S.NO CODE TITLE 1 AVNS13-001 SPAM: A Secure Password
advertisement
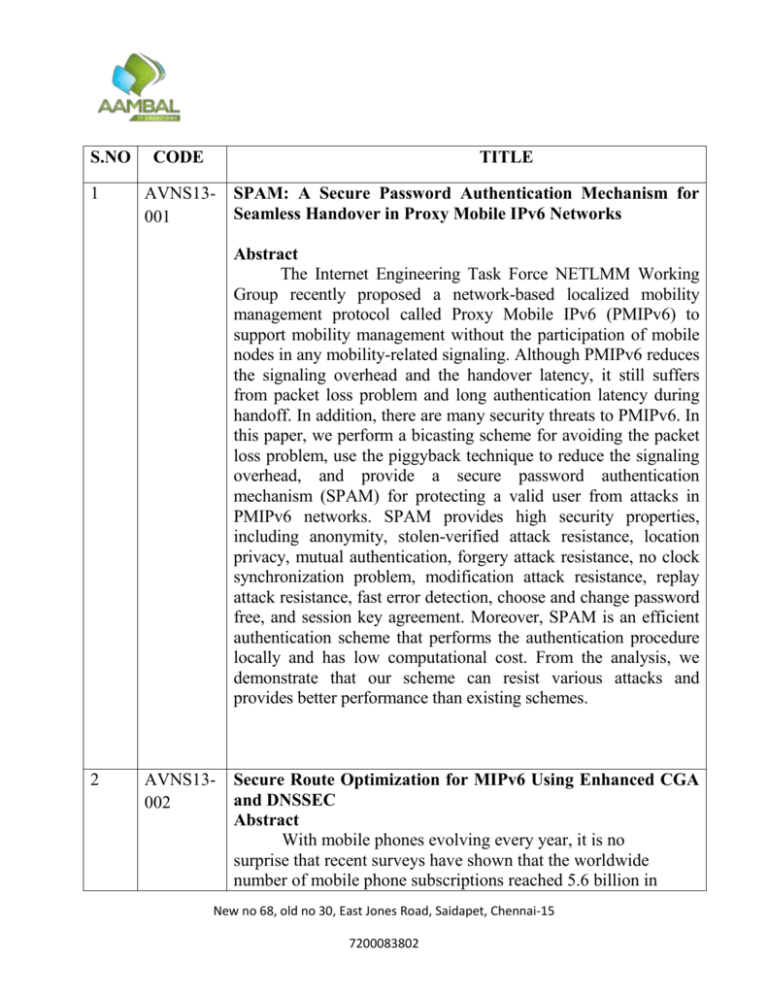
S.NO 1 CODE TITLE AVNS13001 SPAM: A Secure Password Authentication Mechanism for Seamless Handover in Proxy Mobile IPv6 Networks Abstract The Internet Engineering Task Force NETLMM Working Group recently proposed a network-based localized mobility management protocol called Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6) to support mobility management without the participation of mobile nodes in any mobility-related signaling. Although PMIPv6 reduces the signaling overhead and the handover latency, it still suffers from packet loss problem and long authentication latency during handoff. In addition, there are many security threats to PMIPv6. In this paper, we perform a bicasting scheme for avoiding the packet loss problem, use the piggyback technique to reduce the signaling overhead, and provide a secure password authentication mechanism (SPAM) for protecting a valid user from attacks in PMIPv6 networks. SPAM provides high security properties, including anonymity, stolen-verified attack resistance, location privacy, mutual authentication, forgery attack resistance, no clock synchronization problem, modification attack resistance, replay attack resistance, fast error detection, choose and change password free, and session key agreement. Moreover, SPAM is an efficient authentication scheme that performs the authentication procedure locally and has low computational cost. From the analysis, we demonstrate that our scheme can resist various attacks and provides better performance than existing schemes. 2 AVNS13002 Secure Route Optimization for MIPv6 Using Enhanced CGA and DNSSEC Abstract With mobile phones evolving every year, it is no surprise that recent surveys have shown that the worldwide number of mobile phone subscriptions reached 5.6 billion in New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 2011, becoming the largest pool of interconnected devices. Since mobile IP is the most-used protocol by mobile operators, the obvious solution to support more users in their network would be to replace it with MIPv6. In addition to integrating the newest IP stack, MIPv6 adds an important feature meant to replace the inefficient triangle routing by allowing an MN to communicate bidirectionally with the CN without passing through its home agent. However, the lack of preshared information between the MN and CN makes security for this RO mechanism a difficult challenge. MIPv6 adopts the RR mechanism that is only to verify the MN reachability in both its home address and care-of address without being a security feature. Other works have attempted to solve the multiple security issues in RR, but either their design was flawed or their assumptions were unrealistic. This paper presents a secure MIPv6 with a secure and efficient RO that uses DNSSEC to validate CGAs from trusted domains and provides strong authentication rather than the weak sender invariance security property. It integrates an enhanced cryptographically generated address (ECGA) based on a backward key chain that offers support to bind multiple logically linked CGAs together. ECGA tackles the time-memory tradeoff attacks with high efficiency. The validation through both AVANTSSAR and AVISPA platforms show that the proposed solution has no security flaw while still being lightweight in signaling messages on the radio network. 3 AVNS13003 A distributed data storage protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks with mobile sinks Abstract This paper presents ProFlex, a distributed data storage protocol for large-scale Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor Networks (HWSNs) with mobile sinks. ProFlex guarantees robustness in data collection by intelligently managing data replication among selected storage nodes in the network. Contrarily to related protocols in the literature, ProFlex considers the resource New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 constraints of sensor nodes and constructs multiple data replication structures, which are managed by more powerful nodes. Additionally, ProFlex takes advantage of the higher communication range of such powerful nodes and uses the longrange links to improve data distribution by storage nodes. When compared with related protocols, we show through simulation that Proflex has an acceptable performance under message loss scenarios, decreases the overhead of transmitted messages, and decreases the occurrence of the energy hole problem. Moreover, we propose an improvement that allows the protocol to leverage the inherent data correlation and redundancy of wireless sensor networks in order to decrease even further the protocol’s