1.6 The Skeleton
advertisement

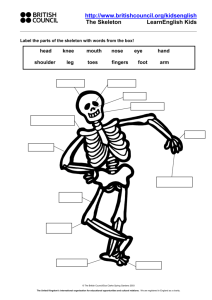
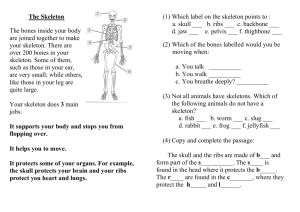
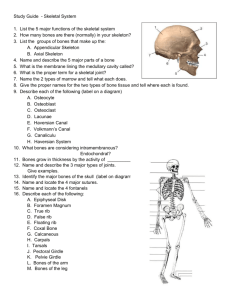
Life Processes 1 Humans 1.6 The skeleton Sc2: Life Processes 1 Humans 1.6 The Skeleton P.O.S. Key Stage 1 Sc2 1b Key Stage 2 Sc2 2e Life Processes 1 Humans 1.6 The skeleton LEARNING OBJECTIVES To be able to feel bones. To know that there are bones inside their own body. To know that the skeleton supports the body and protects parts of the body. To develop the skill of discussing and questioning. ICT Use videos to show skeleton Use CD-ROMs on ‘The Body’ to look at skeletons and movement LINKS VOCABULARY PE - movement Bones, skeleton & bone names e.g. skull, ribcage, hips spine shoulder; strong, hard, X-ray. ACTIVITIES Handle real or replica bones. Handle rag doll; try to make it stand up. Then insert “bones” to make it rigid. Feel bones inside own arms, legs and hands. Use own limbs to stand, push, etc. (feel rigidity). Experience using the body to move in different ways e.g. crawling, rolling. Make own arms, legs, fingers, body floppy, then strong. Show pupils skeleton model. Relate to own body; name some of the bones. Sing “Dem bones, dem bones”. Make skeleton model bend and straighten. Pupils bend and stretch – find places where they can bend i.e. joints match to skeletons joints. Names some joints e.g. knee, elbow. Watch body video. Look at x-ray pictures – recognise and link to body parts. Match bones to body outline. Assemble paper skeleton parts, with paper-fasteners. Read Funny-bones. Try a simple activity with the hand e.g. pick up objects, and then repeat with lolly-sticks taped to fingers to prevent bending. Compare how easy it was to do this. Discuss what a skeleton is used for. RESOURCES Real or replica bones. Rag doll Lolly sticks or similar to make rigid. Video X-ray pictures Paper skeleton, paper clips. Plastic model skeleton VISITS Museum - zoology POINTS TO NOTE Be sensitive to possible invasive procedures e.g. moving limbs etc with non-mobile pupils – may be appropriate to set up separate, more private sessions for them (possibly involve physio staff). Pupils do not need to know the names of joint types e.g. hinge, ball & socket nor do they need to know the names of all bones or Latin names Life Processes 1 Humans 1.6 The skeleton OWN ACTIVITIES POSSIBLE INVESTIGATIONS Find out what happens when chicken bones are left to soak in various liquids. Find out which is the strongest finger e.g. by picking up weights, pushing onto bathroom scales or into playdough and measuring the depth of the imprint. Life Processes 1 Humans 1.6 The skeleton Name: Date Record Began: Outcomes: ‘P’ Level 1 NC Level 1 P1 (i) Experiences physio – bend and stretch arms and legs/hands e.g. illustrating “Dem bones” song. May show resistance Is helped to feel specimen bones but may have passive response. P1 (ii) Co-operates intermittently with different movements. P2 (i) Begins to attend during physio movements. Accepts active exploration e.g. feels bone with fingers after adult places hand on bone. Shows more consistent attention to activities e.g. focuses on skeleton model when shown. Shows more active participation e.g. shows random movements to ‘Bone’ songs. Observes results of own actions with interest e.g. watches own limbs bending. Participates in exploring model skeleton with support e.g. looks for places that bend. P3 (ii) Starts to show anticipation e.g. at the same part of the song. P4 Imitates movement actions e.g. makes body floppy, makes fingers stiff. P5 Joins in with a simple experiment e.g. allows lolly sticks to be taped to fingers and then tries to pick up objects. Responds to a simple question about the activity e.g. can you pick up an object with lolly sticks on your fingers? Matches action to song e.g. by shaking or pointing to appropriate bone in song. Begins to make connections between skeleton and bones in everyday contexts e.g. dog bone, chicken/chop bones; spare ribs; butchers shops. Assembles parts of skeleton body with support. Asks one or two questions when doing an activity. Points to some main skeleton parts when named Matches main skeleton parts e.g. skull, ribcage, to body outline. Asks more than one or two questions during an activity. Not all have the same question stem e.g. how, what, why? Is able to demonstrate floppy/strong using their own body. Knows that bones support the body. Knows that bones protect some body parts e.g. heart, lungs, brain. Names some of main skeleton parts Asks a wider range of questions and take turns in discussion P2 (ii) P3 (i) P6 P7 P8 N.C. Level 1 Further Comments