Physics L: Universal Gravitation Worksheet
advertisement

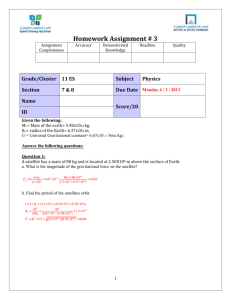
Physics L: Universal Gravitation Worksheet Physics L: Universal Gravitation Worksheet Name ______________________________ Name ______________________________ Conceptual Questions: 1. What quantities does the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of a planet depend upon? Conceptual Questions: 1. What quantities does the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of a planet depend upon? 2. What effect would each of the following changes have on your weight? (Your answer should be double, triple, ½ , not just increase or decrease) a. Double the mass of the Earth, but keep the same radius. b. Triple the radius of the Earth, but keep the same mass. c. You find yourself located at the center of the Earth. d. You move to a distance 4 times as far away from the center of the Earth. 2. What effect would each of the following changes have on your weight? (Your answer should be double, triple, ½ , not just increase or decrease) a. Double the mass of the Earth, but keep the same radius. b. Triple the radius of the Earth, but keep the same mass. c. You find yourself located at the center of the Earth. d. You move to a distance 4 times as far away from the center of the Earth. 3. Which exerts a greater force, the Sun on the Earth or the Earth on the Sun? Support your answer with one of Newton’s Laws. 3. Which exerts a greater force, the Sun on the Earth or the Earth on the Sun? Support your answer with one of Newton’s Laws. Problems: 4. Calculate the force of gravity between two 8.0 kg bowling balls when the distance between their centers is 1.5 m. Problems: 4. Calculate the force of gravity between two 8.0 kg bowling balls when the distance between their centers is 1.5 m. 5. a. Calculate the force of gravity acting on a spacecraft 12,800 km above the Earth’s surface. The mass of the spacecraft is 700 kg and the radius of the Earth is 6.38 x106 m. Mearth = 5.98 x 1024 kg. 5. a. Calculate the force of gravity acting on a spacecraft 12,800 km above the Earth’s surface. The mass of the spacecraft is 700 kg and the radius of the Earth is 6.38 x106 m. Mearth = 5.98 x 1024 kg. b. What would be the escape velocity for the spacecraft at this height. b. What would be the escape velocity for the spacecraft at this height. 6. A hypothetical planet has a mass 1.6 times greater than that of Earth, but has the same radius. What is the value of “g” near the surface of this planet? 6. A hypothetical planet has a mass 1.6 times greater than that of Earth, but has the same radius. What is the value of “g” near the surface of this planet?