Torts Mini Review - The Mutrux Law Firm
advertisement

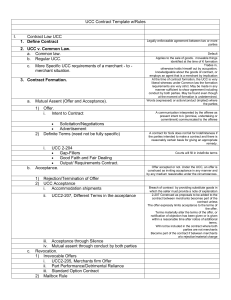
CONTRACTS MINI REVIEW Page |1 FORMATION I. WHAT LAW APPLIES Common Law Real Estate, Services UCC Goods, Structures to be Removed from Land, Crops, Sand, Gravel, Water, Electricity Mix De Minimus, Apportionment (separate elements), Preponderance II. TYPE Formation: Express, Implied (conduct), Quasi (P has Conferred Benefit on D + Reasonable Expectation of Payment + Unjust Enrichment if Not Paid) Validity: Void (Nullity from beginning), Voidable (defect in formation), Unenforceable (No Defect in Formation but Ct Won’t Enforce, S/F, S/L, etc.), Valid Performance: Executed (fully performed) or Executory (not fully performed) III. REQUIREMENTS [LACC] 1. LEGALITY: Illegal subject matter = void; illegal purpose = voidable 2. AGREEMENT: reasonable person/belief (intent) Offer: Willingness to contract – would reasonable offeree believe assent creates a contract Effective: Effective when communicated (actual knowledge; when mail is READ) Essential terms: o Real Estate=description + price o Services = duration (time/task) o Goods = quantity *Requirement/output K = no precatory terms (wish, desire, mandate, want) + in-line w/ prior history Unilateral K: CL (no K until fully performed) UCC (accept by perform or promise to perform) o UCC: Can accept by performance – if ship non-conforming goods must send a NOTICE of accommodation (counteroffer) otherwise acceptance and breach Ads: NOT offer UNLESS specific quantity stated + indication of who can accept Termination: (offer must be viable to be accepted) 4 ways to terminate o Lapse of Time: offer only open for reasonable time unless specifically stated o Revocation by OFFEROR: words/conduct of OFFEROR + awareness of offeree Effective: upon communication (receipt if mail – possession not knowledge) No revocation after acceptance Public: If public, same/comparable publication o Irrevocable Offers: Option K: Promise to keep open + consideration (no set time length) Merchant Firm Offers: Offeror is Merchant + Writing + Signed + Words of Firmness (don’t need consideration) NOT for real estate Time: Irrevocable for promised OR reasonable time (max 3 months) o If have consideration then can be irrevocable forever NOTE: can accept after 3, just able to revoke after 3 months Detrimental Reliance: Det Reliance + Reasonably Foreseeable Unilateral K + Start Performance: Irrevocable for Reasonable Time to Finish o Rejection by OFFEREE: Common Law: 1) Counteroffer (not bargaining) 2) Conditional Acceptance 3) Additional Terms (mirror image rule) = new offer, terminates old Death/Incapacity of either party prior to acceptance terminates Exceptions: Option K OR Part Performance of Unilateral K Acceptance: Assent to the offer Who: Person who knows + person to whom offer is made (options can be assigned) Accept w/ Additional Terms: ***** o CL Mirror Image Rule (no add’l terms/requirements) o UCC Intention controls (objectively) [for goods etc – doesn’t matter if merchants] 1 party NOT merchant: use offered terms BOTH merchants: use acceptance terms UNLESS offer expressly limits, they are *****material alteration, or objection w/in reasonable time Accept by Silence: Prior Dealings, Affirmative Duty to Speak (lawnmower) or Agreement (records club) CONTRACTS MINI REVIEW Page |2 Effective upon Communication: Effective upon dispatch (proper mode + properly dispatched) o Mailbox Rule: never has to arrive so long as proper mode AND properly dispatched o UNLESS offer says acceptance on receipt, option K or rejection arrives 1 st. ***Auctions: Offer (bids), Acceptance (Bang of Gavel), Reserve Presumed o W/o Reserve (seller must sell if bang gavel) W/ Reserve (seller doesn’t have to sell) o Close