ECOLOGY, POPULATION, AND BEHAVIOR STUDY GUIDE
advertisement

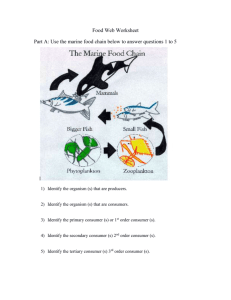
ECOLOGY, POPULATION, AND BEHAVIOR STUDY GUIDE Answer the following questions based on the food web above. 1. Which organisms are primary consumers (first-order heterotrophs)? Rabbit, deer, grasshopper, chipmunk, caterpillar 2. Which organisms are second-order and third-order heterotrophs? Fox, owl, hawk 3. What is the original source of energy for all organism in the diagram? Sun (use the diagram from the first page to answer the following questions) 4. What sequence shows a correct pathway for the flow of energy in a food chain? grass→ grasshopper → mouse → hawk 5. Which organisms would most likely be adversely affected by a continuous decrease in the population of rabbits? Owl and fox 6. Which organisms would represent the group with the least biomass? Hawk, owl, fox 7. If pesticides were used that killed grasshoppers, which organisms would have the most bioaccumulation of pesticides? Third order heterotrophs (owl, fox, hawk) 8. In the above diagram, a student notices that the grasshopper population is really high. Grasshoppers feed on plants. Robins feed on the grasshoppers. Owls feed on robins. Draw a pyramid of energy correctly illustrates these relationships? Owl Robin Grasshopper Grass 9. If the grasshopper population decreased, what would happen to the grass population? It would increase 10. By observing the diagram above in # 8: at each successive level from Grass to Owl, what happens to the amount of available energy? Decreases Use the graphs below to answer the following questions: 2 1 Population A 3 1 Population B 11. What type of graph is represented for population A? S-shaped 12. How would you describe the growth rate of populations A and B at the time of # 1? Exponential 13. How would you describe the growth rate of population A during the time of # 2? Leveling off 14. How would you describe the growth rate of population A at the time of # 3? Carrying capacity 15. What could be some abiotic limiting factors for population A? Water, space, temperature 16. What could be some biotic limiting factors for population B? Food availability, predator population size 17. What type of graph is represented for population B? 18. What shape graph would humans have? J-shape, exponential 19. What shape graph would antibiotic resistant bacteria have? J-shape, exponential 20. What shape graph would represent a deer population? S-shape, with carrying capacity 21. The graph below shows the changes in two populations of herbivores in a grassy field. What is a possible reason for these changes in each population over time? Population B competed more successfully for food than population A 22. An environment can support only as many organisms as the available energy, minerals, and oxygen will allow. Which term is best described by this statement? Carrying capacity 23. In the above question, are these limiting factors biotic or abiotic? Abiotic 24. Examine the diagram below. Which two processes are involved in the cycling of matter shown in the diagram? Photosynthesis (using CO2 and giving off O2 And Cellular Respiration (using O2 and giving off CO2) Use the following terms to answer the questions below: Population Biosphere Community Ecosystem 25. Beneath a log, you will find fungi, termites, pill bugs, ants, millipedes, earthworms, and beetles. What do these organisms represent as a whole? Community (group of different species living together) 26. Put the above terms in order from smallest to largest. Population Community Ecosystem Biosphere 27. In question 26, which term includes the other three? Biosphere 28. Which term includes only one species? Population 29. Which term includes all of the abiotic and biotic factors that interact? Ecosystem 30. What is the difference between niche and habitat? A habitat is the place where an organism lives. A niche is the role that organism plays in the environment. 31. Ants and the acacia tree both help each other. What is this type of symbiotic relationship? Mutualism 32. A mosquito drinks blood from a human. What is this type of symbiotic relationship? Parasitism 33. Spanish moss grows on a water oak tree, but it does neither harm nor benefit to the tree. What is this type of symbiotic relationship? Commensalism 34. What are decomposers and why are they important? Decomposers are heterotrophs that break down dead organisms. They are important in cycling materials by returning nutrients back to the soil, such as nitrogen. 35. Draw a graph that represents a predator-prey relationship. Use the graph above to answer the following questions: 36. In the above graph, what happens if the prey (rabbits) decrease? The predator population will decrease because there are not enough rabbits to feed the predators 37. Once the predator population goes down, what will happen to the rabbit population? It will increase again 38. What greenhouse gas causes acid rain? Where does it come from? Sulfur dioxide emitted from smoke stacks of factories 39. What contributes to global warming? The burning of fossil fuels Animal Behavior 1. What are chemicals used to communicate called? Pheromones 2. What is an example of imprinting? Young gozzlings (geese) follow their mother 3. What is an example of trial-and-error learning? A mouse that has been trained to go through a maze to receive an award at the end 4. How do animals communicate? Sounds, touches, visual (body language), and smells 5. If a chimpanzee figures out that he can screw two poles together in order to reach a banana far away from his cage, and he has never seen this done before, what type of learned behavior is this? Insight 6. Why do raccoons come out mostly at dawn and dusk? Cirdadian rhythm (internal 24 hour clock) 7. Who first demonstated conditioning in dogs? Pavlov 8. What did the biologist above do to make the dog drool? Train the dog to associate that every time it hears a bell, it gets fed. Eventually, all it took was for the dog to hear a bell ring, and it would drool for food that it knows is coming soon. 9. What is rutting behavior in deer an example of? Territoriality (defending space) A form of Aggression 10. When a bird sings to signal to other birds to keep away, what is this an example of? Territoriality (defending space) A form of Aggression 11. When some chickens are subservient, while one chicken always gets to eat first, what is this an example of? Pecking order (dominance hierarchy) 12. What is the difference between hibernation and estivation? Hibernation: slowing of one’s metabolism during COLD weather Estivation: slowing of one’s metabolism during HOT weather 13. If a dog is taken on a walk every day along a sidewalk with very noisy traffic and is no longer scared of the noise, what has taken place? Habituation (ignoring the sounds since they do not pose a threat or reward) 14. How do honeybees communicate to each other where a good food source is located? A waggle dance; bees make a figure-8 shape dance, angled the # of degrees away from the sun to indicate direction and waggling the number of times indicating distance. 15. What is the difference between negative and positive phototaxis? When an organism moves towards light, it is positive phototaxis When an organism moves away from the light, it is negative phototaxis