The Purpose of the Nervous System
advertisement

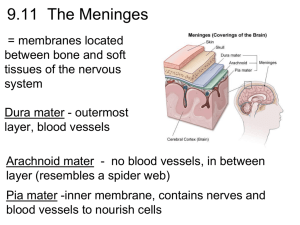
The Purpose of the Nervous System "From the brain and the brain alone arise our pleasures, joys, laughter and jests, as well as our sorrows, pains and grieves" Hippocrates The nervous system controls everything your body does, breathing, digestion, walking, thinking, feeling, blink your eyes, have feelings, think and breathe without thinking and much more. Central Nervous System The brain The spinal cord The nerves QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. The brain is the control center and the spinal cord is the major highway to and from the brain. The brain is also responsible for storing memory and allows you to think. The nerves are located inside your body. They look like a network of thin threads, and they carry the messages between the body and the brain. When the messages come into the brain from the body, the brain decides what action it will take in response to the signals from the nerves. Let’s say you are putting your hand in really cold water. The nerves in your hand will send impulses from your hand up to your brain. The impulses will tell the brain that the water is cold. Not until your brain receives these impulses you will understand that the water is cold. Isn’t pretty cool that messages are traveling from your hand to your brain so fast! What does the nervous system do? 1. It acts as a network with all the nerve cells throughout your whole body. 2. It controls all the systems in your body by sending messages in between your brain and your body. 3. It stores memories, and allows you to think. Let’s play a game where we put out nerves to the test! http://getyourwebsitehere.com/jswb/rttest01.html Diagram of the Nervous System QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Major parts of the nervous system and how they work Brain The brain is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right. The brains main job is to receive all messages from the nerves. Also, the brain is the one that decides what action is done in response to the signals from the nerves. Besides those two jobs, the brain also controls all mental feelings, such as joy, or melancholy. Also, all the memories are stored inside your brain. Yet again the brain has one more job, to control everything else going on in your body! Look at this animation to read about and listen to how to pronounce the tricky names of your brains parts. http://kidshealth.org/misc/movie/bodybasics/bodybasics_brain.html You can be nice to your brain by using it a lot, for example, read, play music and do puzzles. But that is not enough. Also eat healthy food so your brain gets al the important chemicals. Make sure you wear a helmet when you ride your bike or play sports that can injure your head. Spinal cord The spinal cord is the main pathway for messages connecting the brain and the rest of your body. From the spinal cord there are many smaller threads, called nerves that make the connection between the brain and the rest of the body. The human spinal cord is protected by the bony spinal column shown to the right. The spinal column is made up of bones called vertebrae. Although the spinal column is somewhat flexible, some of the vertebrae in the lower parts of the spinal column become fused. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Nerves (neurons) Cells of the nervous system are called nerve cells or neurons. They are similar to other cells in your body. The neurons are specialized to carry "messages" through an electrochemical process in between your brain and your body. The human brain has approximately 100 billion neurons. Sensory nerves send messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain through the spinal cord inside your backbone. Motor nerves carry messages back from the brain to all the muscles and glands in your body. Neurons are the oldest and longest cells in the body! You have many of the same neurons for your whole life. Although other cells die and are replaced, many neurons are never replaced when they die. In fact, you have fewer neurons when you are old compared to when you are young. Different parts of the brain Cerebrum (say: suh-ree-brum) The biggest part of the brain is the cerebrum. The cerebrum is the thinking part of the brain and it controls your voluntary muscles — the ones that move when you want them to. So you will need a cerebrum to dance, think and throw a football. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Your memory lives in the cerebrum, both short-term memories and long-term memories. A short-term memory is for example, what you ate for dinner last night. Long-term memory can be, the name of that roller coaster you rode on two summers ago. The cerebrum also helps you reason, like when you figure out that you'd better do your homework now because your mom is taking you to a movie later. The cerebrum has two halves, with one on either side of the head. Some scientists think that the right half helps you think about abstract things like music, colors, and shapes. The left half is said to be more analytical, helping you with math, logic, and speech. Scientists do know for sure that the right half of the cerebrum controls the left side of your body, and the left half controls the right side. Cerebellum (say: sair-uh-bell-um) The cerebellum is at the back of the brain. It's smaller than the cerebrum. It controls balance, movement, and coordination (how your muscles work together). Because of your cerebellum, you can stand upright, keep your balance, and move around. Think about a surfer riding the waves on his board. What does he need most to stay balanced? The best surfboard? The coolest wetsuit? Nope — he needs his cerebellum! Brain Stem The small but mighty brain stem, sits beneath the cerebrum and in front of the cerebellum. It connects the rest of the brain to the spinal cord, which runs down your neck and back. The brain stem is in charge of all the functions your body needs to stay alive, like breathing air, digesting food, and circulating blood. Part of the brain stem's job is to control your involuntary muscles, without you even thinking about it. There are involuntary muscles in the heart and stomach, and it's the brain stem that tells your heart to pump more blood when you're biking or your stomach to start digesting your lunch. The brain stem also sorts through the millions of messages that the brain and the rest of the body send back and forth. Pituitary Gland (say: puh-too-uh-ter-ee gland) The pituitary gland about the size of a pea! Its job is to produce and release hormones into your body. If your clothes from last year are too small, it's because your pituitary gland released special hormones that made you grow. This gland is a big player in puberty too. This is the time when boys' and girls' bodies go through major changes as they slowly become men and women, all thanks to hormones released by the pituitary gland. Hypothalamus (say: hy-po-thal-uh-mus) The hypothalamus controls the temperature inside your body. The hypothalamus knows that your body temperature should be about, 98.6° Fahrenheit or 37° Celsius. If your body is too hot, the hypothalamus tells it to sweat. If you're too cold, the hypothalamus gets you shivering. Both shivering and sweating are attempts to get your body's temperature back where it needs to be. Diseases that Impact the Nervous System On this site you can find the diseases specifically for, brain, nerves, and spinal cord. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/brainandnerves.html Show What Do You Know Now? Download this worksheet (Word Download) and show what you have learned about the Nervous System