An Algebra II Student's Guide
advertisement

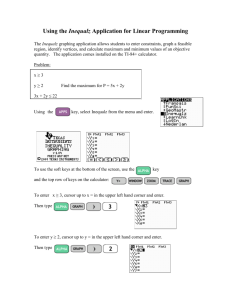
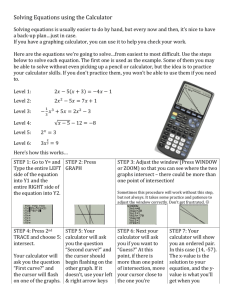
An Algebra II Student’s Guide to the TI-84+ Graphing Calculator prepared by: Mrs. P. Marques Seneca High School Welcome to Algebra II! This guide is intended to assist you as you use your graphing calculator throughout the course. Your teacher will require you to be able to do many problems both with and without the graphing calculator. CONTENTS 1. Getting Started ........................................................................................................................ 1 2. Order of operations .................................................................................................................2 3. Graphing a line ...........................................................................................................................3 4. Adjusting the viewing window.................................................................................................3 5. Finding x-intercepts of a linear function ...........................................................................4 6. Scatter plots and lines of best fit ......................................................................................5 7. Solving a system of linear equations ...................................................................................7 8. Entering matrices ..................................... ..............................................................................8 9. Finding x-intercepts of a quadratic function ...................................................................9 10. Finding the vertex of a quadratic function .....................................................................9 11. Solving polynomial equations ................................................................................................10 12. Permutations and combinations ..........................................................................................11 13. Evaluating rational exponents ............................................................................................12 14. Finding nth roots ....................................................................................................................12 15. Absolute value ........................................................................................................................12 16. Technical Support .................................................................................................................13 GETTING STARTED Whether you are using a TI-84+ or a similar graphing calculator, keep in mind that every function is color-coded. Below is an image of the TI-84+ taken from the following website: 21ctf.fi.ncsu.edu/msms/ti84.html. In order to use the blue functions listed above the keys, you must first press the blue “2nd” key. In order to access the light green letters and functions listed above the keys, you must first press the light green “ALPHA” key. -1- ORDER OF OPERATIONS You must understand and know the order of operations in order to evaluate an 1 2 32 expression correctly using your calculator. To evaluate the expression , you must 2(8) remember that the division bar (vinculum) groups the numerator and denominator, so the equation must be entered with parentheses grouping the numerator and parentheses grouping the denominator in the following way: ( 1 ) ) ENTER ( 2 + 3 x2 2 ( 8 ) If you want the answer to be in the form of a fraction, you can access this function by pressing the MATH key at the end of your expression. You can also avoid retyping an expression by recalling it using the 2ND ENTER keys. 2ND ENTER MATH ENTER ENTER Keep in mind that the TI-84+ family of graphing calculators will only display reduced fractions in either proper or improper form. -2- GRAPHING A LINE In order to graph a line, you must solve it for y . To graph the line 3x 4 y 8 , you 3 must first rewrite it as y x 2 before you enter it into the calculator. 