Kinematic Equations and Problem Solving
advertisement

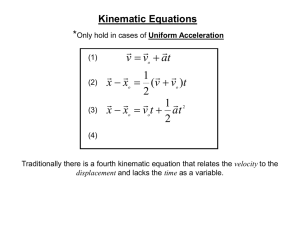
Kinematic Equations and Problem Solving The four kinematic equations which describe the mathematical relationship between the parameters which describe an object's motion are as follows: In the above equations, the symbol d stands for the displacement of the object. The symbol t stands for the time for which the object moved. The symbol a stands for the acceleration of the object. And the symbol v stands for the instantaneous velocity of the object; a subscript of i after the v (as in vi) indicates that the velocity value is the initial velocity value and a subscript of f (as in vf) indicates that the velocity value is the final velocity value. We will investigate the process of using the equations to determine unknown information about an object's motion. The process involves the use of a problem-solving strategy which will be used throughout the course. The strategy includes the following steps: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Construct an informative diagram of the physical situation. [Draw a Picture] Identify and list the given information in variable form. [List knowns] Identify and list the unknown information in variable form. [List unknowns] Identify and list the equation which will be used to determine unknown information from known information. [Find a formula] Substitute known values into the equation and use appropriate algebraic steps to solve for the unknown information. [Plug and Chug] Check your answer to insure that it is reasonable and mathematically correct. [Reality Check] Example A Ima Hurryin is approaching a stoplight moving with a velocity of +30.0 m/s. The light turns yellow, and Ima applies the brakes and skids to a stop. If Ima's acceleration is -8.00 m/s2, then determine the displacement of the car during the skidding process. (Note that the direction of the velocity and the acceleration vectors are denoted by a + and a - sign.) The solution to this problem begins by the construction of an informative diagram of the physical situation. This is shown on the next page. The second step involves the identification and listing of known information in variable form. Note that the vf value can be inferred to be 0 m/s since Ima's car comes to a stop. The initial velocity (vi) of the car is +30.0 m/s since this is the velocity at the beginning of the motion (the skidding motion). And the acceleration (a) of the car is given as - 8.00 m/s2. (Always pay careful attention to the + and - signs for the given quantities.) The next step of the strategy involves the listing of the unknown (or desired) information in variable form. In this case, the problem requests information about the displacement of the car. So d is the unknown quantity. The results of the first three steps are shown in the table below. Diagram: Given: Find: vi = +30.0 m/s d = ?? vf = 0 m/s a = - 8.00 m/s2 The next step of the strategy involves identifying a kinematic equation which would allow you to determine the unknown quantity. There are four kinematic equations to choose from. In general, you will always choose the equation which contains the three known and the one unknown variable. In this specific case, the three known variables and the one unknown variable are vf, vi, a, and d. Thus, you will look for an equation which has these four variables listed in it. An inspection of the four equations above reveals that the equation on the top right contains all four variables. Once the equation is identified and written down, the next step of the strategy involves substituting known values into the equation and using proper algebraic steps to solve for the unknown information. This step is shown below. (0 m/s)2 = (30.0 m/s)2 + 2*(-8.00 m/s2)*d 0 m2/s2 = 900 m2/s2 + (-16.0 m/s2)*d (16.0 m/s2)*d = 900 m2/s2 - 0 m2/s2 (16.0 m/s2)*d = 900 m2/s2 d = (900 m2/s2)/ (16.0 m/s2) d = (900 m2/s2)/ (16.0 m/s2) d = 56.3 m The solution above reveals that the car will skid a distance of 56.3 meters. (Note that this value is rounded to the third digit.) The last step of the problem solving strategy involves checking the answer to assure that it is both reasonable and accurate. The value seems reasonable enough. It takes a car some distance to skid from 30.0 m/s (approximately 65 mi/hr) to a stop. The calculated distance is approximately one-half a football field, making this a very reasonable skidding distance. Checking for accuracy involves substituting the calculated value back into the equation for displacement and insuring that the left side of the equation is equal to the right side of t he equation. Indeed it is! Another in class example Ben Rushin is waiting at a stoplight. When it finally turns green, Ben accelerated from rest at a rate of a 6.00 m/s2 for a time of 4.10 seconds. Determine the displacement of Ben's car during this time period. Notes from Tom Henderson of Glenbrook South High. For additional physics class materials visit http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/phys/Class/BBoard.html