overhead without affecting the quality of the data distribution by storage nodes 4 AVNS13004 Adaptive Position Update for Geographic Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Abstract In geographic routing, nodes need to maintain up-to-date positions of their immediate neighbors for making effective forwarding decisions. Periodic broadcasting of beacon packets that contain the geographic location coordinates of the nodes is a popular method used by most geographic routing protocols to maintain neighbor positions. We contend and demonstrate that periodic beaconing regardless of the node mobility and traffic patterns in the network is not attractive from both update cost and routing performance points of view. We propose theAdaptive Position Update (APU) strategy for geographic routing, which dynamically adjusts the frequency of position updates based on the mobility dynamics of the nodes and the forwarding patterns in New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 the network. APU is based on two simple principles: 1) nodes whose movements are harder to predict update their positions more frequently (and vice versa), and (ii) nodes closer to forwarding paths update their positions more frequently (and vice versa). Our theoretical analysis, which is validated by NS2 simulations of a well-known geographic routing protocol, Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing Protocol (GPSR), shows that APU can significantly reduce the update cost and improve the routing performance in terms of packet delivery ratio and average end-toend delay in comparison with periodic beaconing and other recently proposed updating schemes. The benefits of APU are further confirmed by undertaking evaluations in realistic network scenarios, which account for localization error, realistic radio propagation, and sparse network. 5 AVNS13005 Physical-Layer Security in Distributed Wireless Networks Using Matching Theory Abstract We consider the use of physical-layer security in a wireless communication system where multiple jamming nodes assist multiple source-destination nodes in combating unwanted eavesdropping from a single eavesdropper. In particular, we propose a distributed algorithm that matches each sourcedestination pair with a particular jammer. Our algorithm caters for three channel state information (CSI) assumptions: global CSI, local CSI, and local CSI without the eavesdropper channel. We prove that our algorithm has many desirable properties. First, the outcome of the proposed algorithm results in a stable matching, which is important if the source and jamming nodes are selfish. Second, the secrecy rate of the proposed algorithm converges to the secrecy rate of a centralized optimal solution, if the price stepnumber is sufficiently small. Third, our algorithm converges only after a small number of iterations, and its overhead is relatively New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 small. Fourth, our algorithm has a significantly lower complexity than a centralized optimal approach. 6 AVNS13006 Comparative Handover Performance Analysis of IPv6 Mobility Management Protocols Abstract IPv6 mobility management is one of the most challenging research topics for enabling mobility service in the forthcoming mobile wireless ecosystems. The Internet Engineering Task Force has been working for developing efficient IPv6 mobility management protocols. As a result, Mobile IPv6 and its extensions such as Fast Mobile IPv6 and Hierarchical Mobile IPv6 have been developed as host-based mobility management protocols. While the host-based mobility management protocols were being enhanced, the network-based mobility management protocols such as Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6) and Fast Proxy Mobile IPv6 (FPMIPv6) have been standardized. In this paper, we analyze and compare existing IPv6 mobility management protocols including the recently standardized PMIPv6 and FPMIPv6. We identify each IPv6 mobility management protocol’s characteristics and performance indicators by examining handover operations. Then, we analyze the performance of the IPv6 mobility management protocols in terms of handover latency, handover blocking probability, and packet loss. Through the conducted numerical results, we summarize New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 considerations for handover performance. 