4 Y= ( + 2 (-) 3 4 ) x,T, ,n In order to graph the line in a standard viewing window where the x-axis runs from -10 to 10, and the y-axis runs from -10 to 10, press the the above key strokes. ZOOM 6 keys after entering NOTE: You can always return to the home screen at any time by pressing 2ND MODE . ADJUSTING THE VIEWING WINDOW Let’s say that when you graph the line you cannot see its x- or y-intercepts on the screen. In that case, you must press the WINDOW key in order to adjust the window. For example, if you want to graph the line y 15x 27 you would see: Go to WINDOW to change what you see on the screen. Since you know that the yintercept is 27, you need only to adjust the Ymax entry to a number larger than 27. -3- Press GRAPH . Now you can see the graph and both of its intercepts. There is no specific method to follow in order to adjust the viewing screen window. Sometimes you just have to make educated guesses when changing the maximum and minimum values. FINDING X-INTERCEPTS OF A LINEAR FUNCTION In order to find the x-intercepts of a line on the graphing calculator, you must first graph the line as outlined above. Using the line y 15x 27 from the previous example, let’s find the x-intercept. Start by pressing 2ND Note that a “zero” is equivalent to an “xintercept” in mathematics. TRACE 2 . The calculator will ask you for a left and right bound. This simply means that you should enter a number you think is to the left of the x-intercept and one that is to the right. Just type in these numbers as you are given the prompts. Here, you simply press (-) When the calculator asks you to guess, simply take your cursor close to the point of intersection. 5 ENTER . Finally, press ENTER to view the answer displayed at the bottom of the screen. The x-intercept is at x = -1.8. -4- 0 ENTER SCATTER PLOTS AND LINES OF BEST FIT When you are given a list of data, you can graph it on you calculator. Let’s say you were given the following information: x y 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 -2 2 5 1 6 10 3 5 5 12 9 You must enter this information into your calculator by creating lists for your information. Press the STAT key and select option 1. You will enter the x values in L1 and the y values in L2. This is done by taking your cursor to the top of each list and typing in the number followed by the ENTER key. You will do this for each number entered. To move onto the next list simply move your cursor over to that column and repeat the steps. Once your lists are entered, press 2ND Y= to access the STAT PLOT function. Press ENTER to select Plot 1. NOTE: You may need to Use the cursor keys to navigate through the different selections on the screen. Press ENTER to select an option. Finally, press GRAPH . adjust the viewing window to see a better picture of your scatter plot. Also, if there are other graphs on your viewing screen, press Y= and clear any equations you may have. However, if you need the equations in the Y= screen for a later date, you can simply deactivate them by placing the cursor on the equal sign and pressing ENTER . This allows you to keep the equations, but they won’t be graphed. -5- To find the equation of the line of best fit, press STAT and move the cursor over to CALC and select option 4. Press the GRAPH key and you will see the scatter plot graphed along with the line of best fit. Then press 2ND 1 , , 2ND 2 VARS and move the cursor over to the Y-VARS option and select option 1. Finally, select option 1 again for Y1. What this allows you to do is to get the line of best fit and have it pasted to your Y= screen. Press ENTER to get the line of best fit. (If you press Y= , you will notice that the regression equation you just calculated is in Y1.) Notice that the values for a and b are given. The value of r is the correlation coefficient. The closer the value is to 1, the closer the plotted points are to the line of best fit. If you do not see the value for r, do the following: x 1 and scroll down until you find DiagnosticON. Press ENTER twice and repeat the steps in the previous column. 2ND 0 NOTE: If you return to the Y= screen, you will notice that PLOT1 is highlighted at the very top. It is important to turn all plots off in order to be able to graph equations entered in the Y= . You do this by moving your cursor up to the highlighted plot and press ENTER in order to remove the highlight. This can also be done by pressing 2ND Y= and going into each of the plots to turn them off in the same way you turned them on. If you don’t turn off the plots, your equations will always be graphed together with the scatter plot or you may get an error message. -6- SOLVING A SYSTEM OF LINEAR EQUATIONS When you solve a system of linear equations, you are finding the point of intersection of that system. First you need to graph the lines and ensure that you can see the point of intersection on the screen by adjusting the viewing window as necessary. In 7 x 12 order to find the point of intersection for the linear system 2 , you would do the 3 x 15 following: Enter the equations into the calculator. Graph it on the standard viewing window. Since you can’t see the point of intersection, adjust the window. Now that you can see the point of intersection, press 