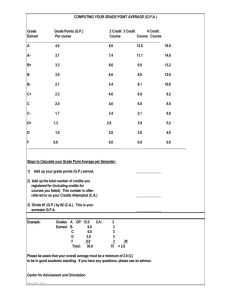
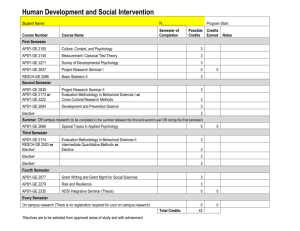
4 - Universität Stuttgart
advertisement

Universität Stuttgart Office of International Affairs Information for Visiting Students and Information Package of the European Course Credit Transfer System (ECTS) for Studies in Business Administration 1999 Universität Stuttgart Office of International Affairs and Faculty of History, Social Sciences and Economics Office of International Affairs General Information Who is considered to be a visiting student? This brochure is designed for all international students who come to study at the Universität Stuttgart on the basis of an exchange agreement with partner institutions or a programme such as SOCRATES/ ERASMUS and who do not plan to complete a degree at the Universität Stuttgart. CONTENTS: A. General Information 5 1. The Universität Stuttgart 5 Description of the Universität Stuttgart The Faculties/ Departments of the Universität Stuttgart and their Web Sites 5 5 2. 6 The Office of International Affairs The Academic Calendar Application Information Academic Prerequisites Application Documents and Deadlines Letter of Admission – Zulassungsbescheid Registration The German Intensive Course The Orientation Seminar The Structure of Studies Which courses must I take? What kind of courses are offered? Transferring Credits 7 7 7 8 8 9 9 9 10 10 10 11 3. 12 Other Facilities at the Universität Stuttgart Libraries Computer Centre and E-mail Sports Activities Meals Information Package 12 12 12 12 2 Office of International Affairs 4. General Information General Information of Practical Use Residence Permits and Visa Regulations Costs of Living Expenses Dormitory Accommodation Temporary Accommodation for Young People Health Insurance Medical Care Public Transport Banking Telephoning The City of Stuttgart Climate How to get to Stuttgart-Vaihingen How to get to the dormitories in Ludwigsburg How to get to the Office of International Affairs What you need to think about before arriving in Stuttgart 13 13 13 14 14 15 16 16 17 17 17 18 18 19 19 20 B. Information for Students in Business Administration 22 1. Business Administration with a Technical Orientation 22 2. ECTS-Coordinators 23 3. Information for all ERASMUS Exchange Students at the Business School 23 4. Information about the European Credit Transfer System at the Business School 24 5. Information for EMBS Students 25 C. Course Catalogue 32 1. Explanation of Terms 32 1.1 1.2 Information about the Description of Syllabus and Courses offered Codification of Courses 32 33 Information Package 3 Office of International Affairs General Information 2. Syllabus of Stage 1 Studies 34 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Structure of Stage 1 Studies Preparatory Courses Business/ Management Studies Economics Basic Features of Jurisprudence 34 34 35 37 38 3. Stage 2 Studies 40 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 3.16 Structure of Stage 2 Studies 40 General Management Studies 40 Economics 42 Special Business Administration: Human Resource Management 43 Special Business Administration: Organisational Design 46 Special Business Administration: Financial Management 47 Special Business Administration: Strategic Management and Corporate Planning 48 Special Business Administration: Management Accounting 50 Special Business Administration: Marketing 51 Special Business Administration: Business Informatics 53 Special Business Administration: R&D Management 54 Economics: Economic Policy 55 Economics: Innovation 57 Economics: Public Finance 59 Jurisprudence 59 Courses in Engineering/ Science (Obligatory Technical Subjects) 60 Information Package 4 Office of International Affairs A. General Information 1. The Universität Stuttgart General Information Description of the Universität Stuttgart The Universität Stuttgart, which was founded in 1829, has integrated the social sciences and the humanities with engineering and the natural sciences to become an internationally renown future-oriented place of teaching and research. Today nearly 17,000 students are studying to complete their degrees in one of the 44 degree courses offered by the 14 faculties. More than 2,900 of these young men and women are international students. The Universität Stuttgart holds a leading position in both basic and applied research and is proud of its tradition of close cooperation with industry as well as with other research institutions such as the Fraunhofer-Society for Production Engineering, the BadenWürttemberg Materials Testing Centre and the German Aerospace Research Institute. These close relationships also stimulate important impulses for teaching at the university. Address: Universität Stuttgart Keplerstr. 7 70174 Stuttgart Germany Phone ++49-711-121-0 Fax ++49-711-121-2271 Faculties/ Departments of the Universität Stuttgart and their Web Sites Most of the Universität Stuttgart is located either in the centre of the city or in a suburb of Stuttgart called Vaihingen. The city centre campus is connected to the campus in Vaihingen by a fast underground train system. The journey takes about ten minutes each way. The following faculties are located In the centre of the city: Architecture and Urban Planning Biological and Geo-Sciences (Geography, Geology) History, Social Sciences and Business Administration Philosophy Civil Engineering and Surveying (partly) Energy Technology, Construction and Production Engineering (partly) Information Package 5 Office of International Affairs General Information The following are in Vaihingen: Biological and Geo-Sciences (Biology) Civil Engineering and Surveying (partly) Chemistry Electrical Engineering Energy Technology, Construction and Production Engineering (partly) Aerospace and Aviation Engineering Mathematics Physics The following are located in a different part of Stuttgart: Process Engineering (Böblinger Straße) Computer Science (industrial area in Stuttgart-Möhringen) A survey of the subjects and courses offered as well as a description of the faculties of the Universität Stuttgart can be found on the web as follows: http://www.uni-stuttgart.de/ia/ http://www.uni-stuttgart.de/organisation/faculties/ 2. The Office of International Affairs The Office of International Affairs is responsible for international relations and coordinates the programmes that the Universität Stuttgart has with partner institutions throughout the world. In addition, it serves as a centre for advising international students on general questions and problems affecting study and life in Stuttgart as well as being the first place for students to go who wish to study abroad. Should you have any questions related to your specific study programme and require academic counselling, please consult your academic advisor. His or her address is available at the Office of International Affairs. The Office of International Affairs also organises an Orientation Seminar (see page 9) as well as short excursions to places of interest in the area around Stuttgart. Once a month, the Office of International Affairs organises an International „Stammtisch“ where visiting students and any German students who may be interested can meet. The contact person for visiting students is: Ms. Gertrud Burger Office of International Affairs Geschwister-Scholl-Str. 24 70174 Stuttgart, Germany Information Package 6 Office of International Affairs General Information Phone ++49 711-121-2276 Fax ++49 711-121-4104 e-mail: incoming.visiting@ia.uni-stuttgart.de The Academic Calendar The academic year is divided into two semesters: the Winter Semester (WS) from October to March and the Summer Semester (SS) from April to September. Each semester covers a period of approximately 15 weeks during which classes take place called the Vorlesungszeit and a period when there are usually no classes called the vorlesungsfreie Zeit. In the WS, the Vorlesungszeit is from the of middle of October to the middle of February and in the SS from the middle of April to the middle of July. Please note that examinations and block courses very often take place during the vorlesungsfreie Zeit. During the month of August no exams are taken at all. Application Information (academic prerequisites, deadlines, registration, etc.) Before you can study at the Universität Stuttgart you have to take the following steps: submit an application to study at the Universität Stuttgart at least three months prior to the date you wish to begin your studies (see below for deadlines) register at the Universität Stuttgart on arrival in Stuttgart Academic Prerequisites Proficiency in German: Virtually all courses at the Universität Stuttgart are held in German. For this reason, you will be expected to have had at least 800 hours of course work in German. We expect that visiting students whose German proficiency corresponds to less than 800 hours of German participate in our German Intensive Course (see page 9). If you would like to receive a certificate about your German proficiency you may take a German examination. This examination is called the DSH (Deutschsprachprüfung zur Hochschulzulassung). It can be taken at the Universität Stuttgart at around the end of September or March. Academic Performance: In order to participate in our exchange programmes visiting students must have grades of C or above. Information Package 7 Office of International Affairs General Information Application Documents and Deadlines An application form Antrag auf Zulassung zum Studium The form is either available - at The Office of International Affairs of your home university or - from your SOCRATES Student Advisor. - You can also obtain a copy by contacting the Office of International Affairs at the Universität Stuttgart (email: incoming@ia.uni-stuttgart.de) or - you can also download the form as pdf file, see: http://www.uni-stuttgart.de/ia/ You must attach the following documents (certified copies, if possible): A Transcript of Courses from your current university Proof of your German proficiency (see above and page 9) 1 Passport photo SOCRATES students: a confirmation from your home university that you are a SOCRATES student. Deadlines: 15 July Submission of the original application papers with the necessary documents if you wish to begin your studies in Stuttgart in the Winter Semester. 15 January Submission of the original application papers with the necessary documents if you wish to begin your studies in Stuttgart in the Summer Semester. SOCRATES-Students must submit their application to the SOCRATES Student Advisors at the individual institutes. All other visiting students submit their complete application to Ms. Gertrud Burger at the Office of International Affairs. Letter of Admission - Zulassungsbescheid If you are accepted by the Universität Stuttgart you will receive the following documents during the first two weeks in August (applications for WS) or the first two weeks in March (applications for SS): A Letter of Admission as well as a transfer form for the payment of the Student Services fee (Studentenwerksbeitrag) which amounts to DM 60 (at the time of print). This fee has to be paid by all students and is charged each semester. It is a general fee towards the cost of running the cafeterias and dormitories and offers a number of other consulting services for students free of charge. Do not pay the 'Studentenwerksbeitrag' until you have arrived in Stuttgart. Information Package 8 Office of International Affairs General Information Registration You must register in person once you arrive in Stuttgart. The necessary steps for registration are explained in the Welcome-Guide which you can get on arrival from the Office of International Affairs. Please do not forget to bring your Letter of Admission (Zulassungsbescheid). It is required for registration. The German Intensive Course This German intensive course is designed specifically for the needs of visiting students within partnership programmes and is taught by the staff of the Intercultural Centre of the Universität Stuttgart. The course starts at the beginning of September (Winter Semester) or March (Summer Semester) and runs for about five weeks. Participants, however, are expected to have some proficiency in German corresponding to 200 hours or two semesters of coursework in German at a university. The course takes place from Monday to Friday from 8.30 a.m. to 1 p.m. and twice a week there are also classes from 2 p.m. to 4 p.m. The objectives of this intensive course are: to achieve proficiency in German at an advanced level corresponding to about 800 hours of German, to improve listening comprehension and active use of German as a scientific language, particularly in respect to the specific subject of the participant, to acquire the learning techniques and communicative competence needed to study successfully at a German university. Application deadline: 15 July for the Winter Semester and 15 January for Summer Semester. Application forms are available from Ms. Gertrud Burger at the Office for International Affairs, e-mail: incoming.visiting@ia.uni-stuttgart.de. The Orientation Seminar The Orientation Seminar immediately follows the German Intensive Course and it takes place the week previous to the beginning of the lecture period. The three-day seminar offers intercultural and regional information as well as a general introduction to studying at the Universität Stuttgart and also includes specialised academic counselling. The seminar concludes with a one-day excursion. All participants have to make a contribution towards the cost. At present this is DM 20. Registration deadline: 15 September for the Winter Semester and 15 March for the Summer Semester. Registration forms are available from Ms. Gertrud Burger, e-mail: incoming.visiting@ia.uni-stuttgart.de. Information Package 9 Office of International Affairs General Information The Structure of Studies A degree course is divided into the Stage 1 Studies („Grundstudium“) and the Stage 2 Studies („Hauptstudium“). Visiting students within partnership programs may take courses in either stage. The Stage 1 Studies last at least 4 semesters and give a general introduction into the chosen field of study. The Stage 1 Studies are completed with a pre-diploma examination („Vordiplom“) in the engineering sciences or with an intermediate examination („Zwischenprüfung“) in the social sciences and humanities respectively before the Stage 2 Studies. In contrast to the Anglo-American system the successfully completed Stage 1 Studies do not constitute an academic degree or professional qualification. During the Stage 2 Studies students continue their studies and extend their knowledge in a more specialised way. At the end of the Stage 2 Studies students have to write a project work (Diplomarbeit) in the engineering sciences or a final thesis (Magisterarbeit) in the humanities. After having successfully passed the final examination students obtain their degree (a Diplom degree in the engineering sciences, a Magister Artium degree in the humanities) which enables them to start their professional career. Which courses must I take? In comparison to the Anglo-American university system, students at German universities generally have more freedom in the selection of the courses they choose to take and when they take them. However, this does vary from subject to subject. Many of the courses in the natural sciences and engineering are obligatory whereas students studying in the humanities and social sciences generally choose the courses they want to take on a more individual basis. One further difference is the time for selecting courses. This does not normally take place at the end of the previous semester but during the first two weeks of the semester itself. This, and the freedom of choice is often confusing for international students. For this reason, the individual faculties offer comprehensive information seminars at the beginning of each semester to help students in their choice. Additional information is given during the Orientation Seminar (see page 9) and can be found in the Welcome Guide. Should you still have difficulties do not hesitate to contact the Office of International Affairs. What kind of courses are offered? The Universität Stuttgart distinguishes between the following types of courses: Lecture held by an instructor in front of a large group of students Exercises the subject matter is reviewed again and deepened in smaller groups; often exercises accompany lectures Information Package 10 Office of International Affairs General Information Seminars student active participation is very important; students present papers on a given topic followed by discussion Practical courses common in the natural sciences and engineering and usually involving experiments in a laboratory As a rule, a class involves two credit hours. One credit hour, Semesterwochenstunde (SWS), corresponds to 45 minutes in the classroom over the whole semester. Generally all courses are taught in German. Transferring Credits There are