Projectile Motion
advertisement
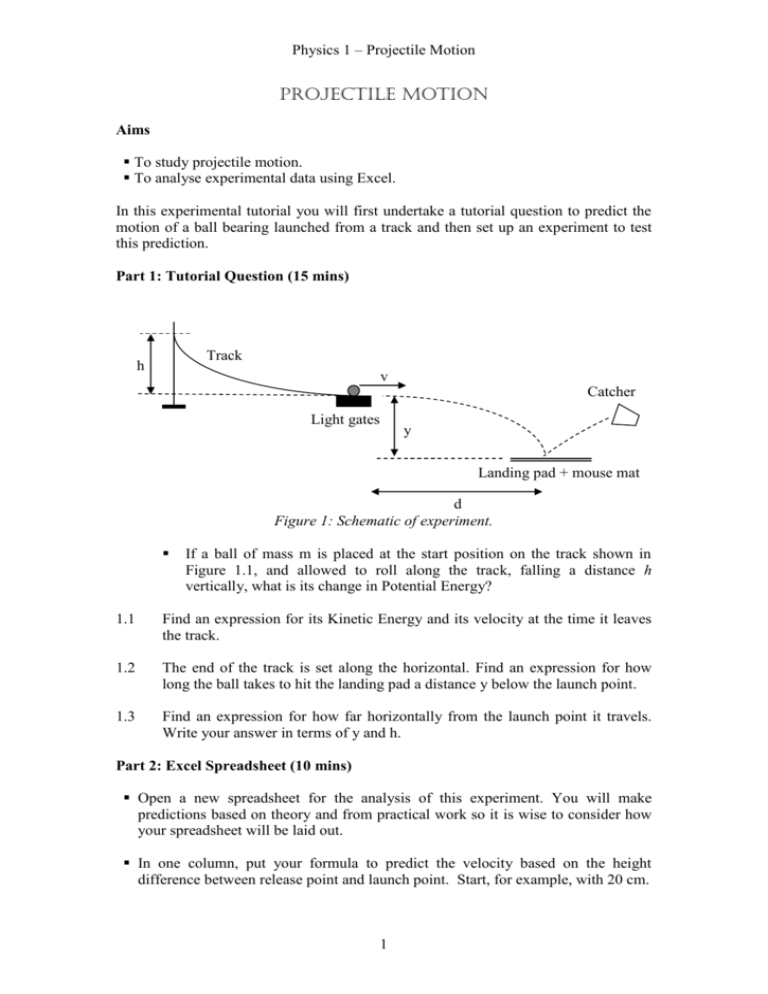
Physics 1 – Projectile Motion PROJECTILE motion Aims To study projectile motion. To analyse experimental data using Excel. In this experimental tutorial you will first undertake a tutorial question to predict the motion of a ball bearing launched from a track and then set up an experiment to test this prediction. Part 1: Tutorial Question (15 mins) Track h v Catcher Light gates y Landing pad + mouse mat d Figure 1: Schematic of experiment. If a ball of mass m is placed at the start position on the track shown in Figure 1.1, and allowed to roll along the track, falling a distance h vertically, what is its change in Potential Energy? 1.1 Find an expression for its Kinetic Energy and its velocity at the time it leaves the track. 1.2 The end of the track is set along the horizontal. Find an expression for how long the ball takes to hit the landing pad a distance y below the launch point. 1.3 Find an expression for how far horizontally from the launch point it travels. Write your answer in terms of y and h. Part 2: Excel Spreadsheet (10 mins) Open a new spreadsheet for the analysis of this experiment. You will make predictions based on theory and from practical work so it is wise to consider how your spreadsheet will be laid out. In one column, put your formula to predict the velocity based on the height difference between release point and launch point. Start, for example, with 20 cm. 1 Physics 1 – Projectile Motion Now measure the depth, y , from the launch point to the landing pad. 2.1 2.2 Predict the time of flight. Predict the horizontal distance travelled after launch. In another column of your spreadsheet, add the formula to calculate velocity based on the time taken to travel the distance between the two light gates, 20 mm. Hint: Put all variable numbers in their own cells in Excel. Do not perform the calculations yourself – enter the equations into excel and get excel to perform the calculations. Here is an example layout: Release Height (m) 0.1 Apparatus Light Gate 1 Light Gate 2 Mat Time (s) 0 Distance Between Gates (m) Horizontal Velocity (m/s) Time in flight (s) Predicted distance (m) Actual distance (m) 0.02 1.370802 0.27919 0.382714 0.335 0.01459 0.29378 Part 3: Taking Data (25 mins) Set up the target at a distance so that the ball will hit the central zone on the carbon paper covering the target. Open the EasySense software package. You are interested in measuring the times of the ball passing through the light gates and hitting the landing pad. From the opening menu select: timing, raw times, next, at A or B, then finish. Now from the Display option at top select Show Table – this will display the times recorded. You can now start the experiment using start button. Release the ball and click stop once the ball has landed. You are only interested in the first 3 measurements although the computer might attempt taking 1000! The first and second times recorded are those of the ball triggering each light gate respectively. The third time recorded is that of the ball hitting the landing pad. Enter these times into your Excel spreadsheet. Once you have transferred the data from your first run, delete this data from the EasySense table. To do