2ND TRACE 5 Notice that the point of intersection is in quadrant IV. Use this fact to help you choose the max/min values and graph the lines again. The calculator will ask you which curves (lines) you want to find the intersection of. The top of the screen displays one of the equations we want. Press ENTER . ENTER -7- The second line we want is displayed on the top so press ENTER . Here, you may just want to move your cursor to the point of intersection although this is not necessary. Press ENTER . You can now see that the point of intersection of the linear system is approximately at (3.5, -12.7) . ENTERING MATRICES 3 7 12 into the calculator, follow the steps 0 9 4 In order to enter the matrix below: 1 Press 2ND and move the x cursor over to EDIT. Select an empty matrix and press ENTER . Use the cursor keys to enter the dimensions of the matrix. Then press ENTER after you type in each entry. To return to the home screen press 2ND MODE . -8- FINDING X-INTERCEPTS OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS You can find the x-intercepts of a quadratic function in the same way as you did when finding the x-intercept of a line. Enter the equation into the Press 2ND TRACE 2 calculator by going to the Y= and follow the prompts as you did screen. Graph the equation in the for finding the x-intercept of a standard viewing window and line. adjust the window as necessary. One x-intercept is at about x = -1.9. To find the other xintercept, follow the same steps as before. When the calculator asks for a guess, simply move the cursor closer to the other xintercept you want to find. The other x-intercept is at about x = 1.2. FINDING THE VERTEX OF A QUADRATIC FUNCTION The vertex of a parabola is either its maximum or minimum point. The vertex of the above parabola is a minimum and can be found by pressing 2ND TRACE 3 . -9- Once the graph appears on the Because the vertex appears to x = 2 appears to be to the screen, follow the left/right be at about (0, -7), the choice of right of the vertex so it is a good bound prompts as you did before. x = -2 for a left bound seems choice for the right bound. appropriate. NOTE: In order to find the vertex of a parabola which is a maximum, follow the previous steps, but select option 4 (maximum) in the CALCULATE screen. When the “Guess” prompt appears, simply press ENTER . The vertex is at (-0.3, -7.3). SOLVING POLYNOMIAL EQUATIONS Suppose you are asked to solve the polynomial equation 3x 3 7 x 2 5x 7 10 . If you tried to set the equation to zero and factor, you would find that this would be impossible. It is only possible to solve using the graphing calculator. Follow the steps below: Enter the left side of the equation into Y1 of the Y= screen. Enter the right side as Y2. Graph the equations. It may be necessary to adjust the viewing window. -10- Press 2ND TRACE 5 . Answer the prompts as you did The second point of when solving a system of linear intersection is at about (-0.4, 10) equations. Remember to move the cursor to the desired point of intersection each time the prompt asks you to “guess.” The first point of intersection is at about (-2.8, 10). The last point of intersection is at about (0.9, 10) From these three points of intersection, we can determine that the solutions to the equation 3x 3 7 x 2 5x 7 10 are at about x = -2.8, x = -0.4, and x = 0.9. PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS The permutation and combination keys can be accessed by pressing the MATH key. You will need to use your arrow keys to highlight the PRB heading. In this screen, you can now access the permutation function (option 2), the combination function (option 3), and the factorial function (option 4). To compute 5P3, for example, press 5 MATH and arrow over to PRB. Then press 2 to select option 2. Finally, press 3 ENTER . Follow the same steps to find a combination selecting option 3 instead. -11- EVALUATING RATIONAL EXPONENTS To evaluate 243 5 simply press 2 4 ^ ( 3 ) / 5 ENTER . FINDING nth ROOTS To evaluate 5 86 simply press 5 MATH 5 8 6 ENTER . ABSOLUTE VALUE To evaluate 2(3) 10 using the graphing calculator, press MATH and arrow over to NUM. Select option 1 by either pressing 1 or ENTER . Type in the rest of the quantity remembering to end with ) . Press ENTER . -12- TECHNICAL SUPPORT If you are having trouble using your calculator, your teacher is a good source of information. Others in your class may also be able to help you. If you have a technical problem with your graphing calculator call 1-800-TI CARES. Texas Instruments has fantastic technical support and can take you step by step in solving your problems. -13-