two possibilities for visiting students to receive credit for work done in Stuttgart: Visiting students can participate in regular courses and take the final written or oral exam in each course in order to be awarded a proof of academic achievement or Schein. In addition to receiving a Schein for successfully completing a written exam or Klausur, it can be awarded for a project paper or Hausarbeit (an essay on a specific topic of between 10 and 20 pages in length) or for an assignment and oral presentation or Referat (a paper presented on a given topic usually as part of a seminar). Grades range from 1 (very good) to 4 (sufficient). If a student receives a grade below 4, then the course has been failed and needs to be repeated. In some courses grades are not given. Students under the SOCRATES exchange-scheme will receive their credits according to the ECTS-agreement (European Credit Transfer System), which is to be discussed between the student and the home and host supervisors. Some advanced visiting students may wish to work on an independent project supervised by a professor. Such independent study corresponds closely to a Studienarbeit, which is required in engineering and many of the natural sciences. Students wishing to do this type of independent study need to find a professor at the Universität Stuttgart who is willing to supervise such a project work. The question of credit transfer to the home universities should also be clarified in advance. The subject advisors or Fachstudienberater/in can assist in finding a supervisor. Their addresses can be found in WWW under http://www.uni-stuttgart.de/studium/beratung/fachberatung.html or from The Office of International Affairs (address see page 6). Please clarify the question of credit transfer with your home universities prior to coming to Stuttgart and make sure that you maintain contact with your home supervisor during your stay here. This is possible via e-mail. Information Package 11 Office of International Affairs 3. General Information Other Facilities at the Universität Stuttgart Libraries There are two university libraries, one on the City Centre Campus and one on the Vaihingen Campus. Students need a library ticket in order to be able to borrow books from the library. This can be obtained at one of the university libraries. Please note that many of the faculties and institutes have their own libraries, too. Computer Centre and E-mail The computer centre of the Universität Stuttgart (RUS) provides a number of terminals for student use. Demand is extremely high so students must be prepared to wait. Should you wish to open an e-mail account, you can do so at the Computer Advising Centre RUSBenutzerberatung on presentation of your registration number (handed to you at registration). Sports Activities The Institute of Sports Science offers a whole range of sporting activities each semester. They are generally free and are frequently organised by students. These can be such regular events as volleyball, hockey and climbing or special excursions such as skiing in winter or sailing in summer. A comprehensive programme is provided at the beginning of each semester and a copy can be obtained at The Office of International Affairs. Meals Students must provide for their own meals. This can be done inexpensively by eating in the Student Union cafeteria or Mensa. In addition to the Mensa on the City Centre Campus and in Vaihingen, there are a number of student cafeterias. The Mensa is open for lunch five days a week. There is always a choice of meal which costs between DM 3 and DM 5. The cafeterias are normally open weekdays between 9 a.m. and 5 p.m. and offer drinks and small snacks. Information Package 12 Office of International Affairs 4. General Information General Information of Practical Use Residence Permits and Visa Regulations SOCRATES-Students from EU-countries and visiting students who are citizens of the USA: Visiting students who are either EU-citizens or citizens of the USA can enter Germany with their passports and apply for their residence permit Aufenthaltsbewilligung at the foreign registration office of the City of Stuttgart Ausländerbehörde after arrival. Since Germany has registration laws, all persons must register at the general registration office Meldebehörde of the city where they are living within seven days of arrival. The following documents must be presented to the Ausländerbehörde and the Meldebehörde and should therefore be brought with you from home: - passport - proof of sufficient financial resources (at present approx. DM 900 per month). This can be a savings book, confirmation from the bank on the credit balance available, a bank statement, proof of stipend or scholarship, a statement from parents with either a notarised signature of the parents or a copy of their passports - two passport photos Visiting students who are citizens of Australia, Canada and non EU-countries: These visiting students must apply for a prospective student visa (Studienbewerbervisum or Studentenvisum) at the German Embassy or a German Consulate in their home country prior to departure. This should be done as early as possible because the processing time for such visas can take very long i.e. up to nine months. The following documents are required from the foreign registration office Ausländerbehörde and from the general registration office Meldebehörde and should be brought with you from home: - prospective student visa (Studienbewerbervisum or Studentenvisum) proof of sufficient financial resources (at present approx. DM 900 per month). This can be a savings book, confirmation from the bank on the credit balance available, a bank statement, proof of stipend or scholarship, a statement from parents with either a notarised signature of the parents or a copy of their passports - two passport photos Costs of Living Expenses In general, students will need about DM 1000/ month. This will cover the following: rent approx. health insurance approx. monthly ticket for public transport approx. Information Package DM 300 to 450 (without meals) DM 95 DM 70 13 Office of International Affairs food other incidentals General Information approx. approx. DM 400 DM 100 Dormitory Accommodation The Office of International Affairs can provide a room in one of the dormitories for all of the visiting students who are admitted to the Universität Stuttgart. SOCRATES students apply for a room by sending the form Application for Student Housing to their relevant SOCRATES Student Advisor not later than 3 months prior to coming to Stuttgart. All other visiting students send this form to Ms. Gertrud Burger at the Office of International Affairs. Most of the dormitories are located on the Campus in Stuttgart-Vaihingen and on the campus of the Pädagogische Hochschule (teachers training college) in Ludwigsburg and they are mixed. All dormitories can be easily reached within 20 min. from the city campus by S-Bahn (commuter train). The rooms are equipped with table, chair, bed, wardrobe/ closet, bookshelf and a washbasin. There is a common kitchen for all the members of an apartment. You must bring your own dishes with you or buy them in Germany. There are also toilets and showers on each floor. Please note: Bed-linen and coverlets are not provided! However, it is best to buy them once you are here. The rent for a room in a dormitory is DM 300 to 450 per month. It has to be paid by standing order (all further information about this you will receive at the Office of International Affairs after your arrival). Rooms can only be rented for a whole month. All students living in the dormitories have to pay a deposit of DM 500. This has to be paid into a bank on the forms provided before you will be allowed to move in. You will receive the necessary forms as part of your Housing Information Package which will be sent to the address you have given in your application form some four weeks prior to the time when you move in. Remember that you can only move into your room on Mondays to Fridays (unless it is a holiday). Should you wish to come to Stuttgart before your contract for your room begins or at the weekend, you can stay overnight at one of the Guest Houses for Young People or at the Youth Hostel (see next paragraph for further information). Temporary Accommodation for Young People Should you come to Stuttgart at a time when you can not move into your dormitory room immediately, you can stay one or two nights at the youth hostel or at one of the guest houses for young people run by the Jugendsozialwerk. The address of the Youth Hostel in Stuttgart is: Jugendherberge Stuttgart Haussmannstr. 27 Phone: ++49 711-24 15 83 Charge for members is about DM 25 and about DM 30 for others. The price is for a bed in a shared room with a number of others and includes breakfast. It is not possible to make Information Package 14 Office of International Affairs General Information telephone reservations. The Youth Hostel is very nice and very conveniently located (approx. 10 min. on foot from the Central Bus and Railway Stations). You can reach the Youth Hostel by taking the streetcar from within the Central Railway Station or Hauptbahnhof at the stop called Arnulf-Klett-Platz (follow the sign with a white U on a blue background). Buy a ticket at one of the orange ticket machines: 1 zone. Take the streetcar U15 travelling in the direction of Heumaden-Sillenbuch. Get off at the stop marked Eugensplatz. Walk down Kernerstrasse (downhill) and follow the youth hostel sign. The address of the Guest House run by the Jugendsozialwerk is: Jugendsozialwerk Richard-Wagner-Str. 2, phone: ++49 711-24 11 32 fax: ++49 711-23 61 10 The price of a single or double room lies between DM 30,-- and DM 45,-- with breakfast. Rooms can be reserved in advance. However, the Guest House is situated somewhat outside of the city centre. You can reach the Guest House by taking the streetcar from within the Hauptbahnhof at the stop called Arnulf-Klett-Platz (follow the sign with a white U on a blue background). Buy a ticket at one of the orange ticket machines: 1 zone. Take the streetcar U15 travelling in the direction of Heumaden-Sillenbuch. Get off at the stop marked Bubenbad. On your right you will find the Richard-Wagner-Straße and the first house on the right hand side is the Guest House of the Jugendsozialwerk. Health Insurance At registration, all students must demonstrate proof of health insurance as prescribed by German law. Those students who fulfil one of the following conditions can obtain the necessary proof at one of the local health insurance companies (the Office of International Affairs will provide you with the addresses upon your arrival). EU-Citizens: EU-Citizens are required to present Form E109 or Form E111 which they can obtain from their home health insurance company. Upon presentation of this form at one of the local health insurance companies the holder will be presented a Certificate of Sickness Insurance called a Krankenschein. This certificate must be presented to the doctor, dentist or at a hospital. If you fail to do so you will be expected to pay in cash. At the same time, you will be given a Krankenversicherungsnachweis which you will need for registration at the university. Further information can be found in the Welcome-Guide which either your SOCRATES Student Advisor will give you on arrival in Stuttgart or which you will receive from Ms. Burger at the Office of International Affairs. Visiting Students from the USA, Canada, Australia and other non-EU-Citizens: The local health insurance companies in Stuttgart can exempt you from the compulsory insurance providing you can demonstrate that you have equivalent coverage from a health Information Package 15 Office of International Affairs General Information insurance in your own country. However, to avoid financial difficulties because you will be expected to pay cash straight away and then claim from your own insurance company yourself, we urgently recommend that you obtain a low-priced health insurance for students in Stuttgart. It costs about DM 95 per month and covers medical treatment by a doctor (inclusively dentist) as well as hospital treatment. This insurance also has the advantage that you do not have to pay for treatment in advance because the insurance company settles directly with the doctor. Further information can be found in the Welcome-Guide which you will receive from Ms. Burger at the Office of International Affairs or from your SOCRATES Student Advisor. The health insurance for students takes effect at the beginning of the Winter Semester (1 October) or the Summer Semester (1 April). Therefore we recommend that students participating in the German Intensive Course purchase a travel sickness insurance in their home country for the month of September or March respectively. Medical Care German universities do not provide medical service on campus. Like all other persons with health insurance, students have a free choice among those doctors who have been registered by the health insurance company. As mentioned under the paragraph Health Insurance, health insurance companies that offer sickness insurance for students settle directly with the doctor, dentist or hospital. If a student has a psychological problem, it is possible to receive assistance from the Psychological Consulting Service of the Student Union Psychologische Beratungsdienst des Studentenwerks free of charge. The address can be found in the Welcome-Guide or can be obtained from the Office of International Affairs. Public Transport Public transport in the Stuttgart region is very good so it is not essential to have a car. There is an extensive underground system called the S-Bahn, a streetcar system, the UBahn, and buses. The airport is about thirty minutes away from the Hauptbahnhof by SBahn. It takes about ten minutes on foot to reach the City Centre Campus from the Hauptbahnhof or the stop called Stadtmitte. The S-Bahn stops in the middle of the Vaihingen Campus. This stop is called Universität. It is ten minutes away from the Hauptbahnhof on the S1 heading for Herrenberg or the S2 and S3 heading for Vaihingen or Flughafen. Students who live on the campus in Ludwigsburg take the S4 heading for Marbach and get off at the station Favoritepark. The S-Bahn ride takes 20 minutes and requires a ticket with three zones. The dormitories in Ludwigsburg are five minutes away from the S-Bahn station Favoritepark. Students who have lectures on both the City Centre Campus and the one in Vaihingen should purchase a Semester Ticket, Semesterfahrkarte, which is valid for the whole semester and costs about DM 290 (two zones). Further information is available at The Office of International Affairs. Information Package 16 Office of International Affairs General Information Banking Cash is still frequently used in Germany. Credit cards (Mastercard, Visa etc.) are not accepted everywhere. You should always check before you order your meal etc., and make sure that you have sufficient cash with you. All visiting students need a bank account because rent for a dormitory room can only be paid for by standing order. The SOCRATES Student Advisor or The Office of International Affairs can assist you in choosing a suitable bank. Tips can also be found in the Welcome Guide. Telephoning The code for phoning Stuttgart from abroad is as follows: ++49-711-phone number (++ = the dialling code for a foreign country; 49 = the area code for Germany; 711 = the local dialling code, e.g. Stuttgart) If you are phoning within Germany add a 0 to the local dialling code e.g. Stuttgart would be: 0711 + phone number If you are dialling a number in Stuttgart from within Stuttgart you do not need the local area code. To phone from a public telephone box you will need DM 0,20 (2 x 10 Pfennige). Telephone Cards are available priced DM 12 or DM 50. There is a telephone on each floor in the dormitory. You can also have your own telephone in your dormitory room. We recommend that you buy a telephone yourself at a cost of about DM 50 depending upon the model chosen. The TELEKOM charges around DM 30 per month for the connection. This is in addition to the charges for the individual calls. The City of Stuttgart Stuttgart, which is the state capital of Baden-Württemberg, has a population of about 560.000. Stuttgart lies in a basin. The lowest point is the River Neckar, which is about 200 metres above sea-level, and the highest is at Stuttgart-Vaihingen at approx. 