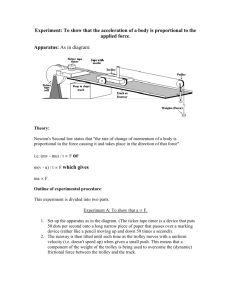
IB Lab - 14 F=ma (DC DPP CE).
advertisement
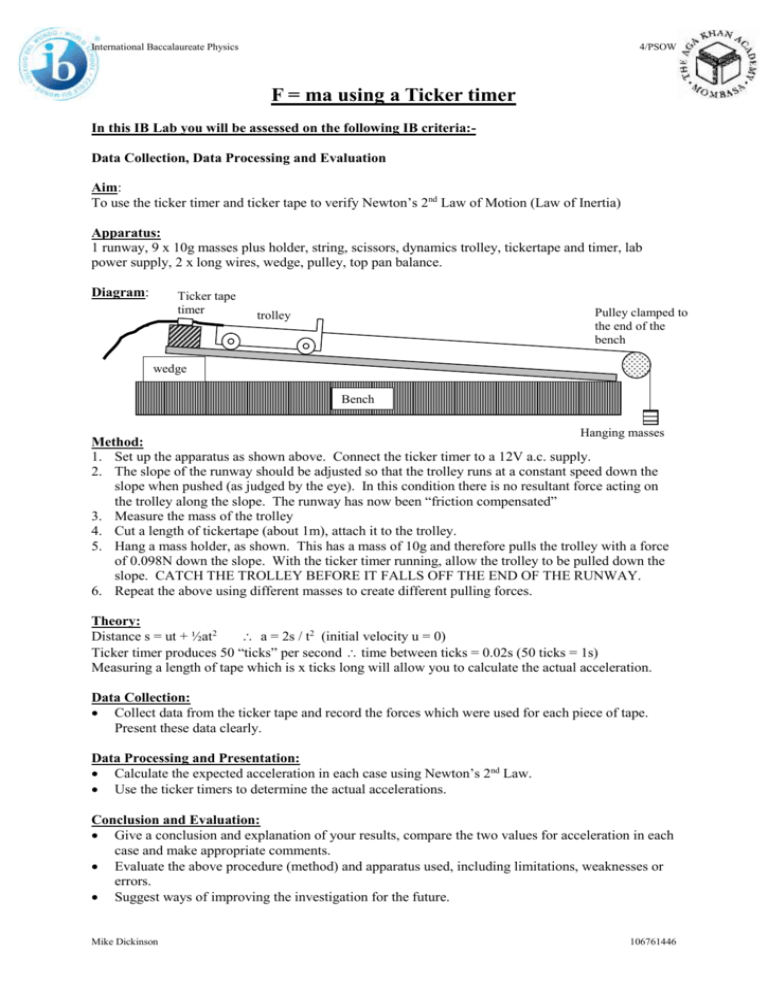
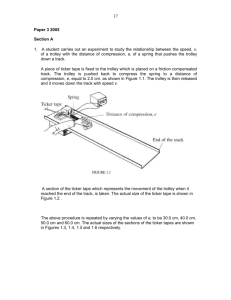
International Baccalaureate Physics 4/PSOW F = ma using a Ticker timer In this IB Lab you will be assessed on the following IB criteria:Data Collection, Data Processing and Evaluation Aim: To use the ticker timer and ticker tape to verify Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion (Law of Inertia) Apparatus: 1 runway, 9 x 10g masses plus holder, string, scissors, dynamics trolley, tickertape and timer, lab power supply, 2 x long wires, wedge, pulley, top pan balance. Diagram: Ticker tape timer Pulley clamped to the end of the bench trolley wedge Bench top Hanging masses Method: 1. Set up the apparatus as shown above. Connect the ticker timer to a 12V a.c. supply. 2. The slope of the runway should be adjusted so that the trolley runs at a constant speed down the slope when pushed (as judged by the eye). In this condition there is no resultant force acting on the trolley along the slope. The runway has now been “friction compensated” 3. Measure the mass of the trolley 4. Cut a length of tickertape (about 1m), attach it to the trolley. 5. Hang a mass holder, as shown. This has a mass of 10g and therefore pulls the trolley with a force of 0.098N down the slope. With the ticker timer running, allow the trolley to be pulled down the slope. CATCH THE TROLLEY BEFORE IT FALLS OFF THE END OF THE RUNWAY. 6. Repeat the above using different masses to create different pulling forces. Theory: Distance s = ut + ½at2 a = 2s / t2 (initial velocity u = 0) Ticker timer produces 50 “ticks” per second time between ticks = 0.02s (50 ticks = 1s) Measuring a length of tape which is x ticks long will allow you to calculate the actual acceleration. Data Collection: Collect data from the ticker tape and record the forces which were used for each piece of tape. Present these data clearly. Data Processing and Presentation: Calculate the expected acceleration in each case using Newton’s 2nd Law. Use the ticker timers to determine the actual accelerations. Conclusion and Evaluation: Give a conclusion and explanation of your results, compare the two values for acceleration in each case and make appropriate comments. Evaluate the above procedure (method) and apparatus used, including limitations, weaknesses or errors. Suggest ways of improving the investigation for the future. Mike Dickinson 106761446