study guide exam i – applied math for chemistry
advertisement

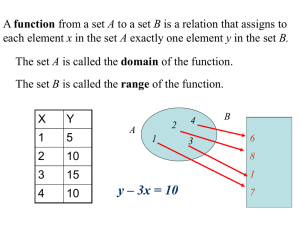
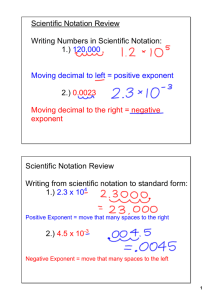
STUDY GUIDE EXAM I – APPLIED MATH FOR CHEMISTRY Thursday September 18th The following concepts from your Course Outcome Guide will be primarily covered on this exam: Decimals and Place Value Exponents and Scientific Notation Units of measurement, both English and Metric Dimensional Analysis, Conversion factor fractions The following skills from the Course Outcome Guide should be reviewed and practiced. Skills: Apply fundamental rules of mathematical operations Examples: addition may be performed in any order and give the same sum, multiplication maybe performed in any order and give the same product, any a number (except 0) divided by itself gives a quotient of 1 ( =1), or the product of a a number and its reciprocal is 1. Perform basic operations with signed numbers; add and subtract signed numbers –32 – (- 8) = -24 Recognize the value of a fraction ( = to 1, greater than 1, or less than 1) and its effect on multiplication Multiply fractions; simplify by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by the same quantity or units (canceling) Convert between fractions and decimals. Divide numerator by denominator. 1 Example: = .20 5 Identify place value of decimal numbers. EXAMPLE: In the number 35.62937 , what value does the digit 9 represent? Write decimal numbers. Example: Write in words: 35.629 Round decimal numbers to a specified place value. Example: 3009.357 rounded to the nearest 10 is 3010, rounded to the nearest tenth is 3009.4 Multiply and divide numbers by a power of ten without a calculator by moving decimal point Perform basic manipulations involving exponents- Handout: Rules of Exponents Identify base and exponent 53 5= base, 3 = exponent 3 5 = 5x5x5=125, multiplying numbers with like bases add the exponents, dividing numbers with like bases, subtract the exponents, Zero as an exponent 30 1 This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner. Understand the relationship between positive exponents (numbers greater than or equal to 1, and numbers with negative exponents (numbers that are less than 1) Write numbers in proper scientific notation (coefficient must be between 1 and 10) Example: 35600 = 3.56 x 104 Convert between standard and scientific notation Use calculators for exponents and scientific notation Correctly interpret the display on a scientific calculator when the result is expressed in scientific notation. Use mental math to estimate answers. Example: 49 x 95 50 x 100 = 500 Identify the base units in the metric system: mass(gram), volume(liter), length(meter) Know the meaning of metric prefixes (nano, micro, milli, centi, deci, deka, kilo, mega, giga) Identify a metric prefix with its power of ten equivalent. Example: milli=10-3 (Metric Prefix Table handout) Construct conversion factor fractions from an equality statement. Example: 1 meter = 1000 mm 1meter 1000mm or 1000mm 1meter Use a conversion table to obtain conversion factor fractions Utilize dimensional analysis as a tool for converting units (convert from mg to kg) Checklist for Dimensional Analysis handout Convert between metric units Convert between English units (conversion table provided) Convert between metric and English units (conversion table provided) Calculate answers using appropriate significant digits Use density as a conversion factor to calculate mass or volume Convert multidimensional unit, unit changes in both numerator and denominator 250miles km ( =? ) hr sec Know and understand the relationship: 1 cm3 = 1 cc = 1 mL Calculate area and volume of a rectangle and convert units between metric and English system. Example: length= 3.6 in, width =1.7in, and height=1in, volume =3.6(1.7)(1) in3 = ? cm Convert between temperature scales if given the formula UTILIZE YOUR QUIZZES, HOMEWORK, AND HANDOUTS AS STUDY TOOLS. Our Blackboard site also has some excellent tutorials from the SWTC Math Science Resource Center web site. Do not hesitate to contact me for questions and clarification. This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.