550 metres. Stuttgart is the cultural centre of the State of Baden-Württemberg with a wealth of theatres and concert halls. It is also the home of the world-famous ballet and there are museums and art-galleries as well as academies of music and art. "Miss Saigon" is being performed in one of the music halls and “Beauty and the Beast” in the other. Every year thousands come from far and near to enjoy the Cannstatter Volksfest, a public festival with a huge amusement park which takes place at the end of September on the common called the Cannstatter Wasen. In the course of time this festival has become second only to the Oktoberfest in Munich. Stuttgart is also one of the largest agriculture, fruit and viticulture centres in the Federal Republic. Many of the most renown companies like Mercedes-Benz and Bosch have factories here. In addition, there are numerous smaller companies involved in the production of machine tools, textiles and clothes, precision instruments, food and luxury items. There are also companies that specialise in woodworking, leather processing and making shoes or musical instruments as well as a number of large breweries. There is Information Package 17 Office of International Affairs General Information also a small paper and chemical industry. Over 300 publishing houses and a highly developed graphic industry has given Stuttgart the reputation of being Germany's "Book Town" No 1. Climate The climate in Stuttgart is moderate and the average annual temperature is 10 °C. The relatively warm summers and mild winters are characteristic of the Stuttgart climate. However, it is quite possible that the temperature in winter will go far below freezing-point which makes it necessary to have winter clothes as well as rainproof clothing. How to get to Stuttgart-Vaihingen By train: You will arrive at the Central Railway Station in Stuttgart called Hauptbahnhof. Buy a ticket at one of the orange ticket machines: 2 zones (about DM 3,50). Go to the S-Bahn station which is on the bottom floor. Take the S-Bahn S1 travelling in the direction of Herrenberg or the S2 or S3 travelling in the direction of Vaihingen or Flughafen. Get off at the stop marked Universität. Take the exit Universitätszentrum. See the map of Vaihingen for further assistance. By plane: In the Arrival Hall at Stuttgart Airport you will see the sign directing you to the S-Bahn. It is a white S on a green background. Buy a ticket at one of the orange ticket machines: 2 zones (DM 3,30). Go to the S-Bahn station which is on the bottom floor. Take the S-Bahn S2 going in the direction of Schorndorf or the S3 travelling in the direction of Backnang. Get off at the stop marked Universität. Take the exit Universitätszentrum. See the map of Vaihingen for further assistance. By car: If you are arriving from Munich or Karlsruhe, take the motorway A 8 to Stuttgarter Kreuz. Then, follow the sign to the City Centre Zentrum/Vaihingen via the A 831/B 14 till the exit showing Universität. Turn left at the first traffic light and you are now in the Universitätsstrasse. See the map of Vaihingen for further details. If you are arriving from Zurich/Singen, take the A 81/A 831 till the exit Universität. Turn left at the first traffic light and you are now in the Universitätsstrasse. See the map of Vaihingen for further details. If you are arriving from Mannheim/Heilbronn, take the A 6/A 81 till you reach Autobahndreieck Leonberg. Then take the motorway A 8 in the direction of Munich until you reach the Stuttgarter Kreuz. Follow the sign to the City Centre Zentrum/Vaihingen via the A 831/B 14 till the exit showing Universität. Turn left at the first traffic light and you are now in the Universitätsstrasse. See the map of Vaihingen for further details. Information Package 18 Office of International Affairs General Information How to get to the dormitories in Ludwigsburg By train: You will arrive at the Central Railway Station in Stuttgart called Hauptbahnhof. Buy a ticket at one of the orange ticket machines: 3 zones (about DM 5). Go to the S-Bahn station which is on the bottom floor. Take the S-Bahn S4 travelling in the direction of Marbach. Get off at the stop called Favoritepark. The dormitories are 5 minutes away from this S-Bahn stop on the left hand side of the track in the travelling direction of the train. By car: If you are arriving from Munich or Karlsruhe, take the motorway A 8 till you reach the Autobahndreieck Leonberg. Then take the A 6/A 81 (direction Heilbronn) till the exit showing Ludwigsburg Nord. If you are arriving from Mannheim/Heilbronn, take the A 6/A 81 till you reach the exit showing Ludwigsburg Nord. Turn right (direction Ludwigsburg) at the first traffic light and you are now on the B 27. Follow the B 27 for about 4 km till you pass under a bridge. Then turn left into the Reutteallee (follow the sign "Hochschulen"). See the map of Ludwigsburg for further details. How to get to the Office of International Affairs By train: You will arrive at the Central Railway Station in Stuttgart called Hauptbahnhof. It takes 5 minutes to walk from the station to The Office of International Affairs. Take the Lautenschlagerstraße, turn right into the Kronenstraße which is crossed by the Friedrichstraße. Take the pedestrian crossing and turn left into the Friedrichstraße. After 50 m turn right into the Geschwister-Scholl-Straße. The entrance to No. 24 is on the right side opposite a furniture store called „Interio“. You will find The Office of International Affairs on 1st floor. By plane: In the Arrival Hall at Stuttgart Airport you will see the sign directing you to the S-Bahn. It is a white S on a green background. Buy a ticket at one of the orange ticket machines: 2 zones (about DM 3,50). Go to the S-Bahn station which is on the bottom floor. Take any S-Bahn (S2 or the S3). Get off at the stop marked Hauptbahnhof. Take the exit Kronenstraße. See map for further details. The entrance to the Geschwister-Scholl-Str. No. 24 is on the right side opposite a furniture store called „Interio“. You will find The Office of International Affairs on 1st floor. By car: If you are arriving from Munich or Karlsruhe, take the motorway A 8 to Stuttgarter Kreuz. Then, follow the sign to the City Centre Zentrum via the A 831/B 14. Follow the B 14 until downtown Stuttgart and then follow the sign to the Hauptbahnhof (central railway station). See map for further details. If you are arriving from Zurich/Singen, take the A 81/A 831 which changes into B 14. Follow the B 14 until downtown Stuttgart and then follow the sign to the Hauptbahnhof (central railway station). See map for further details. Information Package 19 Office of International Affairs General Information If you are arriving from Mannheim/Heilbronn, take the motorway A 6/A 81 till the exit Stuttgart-Zuffenhausen. Follow the sign to the City Centre Zentrum via B 10/B 27. About 200 m after you have passed the Hauptbahnhof (central railway station on the left) in downtown Stuttgart turn right into Geschwister-Scholl-Straße. What you need to think of prior to coming to Stuttgart The following papers and documents have to be brought with you to Germany: Letter of Admission (Zulassungsbescheid) including a bank transaction form for the Studentenwerk fee of DM 60. Housing information package including a bank form for the deposit of DM 500, see page 14 Your passport 3 passport photos, see pages 8 and 13 Visa: Citizens of a non EU-country and non US citizens such as Australia, Canada, etc. need a visa. Citizens of the USA and the EU do NOT need a visa to enter the country, see page 13 Proof of sufficient financial resources, see page 13, e.g. bank statement (a form for a bank statement is available at the Office of International Affairs, e-mail: incoming.visiting@ia.uni-stuttgart.de Students FROM EU-COUNTRIES ONLY: form E 109 or E 111 (health insurance), see page 15 Students FROM NON-EU-COUNTRIES ONLY coming in September or March: travel sickness insurance, see page 15 Items of practical use: If you arrive in Stuttgart on a Saturday/ Sunday please remember that you will not be able to move into your dorm room. We suggest you stay at the youth hostel or at a guest house, see page 14. For room reservations at a guest house in advance, please ask Ms. Gertrud Burger at the Office of International Affairs or your SOCRATES Student Advisor. Make sure that you have enough cash available: You will have to pay a deposit for your room of 500 DM (see page 14) and you will need some cash (about 5 DM) for the S-Bahn ticket from the airport to the Vaihingen campus (see page 18). Most ticket machines accept 10 and 20 DM notes. Do not forget to bring your sleeping bag (bed linen is not provided in the student dorms), clothing for rainy and cold weather (climate see page 18) and any medicine you might regularly need to take. For all electrical appliances you will need a 220 volt adapter. Information Package 20 Office of International Affairs General Information Welcome to Stuttgart and we hope that you have a very pleasant and rewarding stay. Your Office of International Affairs Information Package 21 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration B. Information for Students in Business Administration 1. Business Administration with a Technical Orientation This specific field of study has been taught ever since it was first established in the Winter Semester 1974/75. The Universität Stuttgart is the only university in all of Germany offering this unique course of studies with additional training in technical subjects. Students of any level do have to take classes during their Stage 1 Studies (‘Grundstudium’) and Stage 2 Studies (‘Hauptstudium’)1 to enlarge their knowledge with basic features from technical subjects. Experience has shown that this additional qualification is largely sought for by companies intending to employ business school graduates. The Management School has been able to successfully establish courses in connection with some of the most famous Stuttgart institutes of the School of Engineering. Besides the subjects of Business Administration, Economics and Jurisprudence, Stage 1 students do have to take classes with the School of Engineering which are an important part of their study design. As Stage 2 students they do have to choose one technical subject as their major out of a group of nine possible subjects (Building and Construction, Electrical Engineering, Energy Engineering, Production Engineering, Informatics, Vehicle Engineering, Logistics, Process Engineering, Transport and Communications). Not only companies have realised the immense value of these interdisciplinary studies but students have, too. The numbers for registration at the School of Management have been steadily increasing. 1200 students make the “technically oriented" Business Administration Studies one of the most important ones at Stuttgart University together with Aerospace Engineering and Computer Science ranked fifth just behind Mechanical Engineering, Architecture, Electrical Engineering as well as Building and Construction Engineering. Each Winter Semester approximately 200 beginners are registered. The departments who are presently teaching Business Administration are listed below: Department I: Business Administration and Human Resource Management (Prof. Dr. K.-F. Ackermann) Department II: Business Administration and Organisational Design (Prof. Dr. M. Reiß) Department III: Business Administration and Finance (n.n.) Department IV: Business Administration, Strategic Management and Corporate Planning (Prof. Dr. E. Zahn) Department V: Business Administration and Management Accounting (Prof. Dr. P. Horváth) Department VI: Business Administration, Business-to-Business Marketing and Purchasing (Prof. Dr. U. Arnold) 1 See page 10/ Part A Information Package 22 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration Department VII: Business Administration and Applied Business Informatics (Prof. Dr. H. Heilmann) Department VIII: Business Administration and R&D Management (Prof. Dr. H.D. Bürgel) Additionally, academic and non-academic lectures, seminars and courses are offered together with study trips to companies and an immense amount of papers, Ph.D. theses and research projects contribute highly to a fundamentally well based and very profound education. 2. ECTS-Coordinators For all sorts of questions or problems concerning the field of study as such or any part of its content you may contact any of the two coordinators at the Institute for Management Studies who will be happy to help you out : Dipl.-Kfm. Claus Herbst Dipl.-Kffr. Silke Münter Universität Stuttgart Universität Stuttgart BWI, Abt. IV BWI, Abt. VI Keplerstr. 17 Keplerstr. 17 70174 Stuttgart 70174 Stuttgart Phone: +49 711 121 3471 Phone: +49 711 121 3167 Fax: +49 711 121 3191 Fax: +49 711 121 3131 e-mail: claus.herbst@po.uni-stuttgart.de e-mail: silke.muenter@po.uni-stuttgart.de Web-pages: General information about the Universität Stuttgart: http://www.uni-stuttgart.de/ Information about the Business School: http://www.uni-stuttgart.de/bwi/ Information for exchange students: Erasmus at: http://gandalf.bwi.uni-stuttgart.de/ 3. Information for all ERASMUS Exchange Students at the Business School The ERASMUS programme supports the exchange of students throughout Europe on a basis of acknowledging academic work that has been credited at the foreign/ exchange university for their study at the home university. However, German universities differ quite a lot from the system and courses you are used to at your home university. Therefore, it is absolutely necessary that you try to get all the information you need mostly by yourself. This means, for example, that you select the courses you will have to take according to your home university from the large choice that we provide and that you will have to figure out your own time-table. Which course you would like to choose is completely up to you. You may choose those courses which you Information Package 23 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration like most. There are separate agreements between your individual home universities and the Universität Stuttgart on the number of courses and credits that you need. For more information on what you need please ask your own university/ advisor before your stay in Stuttgart. While planning a year abroad or during your stay at a university abroad a lot of questions or problems may arise which other students have also experienced and solved successfully. Therefore, each ERASMUS exchange student in Stuttgart will be given the name and address of a student from the Universität Stuttgart who will then be able to assist you whenever necessary to make your stay and life easier for you. 4. Information about the European Credit Transfer System at the Business School After your arrival in Stuttgart you will be provided with the courses you can choose and we will also assist you with arranging your time-table successfully. We would, however, be very pleased if you figured out an agreement with your home university on what you should take part in, how many credits you need and so on before arriving here (Learning Agreement). The European Credit Transfer System (ECTS) will be the basis for transferring our marks into marks and credits that you will need. We will differentiate between the amount of work on the one side and the key to transfer the credits on the other. ECTS defines the workload of a German student with 60 credits per year. You will find the detailed correlation between the individual course and the credits you will be given in PART C. Our crediting system usually follows the modes listed below: (SWS = weekly hours per semester) 3.5 credits for 2 SWS Lecture (L) with an additional exam 7.5 credits for 2 SWS Exercise (E) or Seminar (S) You may find the table helpful for the credit transfer and the grades in your system German Grades 1,0 1,3 1,7 2,0 2,3 2,7 3,0 3,3 3,7 4,0 4,0 5,0 5,0 Information Package ECTSGrade A A B B B C C C D D E FX F French Grades >18 17,9 - 17 16,9 - 16 15,9 - 15 14,9 - 14 13,9 - 13 12,9 - 12 11,9 - 11 10,9 - 10 9,9 - 9 8,9 - 8 <8 <8 British Grades >73 % 73 - 70 % 69 - 68 % 67 - 65 % 64 - 62 % 61 - 60 % 59 - 58 % 57 - 56 % 55 - 51 % 50 - 47 % 46 - 40 % 39 - 35 % < 35 % Finnish Grades 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 24 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 5. Information for EMBS Students The European Master of Business Sciences (EMBS) programme is a carefully designed scheme of study leading to a qualification of Master's standard. An integral part of the programme is a study year abroad. The scheme is collectively administered by a consortium of European universities and business schools and aims to meet the requirements for the academic education of business and management graduates in Europe. Close cooperation between the institutions involved and a jointly agreed programme structure provides a programme of academic excellence, leading to full competence in another community language and an in-depth understanding of the business environment and culture of other European countries. Unlike MBA programmes, the EMBS scheme is not aimed at graduates in other disciplines or practising managers, but at high calibre students who have completed the initial part of a business and management degree scheme at one of the participating institutions. There is ample evidence that the specific skills, insights and experience which the EMBS programme provides are much in demand in the European employment markets. Successful