cp physics - Brookwood High School
advertisement

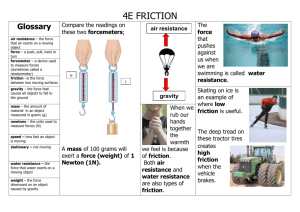
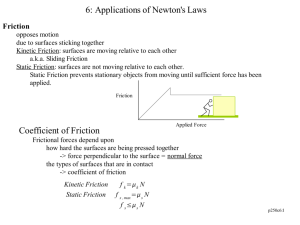
CP PHYSICS FORCES NOTES Four kinds of Forces: 1) Gravitational force force of attraction between two masses weakest of the four forces 2) Electromagnetic force force resulting from moving electric charges gives materials their strength, ability to bend, squeeze, stretch, or shatter 3) Strong nuclear force holds particles in nucleus of the atom together strongest of the four forces 4) Weak force (weak nuclear force) form of electromagnetic force involved in radioactive decay NOTE: contact between objects not necessary some forces act over a distance Equilibrium Forces: concurrent forces are two or more forces acting on the same point at the same time the resultant force equals the concurrent forces added together when all external forces acting on an object cancel out, then Fnet = zero, the object is said to be in a state of equilibrium (object is at rest or moving at constant speed – 1st Law) single force that can put an object in state of equilibrium = equilibrant force, it is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the resultant force ex. resultant = 45 N, east, the equilibrant = 45 N, west Friction: force that opposes motion objects must be in direct contact with each other acts parallel to surfaces involved opposite direction as the motion of the objects 2 causes: 1) microscopic bumps 2) electromagnetic force (temporary attractions between contact points) 2 types: 1) static – opposes the start of motion 2) sliding – force experienced by objects already moving against each other CP PHYSICS, FORCES NOTES, page 2 Friction: (cont’d) static friction is always greater than sliding friction force of friction depends on: 1) nature of the two surfaces 2) smoothness of the surfaces 3) normal force pressing surfaces together Normal force = force equal in magnitude to weight by opposite in direction to weight (points upwards) Centripetal Force: causes object of follow a circular path centripetal = “center seeking” examples: 1) moon in orbit around the earth 2) electrons moving around the nucleus of an atom 3) the tub in a washing machine a) force acts on the clothes not the water b) water has inertia and leaves the tub through the holes c) water has a straight path 4) car going through curve experiences friction between the tires and road which provides the centripetal force centrifugal force – NOT real force, due to object’s inertia (wanting to move in a straight line not a circular path *rubber stopper on a string swung in a circle – the force stops when the string breaks and the stopper moves off in a straight line path according to Newton’s 1st law *way to simulate gravity on a space station is to rotate it so inertia provides the sensation of weight