Activity Template
advertisement

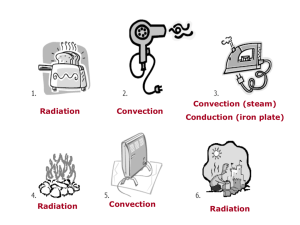
Lesson Proposal Form – Winter Quarter 2012 Your name: Sonya Lopez Title of Lesson: It’s getting hot, hot, HOT! Grade Level: 6th Grade Subject(s): Earth Science Time required/planned for: 90 minutes Summary: The purpose of this lesson is to demonstrate the three types of heat transfer: radiation, conduction and convection. The students learn about the types of heat transfer from a takehome worksheet and in-class lab. They complete a heat transfer worksheet before the lesson that includes pictures of household items that involve 1 or more methods of heat transfer. The lab includes two demonstrations (done by me) and one performed by the students in groups. The demonstrations I perform include a wax dot and match demonstration. The wax dot demonstration highlights how metal and other materials conduct heat and the match demonstration shows how radiation excites molecules enough to ignite the match from a distance. Then students break into groups to perform a convection experiment using hot and cold water placed under a larger water container. Using color dye they can see how differing water temperatures affect the dye movement. The learning goals are: 1. Students will be able to distinguish between conduction, convection and radiation. 2. They will be able to identify what type of heat transfer is used for household items. 3. They will be able to explain how heat affects molecules in the air, water and through materials. Level of inquiry: Students will need to drawn on their experience with personal household items to identify the type of heat transfer is occurring. They justify if 1 or more heat transfer is being used. For their group experiment, they write a hypothesis based on their prior knowledge with hot and cold water to determine how the dye will move in their experimental apparatus. Introduction / Motivation: Mr. Adamucci and Mrs. Daggett go over the heat transfer presentation they prepare to supply students with their notes. For homework, they are handed my heat transfer worksheet that starts with them completing the definition of each heat transfer. Then using the definitions, they are given 12 pictures to describe which type(s) of heat transfer are occurring. Since they are familiar with the household products they should be able to provide clear justification for their choice. Procedure: Homework (Attachment #1): Students complete the following worksheet (answers provided) Lab (Attachment #2): 1. Read through the laboratory description (Page 1 and 2) 2. Draw the experimental set-up on Page 1 for the Wax and Match demonstrations 3. After the demonstrations the students fill the heat source, direct heat moves and the type of heat transfer occurring for each demo. 4. Students then break into groups to perform their experiment showing heat convection (see attachment for procedure) a. Must read procedure and concisely formulate a hypothesis b. Follow instructions and create set-up (similar to what’s shown in Results section). c. Answer discussion question about molecule movement d. Readdress hypothesis within the conclusion Lesson Closure: We used the discussion question as the lesson closure. Most students needed some guidance for this section because they understood what happens to hot water (rises) and cold water (sinks), but did not understand from the perspective of molecules. We openly discussed how the molecules were excited within the hot section of the container and this allowed them to move quickly and the red dye dispersed. We also discussed the molecule movement in the other two demonstrations. Is this lesson based upon or modified from existing materials? If yes, please specify source(s) and explain how related: No. References: Power Sleuth, 2009. Energy Heats Maine—Lesson 5 PDF, Main Energy Education Curriculum Available at: http://www.powersleuth.org/docs/EHM%20Lesson%205%20FT.pdf Conduction, Convection and Radiation Worksheet. Available at: http://cyfair3.schoolwires.net/195120511192812467/lib/195120511192812467/_files/CCR_ Practice.pdf Youtube videos: Convection (Pie dish lab): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OojnMRWoucE&feature=related Conduction (wax dot) : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-UcBRveX_78 Attachments: 1. Heat Transfer worksheet 2. It’s getting hot, hot, HOT lab 3. Classroom PowerPoint presentation List CA Science Standards addressed: Heat (Thermal Energy) (Physical Science)—Heat moves in a predictable flow from warmer objects to cooler objects until all objects are at the same temperature. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: energy can be carried from one place to another by heat flow, or by waves including water waves, light and sound, or by moving objects. when fuel is consumed, most of the energy released becomes heat energy. heat flows in solids by conduction (which involves no flow of matter) and in fluids by conduction and also by convection (which involves flow of matter). heat energy is also transferred between objects by radiation; radiation can travel through space. Supplemental questions: How do the activities of the lesson support the learning goals? Using the worksheet, extensive discussion and demonstrations the students are overly exposed to the types of heat transfer that occur. How will you connect and make this relevant to the students’ lives? The connection is made when the students are asked to identify the type of heat transfer that occurs when using their household products. There shouldn’t be guessing because the students should know if direct contact is involved (conduction), air or fluid is warmed (convection) or if there is a light source emitting electromagnetic waves (radiation). How will you foster student-student interactions, and/or student engagement in general? They will have to work as a group to fill in their experimental results (drawings), and address whether their original hypothesis was correct. How will you address different learning styles (auditory, visual, hands-on)? Visual—drawing the experimental apparatus Hands-on—performing convection experiement. Unfortunately students cannot handle matches or candles and are unable to perform the conduction and radiation experiments. Auditory—instead of performing the match and wax demo they must pay attention to me as I perform them. Students were encouraged to come closer to the front to observe if they could not see from their seat. How do you plan to assess student understanding? The discussion question was purposely added to address student understanding. They have to clearly explain molecule movement and how it travels from the heat source in each demonstration. **Do you have specific questions or areas for which you would like group feedback? Name _____________________________ Date ______________Period ____ Heat Transfer Worksheet Fill in the blanks using the correct form of heat transfer 1. The transfer of heat through material by direct contact is 2. CONVECTION CONDUCTION . is the transfer of heat in a fluid (gas or liquid) as a result of the movement of the fluid itself. 3. What kind of heat transfer does the sun use? (hint: it transfers heat via electromagnetic waves through space). RADIATION Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer. 1 2 3 RADIATION CONVECTION CONVECTION (steam) CONDUCTION (iron plate) 4 RADIATION 5 CONVECTION 6 RADIATION 7 RADIATION (coals) CONVECTION (air) CONDUCTION (grill) 8 CONVECTION (oven) CONDUCTION (gloves + pan) 9 CONVECTION 10 RADIATION (flame) CONDUCTION (pan) 11 CONDUCTION 12 CONVECTION Last Name ______________________ First Name _____________________ Date ________________Period ____ Methods of Heat Transfer—Laboratory (Conduction, convection, and radiation) Demonstrations In the box below, draw a picture of the demonstration. Label the heat source, the direction(s) heat is moving and describe the type (convection, conduction or radiation) of heat transfer that is taking place. Match Demonstration Wax Dot Demonstration CONDUCTION RADIATION RADIATION HEAT SOURCE HEAT SOURCE Hot/Cold Lab QUESTION What happens when we cold half a container of water and warm the other half? How will the heat current move? What kind of heat transfer is occurring? HYPOTHESIS If we add blue dye above the cold section of the container, then the dye will ____________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ If we add red dye above the hot section of the container, then the dye will ____________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ PROCEDURE 1. Fill the plastic container with room temperature water—about 5 cm deep 2. Place a cup of ice under one side of the container and a cup of hot water under the other 3. Let the water settle (allow time for the cold section to cool and warm section to warm) 4. Use two droppers for the dye colors – Cold section—Blue dye – Hot section—Red dye 5. At the same time release 2-3 drops of dye above the correct sections 6. Use words and pictures to describe what you observe – Where is the cold water (blue dye) moving? – Where is the hot water (red dye) moving? 7. Clearly state what type of heat transfer this is RESULTS In the box below, draw a picture of the set up. Label the heat sources, the direction(s) heat is moving and describe the type (convection, conduction or radiation) of heat transfer is taking place. Cold water Hot Water CONVECTION Discussion What happens to the heat when it leaves the energy source? Explain what happens to the molecules. __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Conclusion Was your Hypothesis for the plastic container demonstration correct? Explain __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________