completion of the scheme also offers the possibility of studying for higher degrees, including doctoral programmes. The programme was established in the 1980's, and the first EMBS certificates were awarded in 1992. The number of places available is strictly limited and there is very strong competition for them. The following institutions are members of the EMBS consortium: Universität Wien, Austria Ecole Supérieure de Commerce de Brest, France Ecole Supérieure de Commerce de Clermont, France Ecole Supérieure de Commerce Le Havre-Caen, France Institut d'Administration des Entreprises, Université de Lyon, France Ecole Supérieure de Commerce de Montpellier, France Institut d'Etudes Commerciales Supérieures de Strasbourg, France Otto-Friedrich-Universität Bamberg, Germany Universität Mannheim, Germany Universität Regensburg, Germany Universität Stuttgart, Germany Universidad de Alcalá, Spain Universidad de Cordoba, Spain Universidad de Granada, Spain Aston University, Birmingham, UK The University of Birmingham, UK Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK University of Reading, UK University of Wales Swansea, UK Information Package 25 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration Structure of the Scheme The qualifying stage of the scheme is spent at what is referred to as a student's -'home institution'. This is the university or business school at which a candidate is provided with the basic grounding in business related subjects. At the Austrian and German universities this stage is completed with the 'Vordiplom'/'Erste Diplomprüfung' examinations. At French business schools it encompasses the 'Classes Préparatoires' and the first year of study, while at UK universities it corresponds to the first two years of a Bachelor's degree scheme. Only the top 30% of students who have successfully completed this stage are eligible to be considered as candidates for the second stage, the EMBS programme as such. This includes a mandatory study period of at least one academic year abroad. EMBS candidates are required to complete a total of 7 modules. Each module amounts to the workload of approximately a third of an academic year - i.e. represents 20 ECTS credits - and the courses involved are structured so as to allow a candidate to complete a module within a single academic year. A module in European Affairs and a project paper are compulsory for all candidates. In addition, candidates select 5 subject modules from the following 9 options available: - Accountancy Business Informatics Economics Finance General and Strategic Management - Human Resources Management Marketing Production Quantitative Methods The descriptions of the subject modules available are listed below. Also included are details of the minimum requirements for completing a module. Codification of Course Title Courses Type SWS Credits 1. Accountancy H 5 W S 05 a Management Oriented Accounting L 2 3,5 H 6 S S 05 b Coordination of Planning L 1 1,75 H 6 S S 05 c Information Supply Management L 1 1,75 H 6 S S 05 d Management Accounting: Exercise E 2 7,5 H 7 W S 05 e Budgeting L 2 3,5 H 7 W S 05 f Management Accounting Seminar S 2 7,5 H 8 S S 05 g Internal Auditing L 1 1,75 H 8 S S 05 h External Auditing L 2 3,5 H 8 S S 05 i Market-oriented Cost-Management L 1 1,75 Information Package 26 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 2. Business Informatics H 5 W S 07 a Structures of Hardware, Software and Networks L+E 2+2 6,5 H 6 S S 07 b Information and Communication Systems Design I L+E 2+2 3,5 H 6 S S 07 e Project Management L 2 3,5 H 7 W S 07 c Information and Communication Systems Design II L 2 3,5 H 7 W S 07 d Applied Business Informatics Seminar S 2 7,5 H 7 W S 07 f Information Management L 2 3,5 H 7 W S 07 e Project Management L 2 7,5 H 8 S S 07 d Applied Business Informatics Seminar S 2 7,5 H 5 W V 09 b Economic Policy II L 2 3,5 H 6 S V 09 c Environmental Policy L 2 3,5 H 6 S V 09 d Economic Systems L 2 3,5 H 6 S V 09 e Regional and Industrial Economics L 2 3,5 H 6 S V 09 f International Economics L 2 3,5 H 6 S V 09 g Seminar in Economic Policy S 2 7,5 H 7 W V 09 h Social Policy L 2 3,5 H 7 W V 09 i Fiscal Policy L 2 3,5 H 7 W V 09 f International Economics L 2 3,5 H 7 W V 09 g Seminar in Economic Policy S 2 7,5 H 5 W V 10 a Research and Innovation L or E 2 or 2 3,5 or7,5 H 6 S V 10 b Diffusion of Innovation L or E 2 or 2 3,5 or7,5 H 6 S V 10 c Seminar in Diffusion of Innovation S 3. Economics 2 7,5 H 7 W V 10 d Technological Integration and Structural Evolution L or E 2 or 2 3,5 or7,5 H 7 W V 10 e Innovation and International Trade L 2 3,5 H 8 S V 10 f Government Research and Technology Policy L 2 3,5 H 8 S V 10 g Technology Assessment L or E 2 or 2 3,5 or7,5 H 4 S V 13 a Basics of Economic Theory (Economic Policy I) L+E 2 7,5 H 5 W V 13 b Business Cycles and Employment L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 H 5 W V 13 c Competition: Theory and Policy L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 H 6 S V 13 d Money and Inflation L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 H 6 S V 13 e Economic Growth and Technical Change L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 H 6 S V 13 f Distribution L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 Information Package 27 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H 7 W V 13 g Environmental and Natural Resource Economics L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 H 7 W V 13 h External Economic Relations L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 H 5 W S 03 a Capital Budgeting L 2 3,5 H 5 W S 03 b International Financial Management L 4 7 H 6 S S 03 c Theory of Investment L 2 3,5 H 5 W S 03 d Exercise on Financial Management E 2 7,5 H 6 S S 03 e Seminar on Financial Management S 2 7,5 H 5 W V 11 a Public Finance L+E 3+1 5,25+3,5 H 6 S V 11 b General Tax Theory L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 H 8 S V 11 c Public Enterprises S 2 7,5 H 5 W A 00 b Management Accounting and Treasury L 3 5,25 H 5 W A 00 a Exercises for General Management Studies E 2 7,5 H 6 S A 00 c Integrated R&D-/Personnel Management L 3 5,25 H 6 S A 00 a Exercises for General Management Studies E 2 7,5 H 8 S A 00 d Decision-Making Processes and Information Systems L 3 5,25 H 7 W A 00 e Seminar in Business Administration S 2 7,5 H 7 W A 00 f Management of Critical Success Factors L 3 5,25 H 8 S A 00 e Seminar on Business Administration S 2 7,5 H 5 W S 02 a Integrated Organisational Design and Human Resource Management L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 H 6 S S 02 b Strategy Oriented Organisational Design L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 H 7 W S 02 c Information Systems for Organisational Design L 2 3,5 H 7 W S 02 d Organisational Seminar S 2 7,5 H 5 W S 04 a Management of Complex Systems L 1 1,75 H 5 W S 04 b Planning Techniques L 1 1,75 H 6 S S 04 c Operative Planning/Management L 2 3,5 H 7 W S 04 d Operations Research E 2 7,5 H 7 W S 04 e Strategic Planning/ Management L 2 3,5 H 7 W S 04 f System Dynamics E 2 7,5 H 7 W S 04 g Project Planning/ Management E 2 7,5 4. Financial Management 5. General and Strategic Management Information Package 28 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H 8 S S 04 h Seminar in Strategic Planning S 2 7,5 H 8 S S 04 i Seminar in System Dynamics S 2 7,5 H 5 W S 08 a R&D-Controlling L 2 3,5 H 6 S S 08 b R&D-Management L 2 3,5 H 6 S S 08 c Training-Course on Basic Instruments of R&DControlling E 2 7,5 H 6 S S 08 d Training-Course on Basic Instruments of R&DProject-Management E 2 7,5 H 7 W S 08 e R&D-Project-Management L 2 3,5 H 7 W S 08 f R&D-Management Seminar S 2 7,5 H 8 S S 08 g Technology- and Innovation-Management L 2 3,5 H 5 W S 01 a Human Resource Planning and Budgeting L 2 3,5 H 5 W S 01 b Motivation & Behaviour Management L 1 1,75 H 5 W S 01 d Human Resource Development and Career Planning L+E 1+1 1,75+ 3,75 H 6 S S 01 e Frame Work of Working-Time Schemes and Attended Time L 2 3,5 H 6 S S 01 f Compensation Management L 2 3,5 H 6 S S 01 g Human Resource Leadership L 1 3,5 H 6 S S 01 h Human Resource Management Case Studies E 2 7,5 H 6 S S 01 d Human Resource Development and Career Planning L 1 1,75 H 6 S S 01 i HR Management Business Game E 2 7,5 H 7 W S 01 j Human Resource Management in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises L 1 1,75 H 7 W S 01 k Human Resource Management Seminar S 2 7,5 H 5 W S 06 a Business-to-Business Marketing L 2 3,5 H 5 W S 06 b Marketing Practice E 2 7,5 H 6 S S 06 c Industrial Purchasing L 2 3,5 H 6 S S 06 d International Marketing L 2 3,5 H 6 S S 06 e Marketing Practice E 2 7,5 H 7 W S 06 f Marketing Research L 2 3,5 H 7 W S 06 g Marketing Seminar S 2 7,5 6. Human Resource Management 7. Marketing Information Package 29 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 8. Production H 5 W T 14 a Human Factors I L 2 3,5 H 5 W T 14 b Technology Management L 2 3,5 H 5 W T 14 c Simultaneous Engineering and Project Management L 2 3,5 H 5 W T 14 d Basics of Machine Tools L 4 7 H 6 S T 14 f Industrial Management I L+E 2+1 3,5+3,5 H 6 S T 14 g Factory Planning I L 2 3,5 H 6 S T 14 h Human Factors II L 2 3,5 H 6 S T 14 i Technology Assessment L 2 3,5 H 7 W T 14 j Factory Planning II L 2 3,5 H 7 W T 14 k Industrial Management II L+E 2+1 3,5+3,5 H 7 W S 04 d System Dynamics E 2 7,5 H 7 W S 04 d Operations Research E 2 7,5 H 7 W T 15 m Simultaneous Engineering L+E 3+1 5,25+3,5 H 8 S T 15 n Application of Computers in Manufacturing Technology - Master Control Technology L+E 1+1 1,75+3,5 H 8 S T 16 o Planning Methods in Energy Economics L+E 2+1 3,5+3,5 H 5 W T 14 e Steering Technique I L 2 3,5 1+1 1,75+3,5 9. Quantitative Methods H 7 W T 14 l CAM, CAP, CAD/NC - Automation of Technological L+E Information - Flow I 10. Europäische Integration (European Affairs) Languages (up to a maximum of 10 credits) H 5 W A 00 a Exercises for General Management Studies E 2 7,5 H 7 W A 00 e Seminar on Business Administration S 2 7,5 H 5 W S 03 b International Financial Management L 4 7 H 7 W R 12 a Principles of the Law of Public Economic Administration L 2 3,5 H 7 W R 12 b Law of Unfair Competition and Antitrust Law L 2 3,5 H 6 S V 09 f International Economics L+E 2 3,5+7,5 H 6 S S 06 d International Marketing L 2 3,5 H 7 W V 13 h External Economic Relations L+E 2+2 3,5+7,5 Information Package 30 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration At most two modules can be in the same subject area. European Affairs and at least two of the other modules must be completed at a 'host institution' in another language area. Modules are assessed on a five grade scale agreed by all institutions. Candidates are generally not permitted to re-sit any of the examinations involved. The Qualification Successful candidates are awarded the consortium's EMBS Certificate. For outstanding candidates this may be awarded 'with merit' or, in exceptional cases, 'with distinction'. The Certificate is accompanied by an Academic Report which contains details of the modules taken and the marks obtained. In parallel the respective home institutions grant nationally recognised academic degrees to their students. Information Package 31 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration C. Course Catalogue 1. Explanation of Terms 1.1 Information about the Description of Syllabus and Courses offered Semester: Type: 1/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+1 -- Examination: written Credits: 6 Semester: recommended semester: WS = Winter Semester SS = Summer Semester Type: L E S Examination: written = written exam (Klausur) assign. = assignment + oral presentation (Referat) writ. + assign. = assignment + oral presentation plus written exam (Referat und Klausur) arrangement = exam by arrangement (Prüfung auf Anfrage) Credits: Number of credits The credit system is based on 60 credits per academic year. Information Package = Lecture (Vorlesung) = Exercise (Übung) = Seminar (Seminar) 32 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 1.2 Codification of Courses 1. Variable: course level G = Grundstudium (Stage 1 Studies) H = Hauptstudium (Stage 2 Studies) 2. Variable: recommended semester level (first, second,...) 3. Variable: W = Wintersemester (Winter Semester) S = Sommersemester (Summer Semester) 4. Variable: subjects/ fields P = Propädeutika (Preparatory Courses) B = Betriebswirtschaftslehre im Grundstudium (Business Studies/ Stage 1 Studies) V = Volkswirtschaftslehre (Economics) R = Recht (Jurisprudence) A = Allg. Betriebswirtschaftslehre im Hauptstudium (General Management Studies/ Stage 2 Studies) S = Spez. Betriebswirtschaftslehre im Hauptstudium (Special Field of Management/ Stage 2 Studies) T = Techn. Schwerpunktfächer im Haupstudium (Courses in Engineering, Science/ Stage 2 Studies) 5. Variable: department codification 00 = Allgemeine Betriebswirtschaftslehre (General Management Studies) 01 = Personalmanagement (Human Resource Management) 02 = Organisation (Organisational Design) 03 = Finanzwirtschaft (Finance) 04 = Planung (Strategic Planning and Corporate Management) 05 = Controlling (Management Accounting) 06 = Marketing (Business-to-Business Marketing and Purchasing) 07 = Wirtschaftsinformatik (Business Informatics) 08 = F&E Management (Research and Development) 09 = Wirtschaftspolitik (Economic Theory) 10 = Innovationsökonomik (Innovation Economics) 11 = Finanzwissenschaft (Public Finance) 12 = Recht (Jurisprudence) 13 = Allgemeine Volkswirtschaftslehre (General Economics) 14 = Fertigungstechnik (Manufacturing Engineering) 15 = Logistik (Logistics) 16 = Energietechnik (Power Engineering) 6. Variable: index Information Package 33 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 2. Syllabus of Stage 1 Studies 2.1 Structure of Stage 1 Studies This field of study named "technically oriented" Business Administration consists of two major parts: the first ends with a pre-diploma examination and the second one with the final diploma examination; each part takes 4 semesters. The Stage 1 Studies are designed to introduce students to the basics of the subjects of Business Administration and Management, Engineering/ Science and Jurisprudence in order to help them choose their majors for the Stage 2 Studies. Stage 1 Studies start each Winter Semester. The following subjects are compulsory [the weekly hours per semester (=SWS) are given in brackets]: Preparatory Courses (19 SWS) Business Studies (18 SWS) Economics (14 SWS) Technical Subjects (17 SWS) Jurisprudence (12 SWS) The Stage 1 Studies end with the pre-diploma examination usually after 4 semesters. As soon as the student is registered at the examination office as having passed all the demanded exams he will be given his pre-diploma certification. The technical subjects demand one two-hour written exam each while all other subjects demand two two-hour written exams. You can take the exams in all subjects immediately at the end of each semester right after the course has finished. 