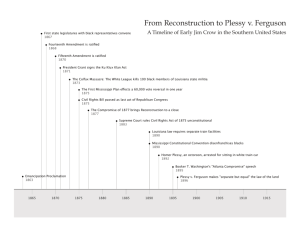
Mallory Frank Lesson Plan: Plessy vs. Ferguson Narrative This
advertisement

Mallory Frank Lesson Plan: Plessy vs. Ferguson Narrative This lesson is part of the Plessy vs. Ferguson unit. The students have already learned the basis of the Plessy vs. Ferguson court case. In this lesson, we are focusing more on the separate but equal aspect. In the guided practice, the students will get a feel of how it felt back then to always have to be separated. Instead of using race, I used their hair color to separate them because it is something they are born with. They do not choose their hair color, just like we don’t choose our race. While they are getting to see a glimpse of how it really was during the early twentieth century, they are learning facts about what happened during that time period—specifically separate but equal laws. 1. Demographics: Name: Mallory Frank Grade level of lesson: 3rd grade Subject/Concept: Social Studies/ Plessy v. Ferguson: Separate but equal Duration of lesson: 50 minutes 2. Objective (s): TSWBAT recall facts about the separate, but equal laws with 80% accuracy. 3. Standard/Benchmark /GLE: W1- Write opinion pieces on topics or texts, supporting a point of view with reasons a.) Introduce the topic or text they are writing about, state an opinion, and create an organizational structure that lists reasons. b.) Provide reasons that support the opinion. 4. Introduction (1 minute): TTW have two sets of the same items in the front of the room. The two sets will include textbooks, crayons, markers, and note cards. One set of materials will be brand new. The other set of materials will be used and old. I will tell the students to look at the two sets of materials and think about which set they would rather use. I will then begin my lesson. 5. Procedures/Activities/Experiences/Concept Development: Guided Practice 1 (20 minutes): We will go on a small “tour” of the school. Throughout the “tour,” there will be 4 stops (bus stop, water fountains, bathroom, and cafeteria). Each stop will be a model of what those places would have looked like during the Plessy v. Ferguson case. For example, the “bus” will be divided into a “Colored” section and a “Whites” section. At each stop there will be sentence strips and real life pictures to look at. Some sentences will have terms that have to do with separate, but equal laws and the others will have the definitions. In groups that I assign, the students will have to put the terms, definitions, and pictures together correctly to move on to the next station. Guided Practice 2 (15 minutes): Once we return to class, each table group will have to talk about how they felt during the activity. They will then write their own paragraph on their opinion of the separate but equal laws. Each paragraph must have an introduction, stated opinions, and reasons to support their opinion. They are allowed to ask their table group questions to get ideas and to hear other’s opinions. We will have a short grand discussion about the facts they learned about separate, but equal laws, as well as how they would feel if they lived during those times when segregation was so prevalent. We will compare our activity to the way America was during the Plessy vs. Ferguson case. We will also discuss why Plessy was going against the separate but equal law. Independent Practice 1 (10 minutes): The students will have a quiz to take independently with questions from what they learned in the class activities. This activity will serve as the formal assessment. (See attached assessments.) 6. Closure/Confirm (4 minutes): TTW revisit the two sets of materials in front of the class and ask them which set they would rather use. I will ask them what court case and law it would remind them of if I told them that a certain group of people had to use the old materials and the rest could use the new materials. I will ask if treating people equally means treating them the same and who tried to put an end to this inequality. 7. Assessment/ Evaluation: Independent Practice #1 acts as formal assessment. See attached. 8. Materials: -Broken or old supplies (textbooks, markers, crayons, note cards) -pictures -sentence strips 9. Resources/References: References: -http://www.loc.gov/index.html -http://myloc.gov/Exhibitions/naacp/prelude/Pages/default.aspx http://www.streetlaw.org/en/landmark/cases/plessy_v_ferguson#Tab=Bac kground 10. Accommodations/Individual Differences/Learners' needs: -Social (Interpersonal) Intelligence-Guided Practice 1 and 2-During the class discussions and group work the students can talk to their classmates about their opinions and thoughts, which accommodates the social intelligences. - Self (Intrapersonal) Intelligence- Guided Practice 2- The students will be able to have the choice to independently write their opinion of the separate, but equal laws and give support. -Spatial Intelligence-Guided Practice 1-Being able to see and physically match the models and pictures will accommodate the spatial intelligence. -Kinesthetic-Guided Practice 1-Walking around the school to the different sections allows these students to get up and move the sentence strips around to learn the facts about separate but equal laws. Modifications: -In guided practice 2, the lower level students will have to state one opinion they have about the separate, but