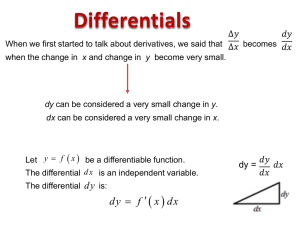
Definition - Moorpark College
advertisement
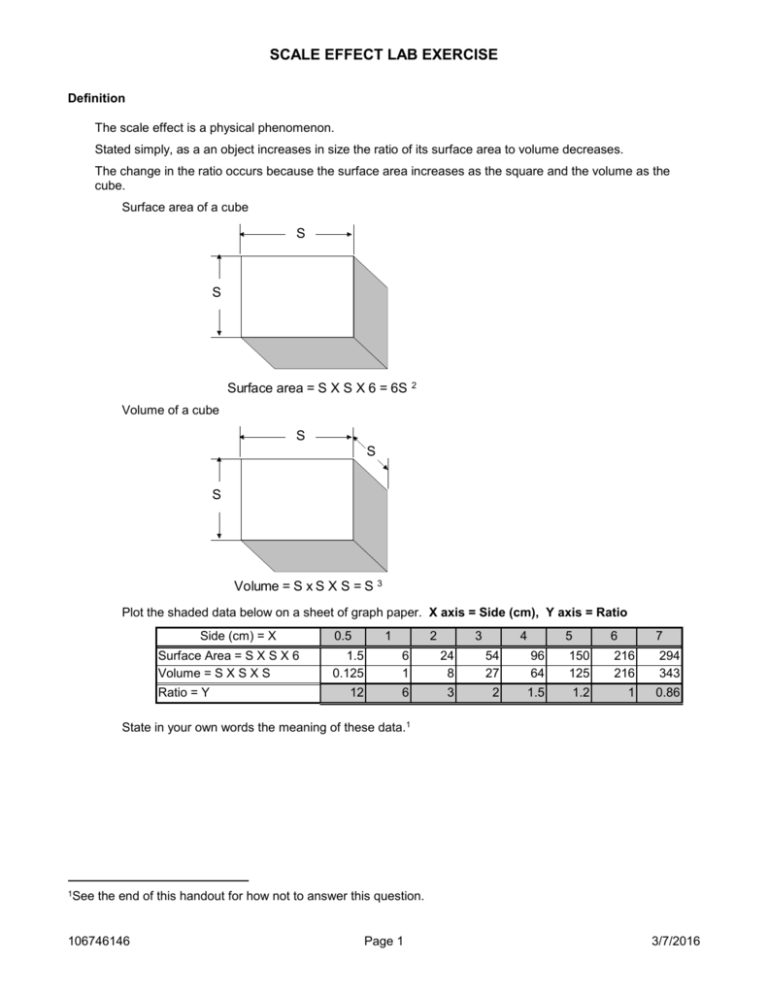
SCALE EFFECT LAB EXERCISE Definition The scale effect is a physical phenomenon. Stated simply, as a an object increases in size the ratio of its surface area to volume decreases. The change in the ratio occurs because the surface area increases as the square and the volume as the cube. Surface area of a cube S S Surface area = S X S X 6 = 6S 2 Volume of a cube S S S Volume = S x S X S = S 3 Plot the shaded data below on a sheet of graph paper. X axis = Side (cm), Y axis = Ratio Side (cm) = X Surface Area = S X S X 6 Volume = S X S X S Ratio = Y 0.5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1.5 0.125 6 1 24 8 54 27 96 64 150 125 216 216 294 343 12 6 3 2 1.5 1.2 1 0.86 State in your own words the meaning of these data.1 1See the end of this handout for how not to answer this question. 106746146 Page 1 3/7/2016 Scale Effect - Physiology Lab Activities Surface to Volume Ratio Milk cartons Measure the surface area of the milk cartons Pint (cm2 ) Side Quart (cm2 ) Half Gallon cm2 ) 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Surface = Measure the volume of the cartons Pint (ml) Quart (ml) Half Gallon (ml) Total Volume= Calculate the surface to volume ratio Pint Quart Half Gallon X =Total Surface Total Volume Y = Ratio of S/V Plot the ratio on a sheet of graph paper Group discussion: Assuming that the density of milk = 1 g/ml, what implications do these data have regarding the potential maximum size of terrestrial organisms? Scale Effect and Diffusion Use the lab computer for the following exercise Time how long it takes the simulation of a diffusing molecule to leave the four circles on the screen. Circle Radius (cm) Trial 1 (sec) Trial 2 (sec) Trial 3 (sec) Average (sec) 1 2 3 4 Plot the results on a sheet of graph paper: X axis = radius, Y axis = average time Group discussion: What implications do these data have regarding the maximum potential size of cells? 106746146 Page 2 3/7/2016 Scale Effect - Physiology Scale Effect and Flow Graduated cylinders Measure the diameters of the openings drilled into the plastic graduated cylinders provided. Time how long it takes for 500 ml to drain through the hole (ml/sec) Cylinder Trial 1 (ml/sec) Diameter (mm) Trial 2 (ml/sec) Trial 3 (ml/sec) Average (ml/sec) A B C D Plot the results on a sheet of graph paper. X axis = diameter, Y axis = Average rate Group discussion: What do these data indicate regarding the rate of flow of blood through blood vessels and air through airways? Scale Effect and Flow Computer Simulation Load PhysioEx in computer and go to module Cardiovascular Dynamics and Experiment Vessel Resistance. Perform the flow exercise above using the following settings: 1. Pressure = 200 mmHg; Viscosity =3; Length = 25 2. Vary the radius starting at 1 mm and increase in increments of 0.2, that is the first recording is at 1.0, then next at 1.2, the next 1.4, etc., up to a radius of 6.0 3. Record the data and graph the results. Compare your graph with the computer generated graph. What is the significance of the shape of the graph? Radius 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 2 106746146 Flow Radius Flow Radius Flow Radius Flow Radius Flow Rate Rate Rate Rate Rate 2.1 3.2 4.3 5.4 2.2 3.3 4.4 5.5 2.3 3.4 4.5 5.6 2.4 3.5 4.6 5.7 2.5 3.6 4.7 5.8 2.6 3.7 4.8 5.9 2.7 3.8 4.9 6 2.8 3.9 5 2.9 4 5.1 3 4.1 5.2 3.1 4.2 5.3 Page 3 3/7/2016 Scale Effect - Physiology 106746146 Page 4 3/7/2016