Name Date Ch 8 Photosynthesis – Biology in Focus Based on AP
advertisement

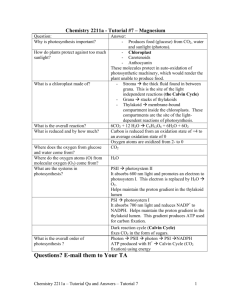
Name _______________________________ Date __________________ Ch 8 Photosynthesis – Biology in Focus Based on AP Biology reading guide by Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Overview 1. As a review, define the terms autotroph and heterotroph. Keep in mind that plants have mitochondria and chloroplasts and do both cellular respiration and photosynthesis! Concept 8.1 Photosynthesis converts light energy to the chemical energy of food 2. Take a moment to place the chloroplast in the leaf by working through Figure 18.3. Draw a picture of the chloroplast and label the stroma, thylakoid, thylakoid space, inner membrane, and outer membrane. 3. Use both chemical symbols and words to write out the formula for photosynthesis (use the one that indicates only the net consumption of water). The formula is the opposite of cellular respiration. You should know both formulas from memory. 4. Using O18 as the basis of your discussion, explain how we know that the oxygen released in photosynthesis comes from water. 5. Photosynthesis is not a single process, but two processes – light reactions and Calvin cycle, each with multiple steps. a. Explain what occurs in the light reactions stage of photosynthesis. Be sure to use NADP+ and photophosphorylation in your discussion. b. Explain the Calvin cycle, utilizing the term carbon fixation in your discussion. 6. Label figure 8.5. Concept 8.2 The light reactions convert solar energy to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH. 7. The most important of the electromagnetic spectrum in photosynthesis is the visible spectrum. What colors are in the visible spectrum? 8. Which colors in the visible spectrum have the most amount of energy? Least energy? 9. Read Figure 8.9. What is the difference between the absorption spectra and the action spectrum? 10. A photosystem is composed of a protein complex called a ___________-__________ complex surrounded by several __________-____________ complexes. 11. Explain what each of the following pigments does in photosynthesis: a.chlorophyll a b. chlorophyll b c. caretenoids 12. Explain what happens when light hits chlorophyll and other pigments. 13. Explain what is happening in Figure 8.12 of a photosystem. 14. There are two photosystems involved in photosynthesis: photosystem I and photosystem II. What is the difference between them? Use the Figure 8.13 to answer questions 16-22. 16. When a photon of light hits the chlorophyll molecule, what happens to an electron? 17. What replaces the electron that got excited? Where did it come from? 18. What is the byproduct of question number 17? 19. Explain what happens in the electron transport chain. 20. Where does the electron go that is passed through the ETC? 21. What is the final electron acceptor after photosystem I? 22. Where does that final electron acceptor go? 23. Using the diagram below, explain how chemiosmosis is involved in photosynthesis. Concept 8.3 The Calvin cycle use the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH to reduce CO2 to sugar. 24. How is the Calvin cycle like the Krebs cycle? How is it different? 25. What is produced from the Calvin cycle? How many times must the Calvin cycle be run to make one of these molecules? 26. Explain what happens in each the stages of the Calvin Cycle. a. Carbon Fixation b. Reduction c. Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor 27. Which enzyme is responsible for Carbon fixation? 28. The net of one G3P requires _____________ molecules of ATP and __________ molecules of NADPH. 29. What is meant by a C3 plant? Give an example. 30. What is photorespiration? When does a plant undergo this? 31. What is the problem with photorespiration? 32. What is a C4 plant? Give an example. 33. How does a C4 plant differ from a C3 plant? 34. What is a CAM plant? Give an example. 35. How does a CAM plant do photosynthesis? 36. How do plants use the photosynthesis products? 37. What is the analogy the textbook makes as to the amount of carbohydrate made per year?