2.2 Preparatory Courses G1WP00a Financial Accounting (Finanzbuchhaltung) History, tasks, legal norms, forms of bookkeeping and double entry bookkeeping, entries of bookkeeping for goods and service companies, closing of accounts, special cases of bookkeeping (e.g. merger, reconstruction, preventive composition, bankruptcy). Semester: Type: 1/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+1 -- Examination: written Credits: 6 G1WP00b Mathematics I for Business Students (Mathematik I für Wirtschaftswissenschaftler) Analysis (inequations, mathematics for finance, sequences and series, functions, differential calculus and extreme value calculus (within one and many variables), integral calculus). Semester: Type: Information Package 1/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: written Credits: 8 34 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration G1WP00c Statistics I for Business Students (Statistik I für Wirtschaftswissenschaftler) Basic statistical terms, tasks of statistical calculus, parameters of frequencies, statistical parameters, relatives, index numbers, time series analysis, probability calculus. Semester: Type: 1/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: written Credits: 8 G2SP00d Mathematics II for Business Students (Mathematik II für Wirtschaftswissenschaftler) Linear algebra (linear equations, vectors, matrix), differential calculus, differences. Semester: Type: 2/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: written Credits: 8 G2SP00e Statistics II for Business Students (Statistik II für Wirtschaftswissenschaftler) Probability calculus (cont.), parameter estimation, testing statistical hypotheses, linear regression, spot checks and statistical errors, outlook on further statistical questions. Semester: Type: 2.3 2/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: written Credits: 8 Business/ Management Studies G1WB00a Introduction to Decision-Oriented Business Administration (Einführung in die Betriebswirtschaftslehre) Study purpose and course content of Business Administration; decisions in private enterprises and public institutions; models of rational decision-making, methods and techniques of decision-making; illustrative application possibilities: constitutive decisions (corporate targets and strategies; organisational charts, etc.): level-oriented decisions (foundation, growth, crisis and liquidation), function-oriented decisions (perspectives of longitudinal- and cross-section functions of enterprises); methods of applicable Business Administration in scientific research. Semester: Type: 1/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 4 G3WB00b Cost Accounting (Kosten und Leistungsrechnung) Accounting as foundation of cost accounting; subject, concept and goal of cost accounting; cost finding and cost allocation (cost type-, cost centre-, job order cost accounting); costing systems based on full cost (effective and budgeted cost); costing systems based on portion of overall cost (effective and budgeted cost). Semester: Type: Information Package 2/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination Credits: arrangement 4 35 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration G3WB00c Cost Accounting (Kosten und Leistungsrechnung) Accounting as foundation of cost accounting; subject, concept and goal of cost accounting; cost finding and cost allocation (cost type-, cost centre-, job order cost accounting); costing systems based on full cost (effective and budgeted cost); costing systems based on portion of overall cost (effective and budgeted cost). Semester: Type: 3/WS E Hours per Week: 1 Examination: arrangement Prerequisites: G2WB00b Credits: 2 G3WB00d Financial Reporting (Bilanzierung) Tasks, aims, nature and format of the balance sheet; accounting principles, valuation (standards of valuation by commercial law and law of taxation); balance sheet analysis and balance sheet ratios; accounting theories. Semester: Type: 3/WS L. + E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6 G3WB00e Primary Functions in Business Administration (Leistungswirtschaftliche Funktionen) Purchasing and Marketing: objectives of marketing, basics of business transactions, transaction cost theory, existence of trading companies; subfunctions and decision problems of Business Administration, subfunctions of marketing, marketing concepts, marketing instruments. Production: production systems as objects of production management; aims and tasks of production management; basics of production and cost theory; strategic challenges for production; need for decision-making in strategic and operative production management; basics for environmentally friendly production. Semester: Type: 3/WS L. + E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6 G4SB00f Introduction to Information Management (Einführung in das Informationsmanagement) Contents and methods of applied business informatics. Providing information within companies. Targets and tasks of information management. Hard- and software as technologies in iInformation management. Classes of computers, decentralisation; types of software, individually developed or standard software. Design, implementation and control of integrated information systems: components and fields of integration through examples. Information and software engineering: design, development and maintenance of information systems and their innovation. Project management, quality assurance and ergonomic aspects of design. Data privacy protection and system security; economic information processing. Semester: Type: Information Package 4/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 2 36 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration G4SB00g Human Resource Management and Organisational Design (Personalmanagement und Organisationsgestaltung) Human Resource Management: basic concepts and change in meaning; prime targets and contributions to competitive abilities of enterprises; current and future priorities; representatives in HR management; importance and function of HR departments as service carriers; decentralisation programmes; computer-based HR management; efficiency measurement; possibilities and limits of scientific consolidation; interrelations between HR management and organisational design. Organisational Design: integration and subdivision of organisational design, organisational charts, processes of organisation; centre-concepts; matrix organisation; coordinating body; context factors: strategy, personnel and technology; organisational charts in export trade; organisational management techniques. Semester: Type: 4/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 4 G4SB00h Finance and Investment (Finanzierung und Investition) Decision-making oriented markets for money, capital credits as well as capital sources to finance enterprises. Methods for investment count. Semester: Type: 4/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6 G4SB00i Introduction into R&D-Management (Einführung in das F&E-Management) Explanation of the terms research, development, innovation, invention, technology, technique etc.; role of R&D in the corporate value chain; importance of R&D for the innovation process; characteristics of R&D; necessity and particularities of commercial control of R&D; explanation of tasks of Business Administration in R&D (strategic and operational R&D-Management, R&D-Controlling, R&D-Project-Management, Innovationand Technology-Management, Interface-Management - internally towards production and marketing, externally towards public research). Semester: Type: 2.4 4/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 2 Economics G1WV00a Introduction to Economics (Einführung in die Volkswirtschaftslehre) Economic systems: market economies and socialist economies; introduction to microeconomics: consumers theory and theory of the firm ; market structure and market equilibrium, competition and innovation, economic welfare and external effects; introduction to macroeconomics: national income and product accounts, employment and money. Stabilisation policy, goals and instruments, the classical and the Keynesian model, business cycles and growth. Semester: Type: Information Package 1/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 4 37 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration G1WV00b Microeconomics (Mikroökonomik) Household theory: preferences and indifference curves, exchange relations, household equilibrium, price and income dependent functions of demand. Theory of production and costs: production functions, cost functions and their derivatives, derivation of supply functions. Theory of the market: interaction of demand and supply in different markets. Theory of forming the prices in the polypol, oligopoly and monopoly as well as in the monopolistic competition. Forming the prices in special markets. Semester: Type: 1/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 3+1 -- Examination: written Credits: 8 G2SV00c Macroeconomics I (Makroökonomik I) Basics of the national economies: stocks, national wealth. Analysis of flows: analysis of circulation, construction and uses of input- output- tables, input- output- analysis as a prognostic instrument. National accounting system and related concepts. Financing matrices, balance of payments, price indices, critics of social accounting. Macroeconomic analysis of demand: consumption- function, investment- function, equilibrium of the goods market in a closed economy without state, analyses of multipliers. Semester: Type: 2/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+1 -- Examination: written Credits: 6 G3WV00d Macroeconomics II: Income, Employment and Price Level (Makroökonomik II) Overall targets, methods and national patterns of thinking, employment and overall demand: derivation of a total demand function; employment and total supply: derivation of a total (overall) supply function; comparative-statistical efficiency analysis: total supplydemand analysis; total economic objectives in an open economy and incentives for its control. Semester: Type: 2.5 4/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 3+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 10 Basic Features of Jurisprudence G1WR00a Constitutional Law (Grundzüge des Staatsrechts) Constitutional Law: form of government, polity; state area, citizenship, supreme power; principles of democracy; constitutional rights; universal suffrage; separation of powers. Semester: Type: Information Package 1/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: written. Credits: 4 38 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration G2SR00b Public Law (Grundzüge des Verwaltungsrechts) Basics of administrative law: legal administrative procedural practise and administrative acts; system of administrative jurisdiction. Semester: Type: 2/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: written. Credits: 4 G3WR00c Civil, Commercial, and Company Law I (Privatrecht I) Civil Law: definition, kinds, and sources of law, the German civil code (BGB), interpretation and application of law, kinds of (civil) rights, natural and artificial persons, objects, legal transactions, declaratory acts and legal acts, set-up and end of obligations, breach and other violations of contract, sales and work contracts, principles of unjust enrichment and of tort, possession and property, credit securities. Commercial and Company Law: merchants, legal protection of firms, commercial register, firm name, principles of general trade regulations and of commercial sales contracts, principles of company law (kinds, demarcations, establishment, representation and liability with regard to selected companies). Semester: Type: 1/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 5+2 -- Examination: written. Credits: 14 G4SR00d Labour Law I (Arbeitsrecht I) Incorporation of labour law into the general legal order, social function and importance in practice, historical development, general definitions, determinant factors. Semester: Type: Information Package 4/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 2 39 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 3. Stage 2 Studies 3.1 Structure of Stage 2 Studies Prerequisite for Stage 2 Studies is the pre-diploma examination and certificate. Stage 2 Studies are designed for four semesters. They are based on the following sections: a. c. three obligatory subjects from the field of General Management and Business Administration Studies (General Management Studies, Economics, special fields of management), one compulsory subject of your own choice from the fields of management studies, sociology or jurisprudence, one (obligatory) technical major subject. 3.2 General Management Studies b. H5WA00a or H6SA00a Tutorials for General Management Studies (Übungen zur Allgemeinen Betriebswirtschaftslehre) Tutorials in connection with the lecture on chosen examples of general management. Semester: Type: 5-6/WS-SS Hours per Week: L Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 H5WA00b Management Accounting and Treasury (Controlling and Treasury) Profit and liquidity orientation of companies: The Treasury Concept: cash management and banking relations; instruments of shortterm financial funds and investment; balance sheet structure and rules for structuring debt capital; management of operative and financial risk-situations. The Management Accounting Concept: coordination of the planning and monitoring system; coordination of the information supply system; organisational aspects of management accounting; internal auditing; new tools and trends of management accounting. Semester: Type: 5-6/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 3 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SA00c Integrated R&D-/ Personnel Management (Integriertes F&E-/ Personal-Management) R&D-Management: position of R&D in the product development process; R&D as cost- or profit-centre; commercial changes in the context of R&D; commercial consequences of different management methods of R&D; controlling instruments for R&D; cost- and management accounting of R&D; R&D in the balance sheet and the profit and loss statement; R&D- portfolio and strategic business units; success- and failure-factors in R&D; efficiency and effectiveness in R&D; calculation of R&D; financing of R&D; Information Package 40 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration information-management in R&D; Business Administration in R&D, seen under the angle of a technician. Personnel Management: importance of personnel management for successful R&D; particularities of a quantitative and a qualitative personnel need planning in R&D; personnel marketing, motivation and remuneration management for R&D personnel; leadership and personnel development in R&D; R&D-conform work- and production-time design; actors and organisational forms of personnel administration in R&D, models of cooperation between R&D and personnel; the way from R&D-guided personnel management towards innovation facilitating personnel management; possibilities and limits of innovation-support via personnel management in the companies. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 3 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H8SA00d Decision-making Processes and Information Systems (Entscheidungsprozesse und Informationssysteme) Information Systems: 1. Information Management, aims and tasks 2. Overview and detailed examples for use in the field of Business Administration 3. Integration of use of Business Administration, integration models - integration by means of PC in process orientation Semester: Type: 8/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7SA00e or H8WA00e Seminar on Business Administration (Seminar zur ABWL) Seminar for advanced students: changing examples and topics according to the newest subjects of interest in Business Administration. Semester: Type: 7-8/WS-SS Hours per Week: L Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 H7WA00f Management of Critical Success Factors (Management betriebswirtschaftlicher Erfolgsfaktoren) (a) Integration management, quality management, cooperation management, management of corporate cultures, management of complexity, project management, change management. (b) The marketing management approach and alternative concepts; explanation of exchange relationships between economic subjects; buying decisions in business to business marketing; planning, leading and monitoring of marketing tasks; marketing instruments and optimisation within the marketing mix; problems of effect measurement; organisation of marketing activities. Semester: Type: Information Package 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 3 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 41 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 3.3 Economics H4SV13a Basics of Economic Theory: Economic Policy I (Grundlagen der Wirtschaftspolitik) Definition of Economic Policy; political systems and economic systems; social market economy; political and economic institutions; economic and social objectives; economic policy tools; rational economic policy and political consulting. In addition to the lectures of Economic Policy I there will be each Winter Semester non compulsory courses in Economic Policy. Semester: Type: 4/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3 H5WV13b Business Cycles and Employment (Konjunktur und Beschäftigung) History of business cycles; definition and measurement of business cycles; theories of business cycles: the models of Hicks and Goodwin, the neo-classical approach and the neo-Keynesian model from Malinvaud. Theoretical and empirical analysis of the labour market, fiscal policy, problems of government budget constraint and public debt. Semester: Type: 5/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H5WV13c Competition: Theory and Policy (Wettbewerb: Theorie und Politik) Basics of competition theory: determinants, functions and concepts of competition, types of rivalry, workable competition, the optimal intensity of competition and other concepts (e.g. countervailing power, contestable markets) types of restraints of trade. Different approaches and types of competition policy. Competition laws and competition policy in Germany, US and the EU. Semester: Type: 5/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H6SV13d Money and Inflation (Geld und Inflation) The financial sector in the FRG; money flow and stock accounts; demand for money; supply of money; monetary markets and the determination of the interest rate; the transmission mechanism of monetary impulses; inflation theory and anti-inflation policy; the instruments of the Bundesbank for monetary policy; from anticyclical to potential output orientated monetary policy. Semester: Type: 6/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H6SV13e Economic Growth and Technical Change (Wirtschaftswachstum und technischer Wandel) Quantitative and qualitative economic growth: terms and measurement, equilibrium