7 AVNS13007 Mobility Increases the Connectivity of Wireless Networks. Abstract In this paper, we investigate the connectivity for large-scale clustered wireless sensor and ad hoc networks. We study the effect of mobility on the critical transmission range for asymptotic connectivity in -hop clustered networks and compare to existing results on non-clustered stationary networks. By introducing -hop clustering, any packet from a cluster member can reach a cluster head within hops, and thus the transmission delay is bounded as for any finite .We first characterize the critical transmission range for connectivity in mobile -hop clustered networks where all nodes move under either the random walk mobility model with nontrivial velocity or the i.i.d. mobility model. By the term nontrivial velocity, we mean that the velocity of a node is ,where is the transmission range of the node. We then compare with the critical transmission range for stationary -hop clustered networks. In addition, the critical number of neighbors is studied in a parallel manner for both stationary and mobile networks. We also study the transmission power versus delay tradeoff and the average energy consumption per flow among different types of networks. We show that random walk mobility with nontrivial velocities increases connectivity in -hop clustered networks, and thus significantly decreases the energy consumption and improves the power–delay tradeoff. The decrease of energy consumption per flow is shown to be in clustered networks. These results provide insights on network design and fundamental guidelines on building a large-scale wireless network. New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 8 AVNS13008 Game Theory for Network Security Abstract As networks become ubiquitous in people’s lives, users depend on networks a lot for sufficient communication and convenient information access. However, networks suffer from security issues. Network security becomes a challenging topic since numerous new network attacks have appeared increasingly sophisticated and caused vast loss to network resources. Game theoretic approaches have been introduced as a useful tool to handle those tricky network attacks. In this paper, we review the existing game-theory based solutions for network security problems, classifying their application scenarios under two categories, attack-defense analysis and security measurement. Moreover, we present a brief view of the game models in those solutions and summarize them into two categories, cooperative game models and non-cooperative game models with the latter category consisting of subcategories. In addition to the introduction to the state of the art, we discuss the limitations of those game theoretic approaches and propose future research directions. 9 AVNS13009 Cyber Security of Networked Critical Infrastructures Abstract A new era of cyber warfare has appeared on the horizon with the discovery and detection of Stuxnet. Allegedly planned, designed, and created by the United States and Israel, Stuxnet is considered New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 the first known cyber weapon to attack an adversary state. Stuxnet’s discovery put a lot of attention on the outdated and obsolete security of critical infrastructure. It became very apparent that electronic devices that are used to control and operate critical infrastructure like programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems lack very fact that when these devices were designed, the idea of exposing them to the Internet was not in mind. However, now with this exposure, these devices and systems are considered easy prey to adversaries. In this Special Issue, we focus on the advances of research in the area of basic security and protection measures. Part of that is due to the the security of networked critical infrastructure. SCADA systems and the Internet and its components are a few examples of networked critical infrastructure. The objectives of this Special Issue are twofold. First, we aim to present the latest advances in the security of networked critical infrastructure research. Second, we hope that this Special Issue will encourage and stimulate more activities in the field. This Special Issue brings together some of the latest research studies in the field of networked critical infrastructure security. It comprises four articles that discuss a wide range of problems. 