equal laws and give only ONE reason to support their opinion. -In guided practice 2, the higher level students will have to state one opinion they have about the separate, but equal laws and give THREE reasons to support their opinion. They must add in facts and examples to support their opinion that they learned from the class. I will also have them write what they think Homer Plessy’s opinion was of the separate, but equal laws. Assessment for Lower level students: Directions: Place a + in the blank if the statement is true, and 0 if the statement is false. (1 pt. each=5 pts total) _____1. The Separate Car Act was a law passed by Homer Plessy saying that Black Americans could not ride in the same car as White Americans. _____2. The Separate but Equal legal doctrine made segregation legal. _____3. An example of segregation is forcing Black Americans to sit in the back of a train away from the White Americans. ______4. Separate but equal laws only applied to riding in trains. _____5. John Howard Ferguson found Plessy guilty and said The Separate Car Act was constitutional. Assessment for average level students: Directions: In the blank provided, place the LETTER of your choice from column B in the corresponding statement in Column A. (1 pt each=5 pts total) Column A _____1. A law passed in Louisiana stating that separate, but equal accommodations must be made in train cars for Black Americans and White Americans. _____2. The Separate but equal legal doctrine made segregation _____. _____3. An example of this would be forcing Black Americans to sit in the back of a train away from the White Americans. _____4. These type of laws made it legal to separate Black and White Americans in hotels, buses, school, and even cemeteries. _____5. The man who found Homer Plessy guilty and stated that the Separate Car Act was constitutional. Column B A. Separate but Equal B. Segregation C. Homer Plessy D. Separate Car Act E. Legal F. John Howard Ferguson Assessment for Higher Level Students: Directions: Place the word of your choice in the corresponding blank provided. (1 pt each=5 pts. total) Separate but Equal Separate Car Act Segregation Homer Plessy Legal John Howard Ferguson ____________________1. A law that was passed in Louisiana stating that separate, but equal accommodations must be made in train cars for Black Americans and White Americans is known as the ___. ____________________2. The Separate but equal legal doctrine made segregation ___. _____________________3. Forcing Black Americans to sit in the back of a train away from White Americans is an example of ___. _____________________4. Laws that made it legal to separate Black and White Americans in hotels, buses, school, and even cemeteries were called ___. _____________________5. The man who found Homer Plessy guilty and stated that the Separate Car Act was constitutional is ___. ANSWER KEY: Assessment for Lower level students: Directions: Place a + in the blank if the statement is true, and 0 if the statement is false. (1 pt. each=5 pts total) ___0__1. The Separate Car Act was a law passed by Homer Plessy saying that Black Americans could not ride in the same car as White Americans. __+___2. The Separate but Equal legal doctrine made segregation legal. __+___3. An example of segregation is forcing Black Americans to sit in the back of a train away from the White Americans. ___0___4. Separate but equal laws only applied to riding in trains. __+___5. John Howard Ferguson found Plessy guilty and said The Separate Car Act was constitutional. ANSWER KEY: Assessment for average level students: Directions: In the blank provided, place the LETTER of your choice from column B in the corresponding statement in Column A. (1 pt each=5 pts total) Column A __D___1. A law passed in Louisiana stating that separate, but equal accommodations must be made in train cars for Black Americans and White Americans. __E___2. The Separate but equal legal doctrine made segregation _____. __B___3. An example of this would be forcing Black Americans to sit in the back of a train away from the White Americans. __A___4. These type of laws made it legal to separate Black and White Americans in hotels, buses, school, and even cemeteries. __F___5. The man who found Homer Plessy guilty and stated that the Separate Car Act was constitutional. Column B A. Separate but Equal B. Segregation C. Homer Plessy D. Separate Car Act E. Legal F. John Howard Ferguson ANSWER KEY: Assessment for Higher Level Students: Directions: Place the word of your choice in the corresponding blank provided. (1 pt each=5 pts. total) Separate but Equal Separate Car Act Segregation Homer Plessy Legal John Howard Ferguson ___Separate Car Act___ 1. A law that was passed in Louisiana stating that separate, but equal accommodations must be made in train cars for Black Americans and White Americans is known as the ___. __________legal__________2. The Separate but equal legal doctrine made segregation ___. ___segregation________ 3. Forcing Black Americans to sit in the back of a train away from White Americans is an example of ___. ___Separate but equal_ 4. Laws that made it legal to separate Black and White Americans in hotels, buses, school, and even cemeteries were called ___. John Howard Ferguson 5. The man who found Homer Plessy guilty and stated that the Separate Car Act was constitutional is ___.