Chapter 37: Soil and Plant Nutrition
advertisement

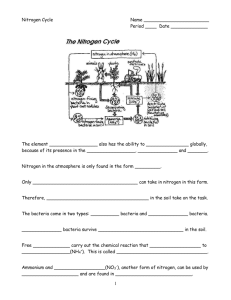
Exam I - Ch. 37 – WS 6 Chapter 37: Soil and Plant Nutrition 1. How do roots absorb inorganic minerals from the soil? Cation Exchange – roots pump out H+ to get other positive ions that the plant needs (Ca2+, K+, Mg2+) - Remember that soil particles are negatively charged, so positively charged ions (cations) form ionic bonds with the soil particles - Cation exchange depends on two things: a) Number of cation adhesion sites on the soil particles b) Soil pH 2. What are the two types of essential elements required for a plant to complete its life cycle and produce another generation? Macronutrients – needed in large amounts (Magnesium) Micronutrients – need in small amounts (Iron) 3. Can you describe the various bacteria that participate in the nitrogen cycle? Nitrogen-fixing bacteria: Atmospheric Nitrogen → Ammonia Ammonifying bacteria: Organic material in soil → Ammonia Nitrifying bacteria: Ammonium → Nitrate Denitrifying bacteria: Nitrate → Atmospheric Nitrogen 4. In what two forms can nitrogen be absorbed by plants? Ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-) 5. Which enzyme helps to convert nitrogen for plants to use? Nitrogenase 6. Can you explain another relationship between plants and bacteria involving nitrogen fixation. Symbiotic relationship between Rhizobium bacteria and Legume roots. - Plant roots send out Flavonoid into the soil - Flavonoid activates transcription genes in bacteria - Bacteria releases nod factor - Activates nodulin genes which allow bacteria to enter plant roots 7. How do nodules form on the plant roots? Bacteria enter plant roots via root hairs (infection threads) Pericycle cells (surrounding the vascular bundle) divide and form nodules Bacteria inside nodules are referred to as Bacteroids Exam I - Ch. 37 – WS 6 8. What is the role of Leghemoglobin? Protein formed by both the plant and bacteria Binds to O2 preventing the deactivation of the nitrogenase enzyme 9. How does fungus play a role in plant nutrition? Fungus attaches to plant roots forming Mycorrhizae (fungus roots) - Increased surface area for water absorption - Fungus sends out digestive enzymes to break down organic material - Fungus can grow factors and antibiotics to aid the plant 10. Carnivorous plants eat insects in order to obtain what nutrient? Nitrogen found in chitin which comprises the exoskeleton of the insect