10 AVNS13010 Vertical and Horizontal Circuit/Packet Techniques for the Future Optical Internet Integration Abstract Hybrid circuit/packet networks where circuit and packet networks coexist are becoming attractive to support future Internet applications. They support both packet/ IP services and circuit/wavelength services. Packet services include traditional data services such as VPN, VoIP, and email, while dynamic circuit services include end-to-end bandwidth-intensive applications such as terascale science experiments. In present hybrid networks, such as ESnet, the bandwidth boundary between the circuit and packet sections of the network is fixed. However, a New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 flexible boundary between the circuit and packet sections will enable cost-efficient bandwidth management in the network. Our study investigates two methods to dynamically migrate capacity between the circuit and packet sections, called vertical stacking and horizontal partitioning, and serves as a tutorial. In vertical stacking, the backup capacity of wavelength circuits can be dynamically exchanged between packet and wavelength services while ensuring survivability. The backup capacity can be used to protect wavelength services in the event of a failure and route packet traffic otherwise. In horizontal partitioning, the excess capacity on links in the packet section can be loaned to circuit services. We have conducted experiments using a snapshot of real traffic on ESnet with horizontal partitioning. Control mechanisms for our approaches that can be operational in ESnet are presented. 11 AVNS13011 A Framework for Secure and Efficient Data Acquisition in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Abstract Intervehicular communication lies at the core of a number of industry and academic research initiatives that aim at enhancing the safety and efficiency of transportation systems. Vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs) enable vehicles to communicate with each other and with roadside units (RSUs).Serviceorientedvehicular networks are special types of VANETs that support diverse infrastructure-based commercial services, including Internet access, real-time traffic management, video streaming, and content distribution. Many forms of attacks against service-oriented VANETs that attempt to threaten their security have emerged. The success of data acquisition and delivery systems depends on their ability to defend against the different types of security and privacy attacks that exist inserviceoriented VANETs. This paper introduces a system that takes advantage of the RSUs that are connected to the Internet and that provide various types of information to VANET users. We New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 provide a suite of novel security and privacy mechanisms in our proposed system and evaluate its performance using the ns2 software. We show, by comparing its results to those of another system, its feasibility and efficiency 12 AVNS13012 Network Security Assessments for Integrating Large-Scale Tidal Current and Ocean Wave Resources Into Future Electrical Grids Abstract Marine energy, especially tidal current and ocean wave resources, bear immense potential for generating renewable power toward meeting global electricity needs. A number of conversion technologies have been successfully demonstrated worldwide and precommercial/commercial deployments are expected to appear in the near future. While electric power utilities foresee renewable technologies as a viable alternative to fossil fuels, marine energy technologies are generally excluded in their energy planning processes. Lack of technological preparedness and unavailability of device information are two major obstacles in that regard. This article provides an insight on how such novel schemes of power generation can be analyzed under conventional network planning exercises using generic information. The first study focuses on wave power integration along the coasts of Oregon, USA for the year 2019 and analyzes the Northwest electrical network. The second study considers both tidal current and ocean wave resources in South Korea for the years 2017 and 2022. The primary objective of these high-level grid scenario analysis is to identify the practical potential for longer term large-scale wave New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 and/or tidal power generation, particularly focusing on the transmission networks. Steady-state (overloading and voltage deviations/ collapses), time-domain (angular stability and dynamic voltage recovery characteristics), and small-signal (eigenvalue) stability analysis are carried out for these systems. Subsequent to establishing a number of study scenarios, N-1 contingencies and various suitable violation criteria are prepared, which are used in identifying the underlying network bottlenecks, especially within the coastal areas. Simplified generic dynamic models of tidal current and ocean wave devices are developed for the time-domain analysis. It is expected that similar studies, once conducted by the interested utilities, will equip them better toward considering marine energy in their future portfolios. In addition, device manufacturers and project developers will have greater confidence in the emerging marine energy marke New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 