growth, premises of growth models, growth motives (models), growth effects. Technical change: terms, measurement, motives and effects, growth- and politically induced consequences. - on development Information Package 42 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration Semester: Type: 6/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H6SV13f Distribution (Verteilung) The distribution of income and wealth; the distribution of income among factors of production; static theory of distribution of income among factors of production; dynamic theory of distribution of income among factors of production; distribution policy. Semester: Type: 6/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H7WV13g Environmental and Natural Resource Economics (Umwelt- und Ressourcenökonomik) Standards: time and space; relation between the ecological and the economic system; cycles; the environment as a public good; external effects and property rights. Conceptions: ecological and social economy; sustainable development. Exhaustible and renewable resources: availability, possibilities of extraction. Environmental targets and standards; principles of environmental policy; governing structures (market, government, negotiations, elections) and modes of internalising (taxes, property rights); measures and methods to reach sustainable development Semester: Type: 7/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H7WV13h External Economic Relations (Außenwirtschaft) FRG and the world economy; welfare and international trade; balance of payments; foreign exchange market; the impact of changes in the exchange rate on the balance of payments; overall equilibrium in an open economy; international trade policy; international monetary policy; the development of the European monetary system. Semester: Type: 3.4 7/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 Special Business Administration: Human Resource Management H5WS01a Human Resource Planning and Budgeting (Personalplanung und Personalcontrolling) Human Resource Planning as an inevitable component of management planning; significance, position and development tendencies within the framework of HR management; strategical, managerial and operational planning levels; course models and organisational principles; methodological planning of quantitative and qualitative HR demand forecast; Zero Base Budgeting as tool for Human Resource Planning in variable performance-/ result-levels; possibilities and limits of methodological HR availability forecast; early diagnosis of need for action; measures to avoid labour surplus (employee retrenchment) or personnel shortage; conceptions of internal labour policy; purpose of HR budgeting. Information Package 43 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H5WS01b Motivation & Behaviour Management Targets; current and future significance of motivation management within the framework of HR management; motivation analysis; basic theories; content- and process theories (e.g. Maslow); theories of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation; results of empirical motivation research; development of contribution- and joint decision concepts; measure design and cost/ benefit analysis; participative motivation management by "action-oriented audits of employees". Case studies include practical exercises in HR management Semester: Type: 5/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 1,75 H5WS01d or H6SS01d Human Resource Development and Career Planning (Personalentwicklung und Karriereplanung) Position and significance of HR development within the framework of HR management; parts of HR development (training, further vocational training, retraining, further education); performance feedback based on behavioural measurement for management of learning processes; inquiry of internal need for qualification; systematic design of HR development; qualification strategies; legal basic conditions; possibilities and limits of cost/ benefit analysis. Objective and subjective careers; career planning as an implement of HR development; concepts of career planning in private industry and public institutions; planning of international careers; career planning for special employee groups (dual career couples; female employees; etc.). Semester: Type: 5+6/WS+SS Hours per Week: L Prerequisites: 1+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H6SS01e Frame Work of Working-Time Schemes and Attended Time (Arbeits- und Betriebszeit-Management) Work schedules and attended time as success patterns in international competition; position and significance of time management within the framework of HR management; targets; scope of action and design of chronometrical and chronological working time flexibility; separation of working-time and attended time; flex-time, part-time, job sharing, shift-work and multiple employment models; costs and employee behaviour patterns connected to various work schedules; methodological planning of working-time in consideration of costs and efficiency (including application examples). Semester: Type: 6/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS01f Compensation Management (Vergütungsmanagement) From wage and salary administration to entrepreneurial compensation management; "Total compensation"-concepts; current and future position and significance within the framework of HR management; strategical, managerial and operational decision levels; legal and union conditions; plant-level scope of action; basic principles of compensation Information Package 44 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration management; possibilities and limits of influencing motivation of employees by "motivecongruent" compensation; planning and realisation performance measuring compensation plans by use of grading or classification systems of work evaluation; meriocratical compensation e.g. Hourly rate, piece wage, incentive wage; incentive bonus based on systematic performance appraisal; profit sharing plans, methodological choice of optimal compensation tools, reflection of structural changes in economy (including case studies) under consideration of efficiency and costs; current approaches of compensation management: "compensation according to qualification", "cafeteria-plans", "compensation plans for executives", profit sharing. Special topic: compensation management in multinational enterprises. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS01g Human Resource Leadership (Personalführung) Position and significance of leadership within the framework of HR management; patterns and new challenges; behaviour related basis (leadership theories); concepts of HR leadership; components of integrated HR leadership: basic principles, leadership styles and behaviour; leadership structures (management-by-principles and management systems); cultural leadership embedded in corporate culture, design of single components; possibilities and limits of "best-fit" approaches; measurement of leadership efficiency. Special topic: leadership of and within work groups. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS01h Human Resource Management Studies (Personalübung) Lecture expanding studies which will combine assignments, oral presentations and discussions of selected main topics in HR management for preparation of the ensuing seminar. Semester: Type: 6/SS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 H6SS01i HR Management Business Game (Personalplanspiel) Computer-based business game Plus-P. Application of corporate problems and HR management related topics within a PC-network for preparation of the ensuing seminar. Semester: Type: 6/SS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3 H7WS01j Human Resource Management in Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (Personalmanagement in kleinen und mittleren Unternehmen) Qualitative and quantitative distinctions of small and medium-sized enterprises (SME); significance and exceptions of HR management in SME; representatives and organisational charts of HR management in SME; HR demand forecast and HR budgeting in SME; HR marketing: compensation in SME; main topic "HR development"; leadership in SME; SME as innovators and imitators of HR management. Information Package 45 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration Semester: Type: 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WS01k Human Resource Management Seminar (Personal-Seminar) Changing topics try to reflect main questions of HR management. Team-written papers and oral presentations are requested for receiving credits. Semester: Type: 3.5 7/WS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 E Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 Special Business Administration: Organisational Design H5WS02a Integrated Organisational Design and Human Resource Management (Integrierte Organisations- und Personalarbeit) Optimising human resource use by coordinated organisational and personnel management activities; integrated examination of organisational and personnel needs; employee orientation; flexibility of HR; leadership models; management of overhead costs; quality assurance; customer orientation; stimulating innovations; management of impacts of new office and manufacturing technologies; corporate culture; structural and human resources management coordination instruments; self organisation; strategic HR management. Semester: Type: 5/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H6SS02b Strategy Oriented Organisational Design (Strategiegerechte Organisation) Support of corporate strategies by internal allocation and coordination structures and external cooperation and relationship structures; strategy-structure-interface; strategy development (portfolio-technique etc.); organisational and cooperation planning; flexible and integrated forms of product-, customer-, and regional oriented organisation; multidimensional forms of organisation; modular, dual and hybrid forms of organisation; organisation of the value chain; hierarchical, competitive, and cooperative forms of organisation. Semester: Type: 6/SS L+E Hours per Week: 2+2 Examination: writ. + assign. Prerequisites: H5WS02a Credits: 10,5 H7WS02c Information Systems for Organisational Design (Informationssysteme für die Organisationsgestaltung) Organisational instruments and techniques: organisational projects (processes and structures); process design; information for organisational purposes (methods, models, data); methods of organisational representation and assessment; organisational goal setting; organisational diagnosis; organisational planning; organisational implementation; EDP-supported organisational design. Semester: Type: Information Package 7/WS L Hours per Week: 2 Prerequisites: H6SS02b Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 46 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H7WS02d Organisational Seminar (Organisationswissenschaftliches Seminar) Selected, extended, and actual organisational issues from various fields. Semester: Type: 3.6 7/WS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 E Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 Special Business Administration: Financial Management H5WS03a Capital Budgeting (Vermögens- und Kapitalstrukturplanung) Aims and development of the finance theory, cash management; instruments and optimisation designs; venture capital; meaning of special finance innovations. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H5WS03b International Financial Management (Internationales Finanzmanagement und Betriebswirtschaftliche Währungsrisikopolitik) International finance, currency aspects, theorems for explaining the making of conditions on international finance markets; currency risk politics, finance and judgement of advantages in direct foreign investments, case studies in international finance. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 4 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H5WS03c Theory of Investment (Investitionsmanagement) Single investment selection vs. investment programme planning; decision-oriented approaches to risk analysis for individual investment objects, theory of portfolio selection, asset allocation and real investment policies. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H5WS03d Exercise on Financial Management (Übung zur Finanzwirtschaft) Additional tasks and approaches. Possible to be given credits if you participate in final written test. Semester: Type: 5/WS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 H6SS03e Seminar on Financial Management (Seminar zur Finanzwirtschaft) Dealing with examples of finance aspects. Semester: Type: Information Package 6/SS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 E Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 47 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 3.7 Special Business Administration: Strategic Management and Corporate Planning H5WS04a Management of Complex Systems (Management komplexer Systeme) Basics of system theories, cybernetics and self-organisation; phenomena and different kinds of economic change; models for explaining and systems for mastering economic change; organisational learning; methods to support change management (system dynamics, concepts for learning labs, gaming). Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H5WS04b Planning Techniques (Planungstechniken) Variety and systematic approach to planning techniques; planning techniques during different phases of planning; exceptional methods for operative and strategic planning, e.g. prognosis methods, creativity techniques, early warning systems, portfolio techniques, PIMS concept, GAP analysis, scoring model. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS04c Operative Planning/ Management (Operative Planung/Führung) Basics of corporate planning, operative planning as part of corporate planning, sections of operative planning (marketing, purchasing, production , R&D, project, finance and result planning); functional and cross-section strategies (technological and innovation strategies, information strategies, quality strategies, concepts of business process re-engineering). Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WS04d Operations Research (Planungsrechnung) Methods for solving linear optimisation problems; simplex algorithms; sensitivity analysis, algorithms for transport and assignment problems as well as numeric optimisation problems; building of linear optimisation models. Tutorial including written final test. Semester: Type: 7/WS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 H7WS04e Strategic Planning/ Management (Strategische Planung/ Führung) Basics of strategic planning/ management: development, current status and range as well as parts of strategic management/ planning. Basic terms, theoretical foundation and conceptual approach to strategic planning. Strategic management as management of planned change: determinants of strategy, evolution of environment and market requirements, management of renewal. Process of strategic management/ planning: questioning strategic orientation - visions and missions, analysis of the planning spectrum, strategy development, evaluation and coordination, mechanisms and approaches to strategy implementation and support, strategic controlling. Information Package 48 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration Semester: Type: 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WS04f System Dynamics (System Dynamics) Basics of system theory and analysis; basic features and principles of "System Dynamics" simulation method; steps of system analysis with System Dynamics; causal diagrams, flow charts; DYNAMO programmes; programming language DYNAMO; validation and implementation of SD models; examples of models and area of use; decision-making support for strategic management with the help of SD models. Tutorial including homework, PC modelling and final exam. Semester: Type: 7/WS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 H7WS04g Project Planning/ Management (Projektplanung und –management) Basics of project management (PM): system-theoretical approach, parts of PM, project organisation, stakeholder management, project phase models; company organisation structure, personnel management in projects: project steering committee and project team; planning and controlling of projects; evolution of PM. Basics of network diagram, network planning technique, e.g. CPM, PERT. Project support systems, training in project planning software. Semester: Type: 7/WS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 H8SS04h Seminar in Strategic Planning (Seminar zur Strategischen Planung) Seminar for advanced students dealing with topics of strategic management and corporate planning. Semester: Type: 8/SS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 E Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 H8SS04i Seminar in System Dynamics (Seminar zu System Dynamics) Seminar for advanced students on topics of operative planning and corporate management by using system dynamics. Each one is asked to develop a PC-based simulation model. Semester: Type: Information Package 8/SS S Hours per Week: 2 Examination: assign. Prerequisites: H7WS04f Credits: 7,5 49 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 3.8 Special Business Administration: Management Accounting H5WS05a Management Oriented Accounting (Führungsorientiertes Rechnungswesen) External and internal accounting; management oriented accounting; cost planning; strategic cost management (target costing, activity-based costing); asset management; statement of changes in financial position; revenue accounting; profit and loss accounting; segmental accounting; instruments of coordination (ratios, transfer prices). Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS05b Coordination of Planning (Planungskoordination) Planning tasks of management accounting; system-building and system-connecting coordination of planning; functional, instrumental and institutional aspects of the coordination of planning; the coordination of planning in the practical business. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS05c Information Supply Management (Informationswirtschaft) Information as an asset; management and information; information management and management accounting; efficiency of information and EDP-systems; information demand assessment, information procurement and reporting, IS-management accounting. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS05d Management Accounting: Exercise (Controlling-Übung) Lecture-complementary event in which students discuss separate management accounting by an essay (theoretical and case study part). Semester: Type: 6/SS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- subjects of Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 H7WS05e Budgeting (Budgetierung) Concept and function of budgeting; the role of budgeting in the planning and monitoring system; types of budgets and budgeting systems; basic features of budgets of selected functional areas (e.g.: production; R&D; investment; treasury; sales); budgeting in overhead areas; budgeting instruments; EDP for budgeting. Semester: 7/WS Hours per Week: 2 Examination: arrangement Type: L Prerequisites: -Credits: 3,5 Information Package 50 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H7WS05f Management Accounting: Seminar (Controlling-Seminar) Annual changing works to actual questions of management accounting which will be processed by the students in an essay and a recitation. Semester: Type: 7/WS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 E Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 H8SS05g Internal Auditing (Interne Revision) Concept and sorts of internal auditing; function and development of internal auditing; methods of internal auditing; organisation of internal auditing; internal auditing of EDP; special auditing areas. Semester: Type: 8/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H8SS05h External Auditing (Wirtschaftsprüfung) Generally accepted auditing standards; auditing-techniques; basic questions of group auditing; basic questions of valuation of an enterprise. Semester: Type: 8/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H8SS05i Market-Oriented Cost-Management (Marktorientiertes Kostenmanagement) Strategical alteration and the role of the business context; market-oriented target cost management; design and preservation of competitive structures; market-orientation in cost management in the practical business; the market oriented controller. Semester: Type: 3.9 8/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 Special Business Administration: Marketing H5WS06a Business-to-Business Marketing (Investitionsgütermarketing) Specialities of business-to-business marketing compared with consumer oriented marketing, objectives and strategies in business-to-business marketing, framework, organisational buying, business related marketing Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H5WS06b Marketing Practice (Marketing-Übung) We offer a practice for the following subjects: business-to-business marketing, organisational buying, industrial purchasing management, distribution policies. Semester: Type: Information Package 5/WS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 51 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H6SS06c Industrial Purchasing (Beschaffungsmanagement) Supply and purchasing function of industrial companies, organisational buying, basic theories of purchasing related decisions, strategic purchasing planning, operational purchasing planning, purchasing organisation, staffing in purchasing, purchasing controlling, information system in purchasing. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS06d International Marketing (Internationales Marketing) Internationalisation/ international management, forms of international business activities, basic theories of international business, structural framework for international business, strategic decisions of international marketing, information basics of international marketing, decision problems and marketing management, marketing organisation of companies with international business activities. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS06e Marketing Practice (Marketing-Übung) We offer a practice for the following subjects: business-to-business marketing, organisational buying, industrial purchasing, distribution policies. Semester: Type: 6/SS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 H7WS06f Marketing Research (Marketingforschung) Objectives and elements of marketing research in Business Administration, information sources, importance of information for the decision making process in marketing, organisational aspects of marketing research, specialities of marketing research, models of buyer behaviour, logical framework of marketing research, data collection, data evaluation, presentation of research results Semester: Type: 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WS06g Marketing Seminar (Marketingseminar) Selected topics of business-to-business marketing, purchasing management, marketing research, and international marketing (only for advanced students). Semester: Type: Information Package 7/WS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 E Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 52 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 3.10 Special Business Administration: Business Informatics H5WS07a Structures of Hardware, Software and Networks through Examples of Microcomputer Systems (Hardware-, Software- und Netzwerk-Strukturen am Beispiel von Mikrocomputersystemen) Overview of hardware and software markets; selection of systems and design contracts. Local and wide area networks of various performance levels. System security for computers. The lecture will be complemented by different labs in the CIP-Pool (outline and realisation of small applications; usage of standard software). Semester: Type: 5/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H6SS07b Information and Communication Systems Design I (Gestaltung von Informations- und Kommunikationssystemen I) Basics and limits; sequence- and life-cycle-models; data-, function- and process modelling; methods, techniques, tools; data privacy protection and system security; quality assurance; encryption; requirements engineering. Software: ergonomic aspects, usability. Semester: Type: 6/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5+7,5 H7WS07c Information and Communication Systems Design II (Gestaltung von Informations- und Kommunikationssystemen II) Data organisation; data modelling; files and databases; database models; data dictionaries; function- and process modelling; workflow-management; methods of design and implementation; object-orientation; introduction, operation and maintenance of ITsystems; CASE. Semester: Type: 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WS07d or H8SS07d Applied Business Informatics Seminar (Wirtschaftsinformatik-Seminar) Each semester the seminar thoroughly deals with either current topics of Applied Business Informatics or – depending on attendance – practical case studies will be worked out and discussed. Semester: Type: Information Package 7/WS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 E Examination: arrangement Credits: 7,5 53 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H6SS07e Project Management (Projektmanagement) Classes of projects, standards of project management; project organisation and hierarchies. Project scheduling: activities resources, time, estimation of cost and time, staff allocation and cost planning. Project control and management. Methods and tools of project management. Efficiency of information processing. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WS07f Information Management (Informationsmanagement) The strategic, tactic and operative level of information management. Leadership and human resource management; decentralisation. Organisational structures/ cooperation with departments. Management of technology, computer centres and networks. Data management, data privacy protection and system security. Information processing controlling. Legal aspects of data processing. Semester: Type: 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 3.11 Special Business Administration: R&D Management H5WS08a R&D-Controlling (F&E-Controlling) Definition and characterisation; national and international conditions; R&D decision processes; organisation and R&D controlling resources; R&D performance, its valuation and financing; R&D investment control; reporting on R&D; tax-treatment of R&D in the balance sheet and the profit- and loss-account; the integration of R&D into cost accounting; new international guidelines for R&D; controlling instruments. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS08b R&D-Management (F&E-Management) History; questions of method; instruments for the appraisal of future developments; concepts and strategies; determination of priorities; commonalties and differences between research and product- or process-development respectively; problems of interfaces; patents, licences; joint ventures; time-, performance-, cost- and balance sheet management; developments in future. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SS08c Training-Course on Basic Instruments of R&D-Management (Übung zu Grundinstrumenten des F&E-Controlling) Course for amendment of the lecture with home tasks, cases and presentations on different topics of R&D-controlling. Semester: Type: Information Package 6/SS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 54 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H7WS08d Training-Course on Basics of Technology- and Innovation-Management (Übung zu Grundinstrumenten des F&E-Projektmanagements) Course for amendment of the lecture with home tasks, cases and presentations on different topics of R&D-project-management. Semester: Type: 7/WS E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: writ. + assign. Credits: 7,5 H7WS08e R&D-Project-Management (F&E-Projekt-Management) Position of R&D-projects in project-management; controlling in the context of project management; the work-break-down-structure; the flowchart of organisation; phases of project performance; the resources, the project cost; the financing; order control; reporting in the context of a project; information flow and EDP-use for project control; instruments to shorten lead time; basic mistakes during project work. Semester: Type: 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WS08f R&D-Management Seminar (F&E-Management-Seminar) Changing topics on actual questions of importance in the area of R&D-management with seminar papers and presentations, presentations of guest-speakers and excursions. Semester: Type: 7/WS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 E Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 H8SS08g Technology- and Innovation-Management (Technologie und Innovationsmanagement Product-development process; product-life-cycle; technology-monitoring and -assessment; options and basic strategies; organisation of processes, control and determination of success of innovation, innovation support, creativity techniques. Semester: Type: 8/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 3.12 Economics: Economic Policy H4SV09a Basics of Economic Theory: Economic Policy I (Grundlagen der Wirtschaftspolitik I) Definition of economic policy; political systems and economic systems; social market economy; political and economic institutions; economic and social objectives; economic policy tools; rational economic policy and political consulting. In addition to the lectures of Economic Policy I, there will be each Winter Semester non compulsory courses in Economic Policy. Semester: Type: Information Package 4/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 55 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H5VW09b Economic Policy II (Wirtschaftspolitik II) The focus of these lectures lies on Ordnungspolitik. Unfortunately, there is no conceptual equivalent outside West Germany. Ordnungspolitik means economic policy proceeding from, and taking as its yardstick of performance, an ideal-type free market system; it is subordinated to the requirements, as the case may be, of the economic framework or »Ordnung«; the concept goes back to Walter Eucken (Wilhelm Schäfer): private and public ownership; corporate legal structure; market forces and competition; labour market and free collective bargaining. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SV09c Environmental Policy (Umweltpolitik) Basic environmental policy: objectives, principles, agents, and tools of environmental policy. Semester: Type: 8/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SV09d Economic Systems (Wirtschaftssysteme im Wandel) The economic doctrines of A. Smith and K. Marx and the consequences for the construction of economic systems. Analysis and comparison of economic systems, the efficiency of socialist versus market economies and the end of centrally planned systems. Problems of privatisation and reconstructing the economy of Eastern Germany. Transformation of socialist economies in Eastern Europe: privatisation and stabilisation processes. Integration in Western Europe: implications of the changes in Europe for the national economic systems. Consequences from international competition and capital flows to national economic policy. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SV09e Regional and Industrial Economics (Strukturpolitik) Regional and structural change: theories of regional development, theories of economic change and growth and structural consequences. Discussion of policies associated with the full use of productive resources and internal and external constraints: goals, strategies and instruments. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SV09f or H7WV09f International Economics (Internationale Wirtschaftspolitik) Problems of international cooperation and development. International agencies in the international economy; recent developments in international monetary relations. Semester: Type: 6/SS or 7/WS Hours per Week: L Prerequisites: Information Package 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 56 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H6SV09g or H7WV09g Seminar in Economic Policy (Wirtschaftspolitik, Seminar) Discussion of complex economic problems. It is necessary to attend one seminar in economic policy, and to finish it successfully. Students have the choice of different seminars according to the subjects (1) - (8). Semester: Type: 6/SS or 7/WS Hours per Week: 2 S Prerequisites: -- Examination: Credits: assign. 