this you will need to highlight every cell by clicking on 2 Physics 1 – Projectile Motion the top cell, holding shift, and clicking the bottom cell. Now click delete on the top toolbar to clear the cells. Hints: a) It might be wise to number each dot so you can measure the horizontal distance afterwards. b) Delete the data after each run. This will save you from having to restart the software each time. Perform the experiment for three or more different release points of the ball. 3.1 Produce an Excel spreadsheet showing all your results 3.2 Discuss how you expect changing the release point to affect the velocity and the flight time. Perform the experiment with the changed release point and compare your predictions with results obtained. 3.3 Comment on the comparison between your results and predictions. What effects have you neglected in your analysis ? Add a printout of your excel spreadsheet to your lab book. Part 4: Launching at an angle to the horizontal (Optional) 4.1(a) Derive the expression for the flight time and the distance travelled by the ball if it is launched at an angle degrees to the horizontal and falls through a distance y - express your results in terms of , y and horizontal velocity v. (b) Explain what will happen to the horizontal distance travelled if the launch point is raised an angle degrees to the horizontal. (c) Discuss by considering the cases when y tends to 0 and y tends to infinity. Further work The following questions are related to the topic covered by this experimental tutorial. Exercise book questions D1 – D20, notably D11 and D13. Mastering Physics Dynamics 1: Motion in Two or Three Dimensions, notably the Projectile Motion Tutorial. 3 Physics 1 – Projectile Motion Demonstrators' Answers, Hints, Marking Scheme and Equipment List Marking Scheme Section 1.1 1.2 1.3 2.1 2.2 3.1 3.2 3.3 Discretionary mark TOTAL Mark 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 10 Answers 1.1 mgh 1 2 mv 2 1.2 v 2 gh mgh s ut 12 at 2 1.3 working vertically y 12 gt 2 t 2y / g s ut 12 at 2 1.4 working horizontally x vt 2 gh 2 y 2 yh g 3.1 increase height – increase horizontal velocity decrease height – decrease horizontal velocity flight time will remain unaffected 3.2 friction from track, air resistance, precision of equipment, any other assumptions. 4.1(a) initial v HORIZONTAL v cos initial vVERTICAL v sin gt Vertically: y v sin .t 1 2 gt 2 4 Physics 1 – Projectile Motion 1 2 g .t v sin .t y 0 2 1 v sin v 2 sin 2 4 g ( y ) 2 t 1 2 g 2 Flight time: v sin v 2 sin 2 2 gy t g We’re only interested in the positive solution, and to check the validity of the 2y equation try for = 0 t g x v cos t v sin v 2 sin 2 2 gy v cos g Horizontally: distance 2v sin 2v 2 sin cos v 2 sin 2 g g g Consider y = 0: x v cos Maximal when sin2 = 1, i.e. = 450 For y > 0 as y x v cos t t 2y g x v cos 2y g Maximal when cos 1 so 0, so the larger the value of y the smaller the optimal launch angle for maximal distance. flight time is changed, horizontal velocity is decreased, distance travelled will change Equipment List: Track with light gates fitted Stand with boss head Clamp Ball 5 Physics 1 – Projectile Motion Measuring tape or meter stick Landing Pad Mouse mat and carbon paper Stool Catcher Computer with EasySense software 6