13 AVNS13013 Distributed Mobility Management for Efficient Video Delivery over All-IP Mobile Networks: Competing Approaches Abstract The recent proliferation of multimedia mobile devices and a variety of mobile applications are generating an enormous amount of data traffic over mobile net works. The key driver of the mobile traffic growth is mobile video. Currently, mobile networks are evolving to the 4G system, which has a flatter architecture and provides all-IP-based mobile broadband service. In all-IP mobile networks, IP mobility management is a key function that allows mobile nodes to continue their communications even when their point of attachment to the IP network changes. Existing mobile networks employ a centralized mobility management scheme where all intelligence is concentrated in one end-point system, rather than being distribut ed through the internet. However, this cannot satisfactorily support mobile videos, which demand a large volume of data and often require QoS such as session con tinuity and low delay. This motivates distributed mobility management (DMM) solu tions that can efficiently handle mobile video traffic. In this article, we survey different approaches for DMM in standards development organizations such as IETF and 3GPP, and also in research organizations. We focus on three different DMM approaches that are currently being considered by the IETF: PMIPv6-based, MIPv6-based, and routing-based DMMs. We provide a qualitative analysis to com pare the three DMM approaches and discuss which DMM approaches are more suitable for efficient mobile video delivery. 14 AVNS13014 Network Service Authentication Timing Attacks New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 Abstract The common wisdom is that string comparison timing attacks against a hashed password are impossible. However, these attacks can still be effective if attackers give up on the ideal of stealing all the characters representing the user's password or the entire hash. 15 AVNS13015 Mobility-Based Strategies for Traffic Steering in Heterogeneous Networks Abstract The large increase in size and complexity experienced by cellular networks in recent years has led to a new paradigm known as New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 heteroge neous networks, or HetNets. In this context, net works with different cell sizes, radio access technologies, or carrier frequencies can be deployed in the same environment. As the cov erage area of each of these networks is typically overlapped, operators have some degree of free dom to modify user distributions across the net works (i.e., traffic steering) in order to improve network performance. This article introduces different mechanisms of traffic steering in Het Nets, clarifying the specific goals that operators can set and focusing on those techniques that adjust mobility parameters, which are typically more attractive to achieve these goals. In addi tion, some challenging issues arising from partic ular HetNet deployments are discussed and illustrated by example use cases, which are appli cable to an early stage of LTE deployment. Finally, a fuzzy-logic-based algorithm that opti mizes network parameters for traffic steering is proposed. 16 AVNS13016 On Physical Layer Security for Cognitive Radio Networks Abstract In this article we explore the security issues on physical layer for cognitive radio networks. First we give an overview on several existing security attacks to the phys ical layer in cognitive radio networks. We then discuss the related countermeasures on how to defend against these attacks. We further investigate one of the most important physical layer security parameters, the secrecy New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 capacity of a cognitive radio network, and study the outage probability of secrecy capacity of a primary user from a theoretical point of view. Furthermore, we present performance results for secrecy capacity and outage probability between a node and its neighbors. Our work summarizes the current advances of the physical layer security and brings insights on physical layer security analysis in cognitive radio networks. 