7,5 H7WV09h Social Policy (Allgemeine Sozialpolitik) Goals and instruments of social policy, the regulations of the labour market, the social security system and the insurance system in Germany: the „Bismarckian„ system. Competitive social security systems in other European countries: the Beveidge system; consequences of European Union, problems and challenges of the German system. Semester: Type: 7/WS L+S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WV09i Fiscal Policy (Finanzpolitik) Aims and trade-offs of fiscal policy; institutions and tools of fiscal policy; fiscal policy and democracy. Semester: Type: 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 3.13 Economics: Innovation H5WV10a Research and Innovation (Forschung und Innovation) Aspects of technological history; notions and measures of the innovation process; international comparison of research infrastructure; research process; technological trajectories; innovation and technological change; targets of research; system of incentives for research and innovation; technology-push and demand-pull; research, innovation and structural change. Semester: Type: 5/WS L or E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6SV10b Diffusion of Innovation (Innovationsdiffusion) Product and process innovation; evidence of selective diffusion processes; increasing scales of application, learning and imitation; microeconomic analysis: equilibrium, game theoretical approaches, diffusion process as a process of selection; macro economical analysis: diffusion of innovation, capital accumulation, economic growth and employment, profit rate differentials, factor substitution, wage policy. Semester: Type: Information Package 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 57 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H6SV10c Seminar: Diffusion of Innovation or Innovation and International Trade (Seminar zu Innovationsdiffusion bzw. zu Innovation und Außenhandel) Semester: Type: 6/SS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 H7WV10d Technological Integration and Structural Evolution (Technologieverflechtung und Strukturevolution) Concepts of the measurement of technological interconnection. The cone theory, the input-output-tables and the input-output-analysis, the qualitative input-output-analysis, the Minimal-Flow-Analysis (MFA) and other structural methods, technology flows and relevant production structures, structural evolution and their prognostic potential. Semester: Type: 7/WS L or E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WV10e Innovation and International Trade (Innovation und Außenhandel) Neo-classical international trade theory with constant returns to scale: international trade in the specific factors model, impacts of technological progress on international trade, empirical relevance. Neo-classical international trade theory with increasing returns to scale: R&D-expenditure and increasing returns to scale, flows of international trade, elements of trade policy, evolutionary international trade theory: stylised facts regarding to technology, economic growth and international trade; evolutionary innovation theory, technological gaps, international competitiveness and flows of international trade. Semester: Type: 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H8SV10f Government Research and Technology Policy (Staatliche Forschungs- und Technologiepolitik) Justification of government intervention in technology policy (public goods, external effects, indivisibility, dynamic adjustment friction) as a subject of discussion (market failure versus government failure); national and international actors and point of departure for government technology policy; instruments of research and technology policy (infrastructure, financial incentives, direct and indirect R&D promotion, networks, etc.); impacts of government technology policy; methods of research and technology planning. Semester: Type: 8/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H8SV10g Technology Assessment (Technikfolgenabschätzung) Appreciation of the problem and standards; technology and society; theories of technical development; systematic of technological assessment: approaches for Technology Assessment (TA); technically inducted TA; mediation theoretical approaches, problem induced TA; modes of institutionalising of TA. Semester: Type: Information Package 8/SS L or E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 58 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration 3.14 Economics: Public Finance H5WV11a General Finance (Allgemeine Finanzwissenschaft) The targets of governmental activity; public and quasi-private goods; political economy of the government; governmental tasks; government expenditures (the budget). Functions of public activities (labour and social security, welfare state, defence, research, infrastructure, etc.); effects of the fiscal policy on the economic cycle, growth and distribution. Semester: Type: 5/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 3+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H6SV11b General Tax Theory (Allgemeine Steuerlehre) The basics of different kinds of revenue; basic concepts of general tax theory, principles of levying taxes: “ability to pay“- vs. “pay as you use“- principle, theory of tax-tariffs, techniques of levying, the tax system and the most important kinds of taxes, macro economic effects of taxes, policies aimed at preventing economic fluctuation by tax means, ecological policy by tax means. Semester: Type: 6/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 6,5 H8SV11c Public Enterprises (Öffentliche Unternehmen) Definition, different types of public enterprises and formal arrangements, the role of public enterprises in Germany and other European countries mainly in the infrastructure and the service sector of the economy. The constitutional background, the public enterprise in the market economy: goals and regulation strategies; the natural monopoly and the theory of pricing in public enterprises; problems of controlling public firms; deregulation and privatisation. Public enterprises in Germany and consequences of the EU. Semester: Type: 8/SS S Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: assign. Credits: 7,5 3.15 Jurisprudence H5WR12a Principles of the Law of Public Economic Administration (Grundzüge des Wirtschaftsverwaltungsrechts) Public control of economy by support, planning, supervision, and guidance, general principles of possible kinds of economies, constitutionally permitted public effects on economic life; different intensities and directions of public economic administration in selected branches (retail trade, industry, agriculture, credit system, insurance and traffic); optional organisations of economy (associations and chambers). Semester: Type: Information Package 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 59 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H6SR12b Law of Unfair Competition and Antitrust Law (Wettbewerbs- und Kartellrecht) Law of Unfair Competition: The general clause of sec. 1 UWG, the special clauses of sec. 3 ff., law of extras and reductions, substantive and procedural problems of violations of competition law. Antitrust Law: Definition and kinds of cartels, fixation and not binding advises of retail prices, regulations of distribution, interdiction of discrimination, domination over markets by enterprises, merger's control, cartel proceedings, European antitrust law. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WR12c Civil, Commercial and Company Law II (Privatrecht II) Consolidated discussion of selected problems of civil, commercial, and company law, also by written examinations. Semester: Type: 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 3.16 Courses in Engineering/ Science (Obligatory Technical Subjects) H5WT14a Human Factors I (Arbeitswissenschaft I) Ergonomics has an interdisciplinary approach which bears on the human and economical goals regarding work design. Both purposes aim at the creation of humanitarian working conditions in connection with a business structure that is organised for economical success. Therefore, the emphasis of the lecture lies in the fields of ergonomics (Human Factors I) and work system design (Human Factors II). The lecture 'Ergonomics' deals with the fields of physiology and psychology which are important for the human factors. Based on theses facts the ergonomically perfect design of the work environment and work place can be shown. Furthermore, rules and recommendations for the integrated ergonomic product design and for the humancomputer-interface design are discussed. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H5WT14b Technology Management (Technologiemanagement) Competitiveness demands superior problem solutions which base on trend-setting products with a lead in the field of technology and quality. Competition becomes more and more a competition of technologies. Technology management connects business management with technological know-how and includes the following items: technology development, technology design and technology assessment. The lectures impart information about new methods and procedures concerning the handling of technology: for the identification of relevant technology developments and the evaluation of technology tendencies; for the evaluation of strong and weak points of a company in its technology fields; for the development of organisation forms in order to realise new technologies; Information Package 60 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration - for the steering concerning development and introduction of new technologies and for the discovery of possible risks. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H5WT14c Simultaneous Engineering and Project Management (Simultaneous Engineering und Projektmanagement) In order to plan and settle efficiently extensive duties in an enterprise, the following methods of the project management are used: imparting of planning foundations, aids: structuring of projects, network planning, project pursuit, planning check-lists, computer application; applicability of project management: product development, network planning, integrated settlement of orders. The emphasis lies on the concepts for practice of simultaneous engineering, which aim the paralleling of duties and processes, the reduction of machining time and the optimisation of value added chains. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H5WT14d Basics of Machine Tools (Grundlagen der Werkzeugmaschinen) Contents of the lecture: categories of machine tools; basics for the construction and development of machine tools; basics for the production of machine tools; motorised (metal-turning) lathe; dealing with steel products; electrical tools; production cells; FFS; CIM factories; basics of system planning. Semester: Type: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 4 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 7 H5WT14e Steering Technique I (Steuerungstechnik I) Steering Technique I deals with the construction of steering for machine tools, main emphasis is laid on steering by contact, oil-hydraulic and pneumatic steering systems, CNC steering systems. Semester: MP: 5/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6ST14f Industrial Management I (Fabrikbetriebslehre I) It is a prerequisite of any industrial production to know what kind of internal relations exist in a company (organisation - technology - finances) and between companies and their surrounding (procurement - marketing). In its first part the lecture exemplifies types of organisation (company structure, structure of work flow, management style) as well as different forms of business organisation and business mergers. Also a survey is given of production and its adjoining departments (ahead or after or parallel ones), e.g. production design, operation and process planning, testing, procurement, marketing. Semester: Type: Information Package 6/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 7 61 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H6ST14g Factory Planning I (Methoden der Fabrikplanung I) Planning a factory does not only demand a profound knowledge about the design of work stations and material flow, about technical and information-related processes, but it also requires a suitable instrument to handle the "planning" in a target-oriented and consistent way. Factory Planning is a problem definition, from which a multitude of single tasks derives which are to be analysed and coordinated in accordance with the targets established by the company. The focus of the lecture is both on the technical solution of these single tasks and on the coordination of operations. The occurring problems are being exemplified by a case study. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6ST14h Human Factors II (Arbeitswissenschaft II) The methods and basic elements of the work system design play the major role in the second part of the lecture. The discussion covers work analysing methods, proceedings of work pattern, qualification of staff and work organisation. In this connection, the introduction of new work structures (teamwork) is emphasised. Exercises and examples show the proceedings at the planning of new work structures. With task design the interpretation of work places can be practised and examples present the product improvement which is caused by the ergonomic design of working materials. Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H6ST14i Technology Assessment (Technikfolgenabschätzung) Technology has become an important part in our lives: job and spare time both involve many technical products. At the same time, however, it has become increasingly important to examine the use and causes of technology in advance to prevent others from unexpected causes or risks - Technology Assessment (TA) becomes the basis of a social and environmentally friendly technological development and use. Famous lecturers (different people each time) will be dealing with various aspects of TA and will be introducing you to results from TA projects within the lecture which will take place each week . Semester: Type: 6/SS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 H7WT14j Factory Planning II (Methoden der Fabrikplanung II) Material flow is considered as a unit, in regard to public traffic network as well as to single work stations. At the beginning the location needs to be chosen, then the long-term planning of a company require, for example, a master plan for house building. The determination of production facilities within single operation areas makes it possible to calculate the necessary building volume. After defining the material flow you can join together various areas to an optimum lay-out, using methods of operation research. Case studies will emphasise this focus. Semester: Type: Information Package 7/WS L Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 62 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H7WT14k Industrial Management II (Fabrikbetriebslehre II) The second part views cost accounting, efficiency calculation and capital investment planning. Apart from that, basic matters of factory planning are discussed. The practical courses deal with selected chapters of the lecture, applying activity-based teaching methods. Topics of part I of the course are: value analysis, working programmes, production control, quality assurance, inventory and order accounting, determination of demand. Topics of part II of the course belong to the field of cost accounting and economic efficiency calculation. Semester: Type: 7/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 7 H7WT14l CAM, CAP, CAD/NC - Automation of Technological Information - Flow I (CAM, CAP, CAD/NC-Automatisierung des technischen Informationsflusses I) This lecture deals with requirements, solutions and development with regard to automated process planning, test planning and assembly planning, in particular computer-aided programming of NC machine tools as well as the combination of CAD and NC programming. Semester: Type: 7/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 5,25 H7WT15m Simultaneous Engineering (Simulationstechnik) Introduction to digital simulation of dynamic systems; iterative methods for solving algebraic equations; numerical integration methods for solving ordinary differential equations, differential and algebraic equations, and boundary value problems; numerical solution of partial differential equations; simulation tools ISRSIM and ACSL; discrete-event systems; simulation tool SIMAN for discrete-event systems. The practical computer work gives students the chance to work on the tasks studied in the exercises, using personal computers and the simulation tools ISRSIM, MATLAB, ACSL and SIMAN. Semester: Type: 7/WS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 3+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 8,75 H8ST15n Application of Computers in Manufacturing Technology - Master Control Technology (Prozeßrechnereinsatz in der Fertigungstechnik – Prozeßleittechnik) This lecture deals with the application of computers for automated manufacturing (CAM), especially the monitoring and controlling of linked production systems and the control functions in structure and systematic design. Semester: Type: Information Package 8/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 1+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 3,5 63 Faculty of History, Social Sciences and EconomicsBusiness Administration H8ST16o Planning Methods in Energy Economics (Systemtechnische Planungsmethoden in der Energiewirtschaft) Basics of system analysis and system theory; goals of energy planning; modelling; time series and regression analysis, input-output-analysis, linear and dynamic optimisation, planning under uncertainty, system dynamics, cost-benefit analysis; energy demand models; energy system models; energy economic models; planning tools for the electricity and oil industry. Semester: Type: Information Package 8/SS L+E Hours per Week: Prerequisites: 2+1 -- Examination: arrangement Credits: 7 64