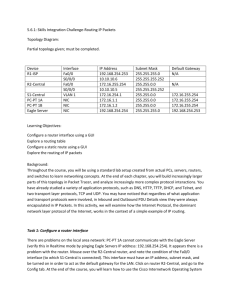
Student Name Date DT021/4 COMMUNICATIONS NETWORKS 2 Laboratory 7 Objective The objective of this exercise is to set up and test a small internetwork consisting of two interconnected networks using 2 Cisco routers, and 3 PCs, using the OSPF routing protocol. You should work in teams of 3 students. Log in as “netengineer” on the PCs, and make sure that the firewalls are disabled. You should reenable the firewall at the end of the laboratory session. Download this document from the web, and complete it as you progress. Print it at the end of the laboratory session. Only one report is required per group. Complete the report on PC that you use to open the hyperterminal to facilitate copy and paste. Network set up Each group will use 2 Cisco routers, and 3 PCs. Set up the Test Network as shown in the figure below (use straight through cables with Hub). Use the following network addresses. 533563635 Page 1/6 Net 1: 10.0.0.0/8 Net 2: 172.16.0.0/16 Net 3: 192.168.100.0/24 List the IP configuration of the PCs you have selected in the table below: Network/Node Net 1/Node A Net 2/Node B IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway IP Address After configuring the PCs, check that the parameters have been included (ipconfig). List the IP parameters to be used to configure the router interfaces. Router 1 Fa0/0 IP Address Mask Fa0/1 IP Address Mask Router 2 Fa0/0 IP Address Mask Fa0/1 IP Address Mask The PC on Network 3 (Node E) will allow you to observe OSPF messages sent between routers. See Appendix to start the Cisco Router. Configuration of the routers interfaces 1) When in privileged mode, to configure any feature of the router, it is necessary to enter configuration mode. This is done by issuing the command configure terminal. Router# configure terminal Router(config)# 2) Configure the interfaces you are using with IP address and subnet mask. Router# configure terminal Router(config)# interface fa0/0 (or fa0/1) Router(config-if)# ip address ipaddress subnetmask Router(config-if)# no shutdown After completing the configuration of the interfaces, you may exit the configuration mode, after turning on the routing function with the command ip routing. Router(config-if)# exit Router(config)# ip routing Router(config)# exit 533563635 Page 2/6 Note: the router ID will be taken as one of the router interface addresses, usually the highest numerical value. You could also configure a loopback interface (interface loopback0), which would then be taken as the router ID. Use the following commands to display the destination networks that each router has in its routing table (directly connected networks). Router# show ip route What routes are displayed in each router: Router 1 Router 2 We will now turn on the OSPF protocol to allow router 1 to learn a route for Network 2, and router 2 to learn a route for Network 1. Start the Wireshark analyser on Node E. OSPF Routing single area In this test, you should use Wireshark to observe the OSPF traffic (Hello packets towards networks). Now configure both routers to use a single area OSPF. Router# configure terminal Router(config)# router ospf 1 Router(config-router)# network network mask area 0.0.0.0 Router(config-router)# network network mask area 0.0.0.0 Router(config)# exit Note: the mask in statements above is called a wildcard mask, and is used to identify the range of interfaces of the router on which OSPF will run; it is different of the subnet mask as in a wildcard mask a 1 means “don’t care”, instead of 0, in the subnet mask . 0.0.0.31 is the wildcard mask corresponding to the subnet mask 255.255.255.224. /8 => subnet mask = 255.0.0.0 => wildcard mask = 0.255.255.255 /16 => subnet mask = 255.255.0.0 => wildcard mask = 0.0.255.255 /24 => subnet mask = 255.255.255.0 => wildcard mask = 0.0.0.255 533563635 Page 3/6 What routes are displayed in each router: Router 1 Router 2 Observe the traffic captured by Wireshark. How frequently are the OSPF Hello packets sent ? Observe the 2 last LSA updates, one from each router. Identify the links advertised. Check the router database: Router# show ip ospf database qualifier Qualifier can be: - router to look at router LSA, - summary to look at network summary LSA, - network to look at declaration of Designated Router in Transit networks. Summarize the links here, per LSA type (router, Summary, network,…). Give: - advertising router - link type (stub, point to point,..), - link ID (router ID, Network Id,…), - metrics. Note: The 100 Mbps Ethernet link has a cost calculated as: 100000000/100000000=1. 533563635 Page 4/6 Appendix: Cisco router The routers used in this lab will be Cisco 2800 series. They have various I/O connections possible. Console Port: Connection to a terminal or PC's serial port for local configuration. Serial Port: Used to make a direct connection between two adjacent routers with a serial cable. 10/100 Ethernet: Ethernet port supporting 10/100 Mbps Ethernet. The 10 or 100 Base Ethernet should be used to connect the routers to the Nets. Connecting a management PC to the Switch 1. Connect the router’s console port using a roll-over cable to the serial (COM) port on PC, Rollover cable 2. Open “Hyper terminal” by clicking: Start > Programs > Accessories > Communication > Hyper terminal. 3. Enter connection name, e.g.: Cisco 4. Select COM3 (or COM1, whichever is available) 5. Under “bits per second” select 9600 and leave all other fields. Bits per second: 9600 Data bits: 8 Parity: None Stop bits: 1 Flow Control: None 6. Switch on power to router when main Hyper terminal window appears. 7. Enter password if prompted (passwords given during laboratory). Note: When first connecting to the router, the lowest access mode, called the EXEC mode is entered. From this mode, the user can only use a limited numbers of unprivileged commands. It is necessary to enter privileged mode to configure the router. This is done using the command enable. Privileged mode will usually be password protected. 8. Type enable and enter the password (if needed) to enter Privileged mode (passwords given during laboratory). 533563635 Page 5/6 It is ALWAYS best practice to begin with a clean RAM configuration. Otherwise, stale configuration commands may have unintended consequences: Erase the Non Volatile RAM configuration file: Router# erase startup-config Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files! Continue? [confirm] <ENTER> [OK] Erase of nvram: complete Reload the router: Router# reload System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: no Proceed with reload? [confirm] <ENTER> Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: n Would you like to terminate autoinstall? [yes]:y When the router reboots, enter privileged mode: Router> enable Router# Note: When in privileged exec command mode, any misspelled or unrecognized commands will attempt to be translated by the router as a domain name. Since there is no domain server configured, there will be a delay while the request times out. This can take between several seconds to several minutes. To terminate the wait, simultaneously hold down the <CTRL><SHIFT>6 keys then release and press x: Router>enabel Translating "enabel"...domain server (255.255.255.255) % Briefly hold down the keys <CTRL><SHIFT>6, release and press x 533563635 Page 6/6