17 AVNS13017 Vulnerability assessment of intrusion countermeasures in Wireless Sensor Networks recovery Abstract Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have become a hot research topic in recent years and are considered to be one of the building blocks of pervasive computing. Many diverse, mission critical applications are deployed, including military, rescue, healthcare, factory floor, and smart homes. Security is a fundamental requirement in such sensitive applications in order to ensure their reliable and stable operation. However, security is a fairly difficult task to achieve. The open nature of the wireless communication, the unrestricted deployment and limitations of New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 WSNs and the existence of a variety of attacks threaten the security of a sensor network. Currently, research efforts have mainly focused on developing prevention and intrusion detection mechanisms in WSNs. Intrusion recovery is also an important aspect of security provisioning that is not given the same attention. Researchers have proposed intrusion recovery protocols to restore the network’s operation when an attack is detected. Their designs are mostly based on simplified threat models, making the intrusion recovery countermeasures vulnerable to advanced threat models. Although the network may recover its operation after an attack is detected, it does not mean that the threat is eliminated. For example, a persistent adversary can adapt his intrusion strategy to compromise the deployed recovery countermeasure. This research work evaluates the robustness and reliability of well-known recovery countermeasures in WSNs against persistent adversaries. Evaluation results have shown that existing intrusion recovery solutions are vulnerable and can be exploited under different attack strategies in order to compromise the applied recovery countermeasures, and thus the network. The vulnerability assessment is carried out using ns-2 simulations in an IEEE 802.15.4 network and within the AODV context. Observations derived from the assessment contribute towards future directions that can drive new designs of intrusion recovery protocols in WSNs. New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 18 AVNS13018 Detection and mitigation of sinkhole attacks in wireless sensor networks Abstract With the advances in technology, there has been an increasing interest in the use of wireless sensor networks (WSNs). WSNs are vulnerable to a wide class of attacks among which sinkhole attack puts severe threats to the security of such networks. This paper proposes two approaches to detect and mitigate such attack in WSNs. It provides a centralized approach to detect suspicious regions in the network using geo-statistical hazard model. Furthermore, a distributed monitoring approach has been proposed to explore every neighborhood in the network to detect malicious behaviors. Our simulation experiments validate the correctness and efficiency of the proposed approaches. New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 19 AVNS13019 Discovery and Verification of Neighbour Positions in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Abstract A growing number of ad hoc networking protocols and locationaware services require that mobile nodes learn the position of their neighbours. However, such a process can be easily abused or disrupted by adversarial nodes. In absence of a priori trusted nodes, the discovery and verification of neighbour positions presents challenges that have been scarcely investigated in the literature. In this paper, we address this open issue by proposing a fully distributed cooperative solution that is robust against independent and colluding adversaries, and can be impaired only by an overwhelming presence of adversaries. Results show that our protocol can thwart more than 99 percent of the attacks under the best possible conditions for the adversaries, with minimal false positive rates. 20 AVNS13020 Fault Node Recovery Algorithm for a Wireless Sensor Network New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 Abstract This paper proposes a fault node recovery algorithm to enhance the lifetime of a wireless sensor network when some of the sensor nodes shut down. The algorithm is based on the grade diffusion algorithm combined with the genetic algorithm. The algorithm can result in fewer replacements of sensor nodes and more reused routing paths. In our simulation, the proposed algorithm increases the number of active nodes up to 8.7 times, reduces the rate of data loss by approximately 98.8%, and reduces the rate of energy consumption by approximately 31.1%. 