Chapter 14 Light
advertisement

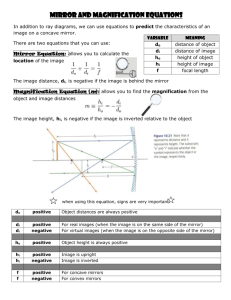
Chapter 14 Light 14.1 Characteristics of Light Electromagnetic spectrum: who, order/ timeframe founded; order of waves- radio, micro… c = f brightness 14.2 Flat Mirrors Specular vs diffuse reflection Reflection- incident and reflected angles Virtual images; same distance from mirror; appear behind mirror Ray tracing for flat mirrors 14.3 Curved Mirrors Mirror equation p is object distance; do q is image distance; di Magnification ho is object height hi is image height know that a negative M is inverted; less than one is smaller; negative also means real Concave = converging; convex = diverging Focal point, center of curvature Ray Tracing: 1. in parallel to principle axis; out through focal point 2. in through focal point; out parallel to principle axis 3. in and out through center of curvature (2f) 4. (know how to extend back reflected lines behind the mirror for virtual images) Concave mirror: Focal distance is positive (in front of the mirror) Object beyond 2f: inverted, smaller, real, between f and 2f Object at 2f: inverted, same size, real, at 2f Object between f and 2f: inverted, larger, real, beyond 2f Object at f: no image Object between f and the mirror: upright, larger, virtual, behind the mirror Know the trends such as: is a real image ever upright? Convex mirror: Object always upright, smaller, virtual, behind mirror *focal distance is negative!! (Even if I don’t give you a negative number) Be able to draw all of these as well as use the equations to find the number that go with them 14.4 Color and Polarization Know how light is polarized, what it means, some applications, what happens when it is reflected White light is composed of all the colors of the spectrum An object looks the color it does because that is the color of light it reflects- it absorbs all other colors of light Primary colors of light Red green blue- additive (all make white) R + B = magenta R + G = yellow B + G = cyan Primary colors of pigments Magenta, yellow, cyan- subtractive (all make black) Magenta reflects only blue and red light Cyan reflects only blue and green light Yellow reflects only red and green light So… if you shine blue light on a green frog, the frog looks black because it only will reflect green-- blue light has no green in it! If you shined cyan light on a green frog, it would look green because there is green light to be reflected. In a room with a red bulb, the only colors you see are red or black. In a room with a magenta bulb, you could see blue objects, red objects, magenta objects- basically you’d see anything that reflects red or blue and everything else would look black. With a magenta bulb, a cyan object would look blue because cyan reflects blue and green—a magenta bulb provided the object with blue light to reflect, but it does not give the object any green light to reflect back. Objects can only reflect certain colors of light- if you don’t give it that color to reflect, it won’t! The test should be an opportunity for you to try to bring your grade up- PLEASE study!!!