Lesson 3 - ratios of special angles bigger than 90 - mhs
advertisement

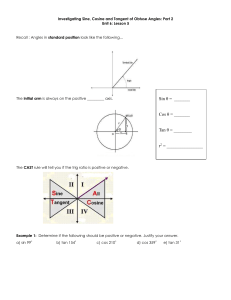
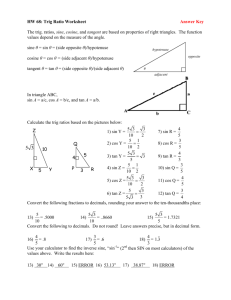
MCR 3U U5 Trigonometric Ratios for Angles > 90 Once you know the trig ratios for angles between 0 and 90 you can use these to determine the trig values of any angle > 90. The ratio values will either be the same or opposite to the values of those angles between 0 and 90. To these relationships we will first explore angles that are multiples of the frequently used angles 0, 45, 60, and 90. The diagram shows the angle 45 drawn on a Cartesian plane. Draw the angles on the other Quadrants and determine the Related Acute Angle. Use CAST or the fact that the x and y values are positive and/or negative in the various quadrants (see below) to come up with the ratios of each angle. opp y 1 hyp r 2 Cos 45 = Sin 135 = y Sin 45 y Cos 135 = 2 Tan 45 = 2 1 x 45 1 Csc 45 = Csc 135 = Sec 45 = Sec 135 = Cot 45 = Sin 225 = Cot 135 = Cos 225 = x 45 1 Sin 315 = y 1 Tan 135 = y Cos 315 = 2 Tan 225 = 2 1 x 45 1 Csc 225 = Tan 315 = Sec 315 = Cot 225 = Cot 315 = x 45 1 Csc 315 = Sec 225 = 1 To remember the sign of the trig ratio for angles in Quadrants 2, 3, and 4 we can use the CAST rule or just use the trig ratios in this form: sin y , cos x , tan y , csc r , sec r , cot x r r x y x y where (x,y) is the point on the terminal arm of the angle touching the circle and x2 + y2 = r2 The “CAST” Rule: Quadrant 1 0 90 y sin r x cos r y tan x All are +’ve Quadrant 2 90 180 y sin r x cos r y tan x Only Sine is +’ve Quadrant 3 180 270 y sin r x cos r y tan x Only Tosine is +’ve Quadrant 4 270 360 y sin r x cos r y tan x Only Cosine is +’ve Example 1: The point P(3, 6) lies on the terminal arm of an angle in standard position. Draw a diagram to represent this angle then determine the exact values of sin , cos and tan . Example 2: Find the exact values of the sine, cosine and tangent of 120 (this means do not use your calculator). Example 3: Evaluate each of the following (to 4 decimal places). a) sin 238 d) csc 175 b) cos 312 e) sec 21 c) tan 197 f) cot 296 Example 4: Find the measure of the angle to the nearest degree (0 360). a) sin = b) cos = 0.7431 c) tan = -14.3007 d) csc = e) sec = 1.0457 f) cot = 1.1504 Practice: 1. The coordinates of a point P on a terminal arm of an angle in standard position are given, where 0 360 . Draw a diagram to represent this angle, then determine the exact values of sin , cos and tan . a) P(8, 15) b) P(-3. 5) c) P(-4, -3) d) P(12, -5) e) P(-2, -7) f) P(3, -2) 2. Find the exact value of each trigonometric ratio: a) sin 45 b) cos 135 c) tan 225 e) cos 60 f) tan 120 g) sin 300 i) tan 30 j) sin 150 k) cos 210 d) sin 315 h) cos 240 l) tan 330 3. Evaluate each of the following (to 4 decimal places). a) sin 172 d) csc 308 b) cos 211 e) sec 159 c) tan 284 f) cot 143 4. Find the measure of the angle to the nearest degree (0 360). a) sin = b) cos = c) tan = 0.7813 d) csc = 4.4454 e) sec = 2.0627 f) cot = 0.0699 Answers to Example Questions: 2 1 1. sin , cos , tan 2 5 5 3 1 2. sin 120 , cos 120 , tan 120 3 2 2 3. a) 0.8480 b) 0.6691 c) 0.3057 d) 11.4737 e) 1.0711 f) 0.4877 4. a) 63 or 117 b) 42 or 318 c) 94 or 274 d) 203 or 337 e) 17 or 343 f) 41 or 221 Answers to Practice Questions: 15 5 15 8 5 3 1. a) sin = , cos = , tan = b) sin = , cos = , tan = 8 3 17 17 34 34 3 3 5 4 5 12 c) sin = , cos = , tan = d) sin = , cos = , tan = 5 4 12 5 13 13 7 2 7 2 2 3 e) sin = , cos = , tan = f) sin = , cos = , tan = 2 3 53 53 13 13 2. a) 1 b) 1 c) 1 d) 1 e) 3 3 1 1 1 1 1 f) 3 g) h) i) j) k) l) 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 2 3. a) 0.1392 b) 0.8572 c) 4.0108 d) 1.2690 e) 1.0711 f) 1.3270 4. a) 15 or 165 b) 14 or 346 c) 38 or 218 d) 193 or 347 e) 61 or 299 f) 94 or 274