21 AVNS13- Improving the Network Lifetime of MANETs Through 021 Cooperative MAC Protocol Design Abstract Cooperative communication, which utilizes nearby terminals to New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 relay the overhearing information to achieve the diversity gains, has a great potential to improve the transmitting efficiency in wireless networks. To deal with the complicated medium access interactions induced by relaying and leverage the benefits of such cooperation, an efficient Cooperative Medium Access Control (CMAC) protocol is needed. In this paper, we propose a novel cross-layer Distributed Energy-adaptive Location-based CMAC protocol, namely DEL-CMAC, for Mobile Ad-hoc NETworks (MANETs). The design objective of DEL-CMAC is to improve the performance of the MANETs in terms of network lifetime and energy efficiency. A practical energy consumption model is utilized in this paper, which takes the energy consumption on both transceiver circuitry and transmit amplifier into account. A distributed utility-based best relay selection strategy is incorporated, which selects the best relay based on location information and residual energy. Furthermore, with the purpose of enhancing the spatial reuse, an innovative network allocation vector setting is provided to deal with the varying transmitting power of the source and relay terminals. We show that the proposed DEL-CMAC significantly prolongs the network lifetime under various circumstances even for high circuitry energy consumption cases by comprehensive simulation study. New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 22 AVNS13022 ReTrust : Attack-Resistant and Lightweight Management for Medical Sensor Networks Trust Abstract Wireless medical sensor networks (MSNs) enable ubiquitous health monitoring of users during their everyday lives, at health sites, without restricting their freedom. Establishing trust among distributed network entities has been recognized as a powerful tool to improve the security and performance of distributed networks such as mobile ad hoc networks and sensor networks. However, most existing trust systems are not well suited for MSNs due to the unique operational and security requirements of MSNs. Moreover, similar to most security schemes, trust management methods themselves can be vulnerable to attacks. Unfortunately, this issue is often ignored in existing trust systems. In this paper, we identify the security and performance challenges New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 facing a sensor network for wireless medical monitoring and suggest it should follow a two-tier architecture. Based on such an architecture, we develop an attack-resistant and lightweight trust management scheme namedReTrust. This paper also reports the experimental results of the Collection Tree Protocol using our proposed system in a network of TelosB motes, which show that ReTrust not only can efficiently detect malicious/faulty behaviors, but can also significantly improve the network performance in practice. 23 AVNS13023 Security and Efficiency in Roaming Services for Wireless Networks: Challenges, Approaches, and Prospects Abstract Seamless roaming over wireless networks is highly desirable to mobile users, but ensuring the security and efficiency of this process is chal lenging. Although the same may be said for all communication systems, roaming services have special requirements and vulnerabilities, and therefore deserve special attention. Over the years, we have seen a variety of authentication protocols emerging to address this issue. Howev er, which protocol is the most effective is still debatable. In this article, we first identify the challenges unique to roaming services as a set of mandatory and optional requirements. Next, we provide a brief state-of-the-art survey of existing work and point out their limitations in securing roaming services, especially in resistance against denial of service attacks, efficient authentication, flexible roaming in mobile contexts, as well as backward and forward non-linkabilities. To com plement the security provided by the New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802 existing work, we then propose some mechanisms that can meet the aforementioned security and effi ciency requirements. Finally, we present chal lenges that need to be addressed in roaming authentication. 24 AVNS13- Optimisation of Energy Efficiency in Wireless 024 Sensor Networks using Error Control Codes Abstract Energy saving optimization is a prime concern in the design of Wireless Sensor Networks as sensor nodes are deployed in different terrains where no source of power supply is available and sensor devices are operated by battery. The energy consumption of a sensor node is a function of internodes distance, desired BER, channel conditions, operating frequency, modulation schemes and error correcting codes (ECC). In this paper, we present a systematic approach to explore a design space to find an energy-optimal ECC in wireless sensor networks (WSN). ECC provides coding gain, resulting in transmitter energy saving at the cost of added decoder power. Further, for coded transmission, it is shown that that benefit of coding gain varies with the transmission distance referred as crossover distance (dxo). New no 68, old no 30, East Jones Road, Saidapet, Chennai-15 7200083802