Case: CL (jury ?) UCC (auctioneer decision) Note: Paying in advance of inspecting does not affect rights to inspect or remedy for breach 3. CAPACITY: Incapacitated Person can Avoid = Voidable When incapacity ends, party can avoid (reasonable time) OR affirm (no new consideration needed) Who Lacks Capacity: Infant (necessities of life exception); Insane; Intoxicated/Drugs ONLY if other party KNOWS; Others (duress, fraud, undue influence etc) 4. CONSIDERATION: Bargained for Legal Detriment Adequacy: Irrelevant Forms: Performance, Forbearance (something legally entitled to do), or Promise of Either Gifts: depends on surrounding circumstances if “bargained for” Past Consideration: NOT consideration (even if they say it is consideration when making deal) Pre-Existing Legal Duty: CL Need consideration to modify a contract o Exceptions: Unforeseen difficulty so severe as to excuse performance (quicksand/bedrock in home construction); OK if owed to 3rd party promises more UCC OK if good faith, no new consideration needed to modify a contract Mutuality: There must be mutuality of consideration (not illusory consideration) Requirement/output mutual unless precatory terms Satisfaction Clauses Not illusory b/c getting good faith presumption of satisfaction Exclusive Agency Not illusory b/c getting best efforts to sell the goods Notification Requirement (Must give x days notice) Not Illusory o If it just says either party may cancel = illusory CONSIDERATION SUBSTITUTES: Promise to Pay Barred by Technical Defense = Written promise to pay a debt barred by a technical defense is consideration sub (credit mgr’s trick) Release of Breach Claim = Written release for breach of sale of goods K is consideration sub Promissory Estoppel (Det Rel) = promise + reliance that is detrimental/foreseeable/and reasonable + enforcement necessary to avoid injustice; PE better that DR b/c dam > or = IV. DEFENSES TO FORMATION 1. Statute of Frauds MY LEGS = Marriage, Year, Land (sale), Executor (promise to pay from personal funds), Goods >$500, Surety (unless benefits surety) K to build building not w/in SOF unless can’t be built w/in a year by its terms Requires: Writing + Signed by D (letterhead OK). Equal dignity rule (agency K can be oral) Exceptions: SWAP Specially Manufactured Goods: substantial beginning + unsuitable for others (Entire K enforceable) Written Merchants Confirmation: (UCC) BOTH merchants + written (by P but not signed by D) confirm of oral K for GOODS + 10 days to object Admission: (in ct/pldgs) Admission of oral K then enforced to extent of admission o NO privilege of self-incrimination; NO privilege of Statute of Frauds; NO objection b/c irrelevant/immaterial; LIE to keep in S/F Performance: Performance by 1 party takes it out of SoF o CL FULL performance by 1 side (unless real estate) o UCC Partial performance to extent of performance 2. Mistake, Misrepresentation or Fraud: Fraud: Fraud (didn’t know signing K) = VOID Fraudulent Misrepresentation = VOIDABLE IF justifiably relied Non-Fraudulent Misrepresentation = VOIDABLE IF justifiably relied + material (would induce reasonable person or knew would induce this person Mistakes: CONTRACTS MINI REVIEW Page |3 Unilateral Mistake -> NOT a defense UNLESS other party knew or should have known Bilateral Mistake -> DEFENSE if basic assumption of fact (basis of the bargain) + materially affects agreed exchange 3. Unconscionability = NO K – Measured at time of contracting (inconspicuous risk shift, adhesion, unreasonable covenant not to compete (not allowed in law at all)) V. **RIGHTS OF NON-PARTIES o 3rd Party Beneficiaries: intended beneficiary (must be stated in K) can hold promisor + promisor can use defenses + CREDITOR beneficiary an hold promisee on original debt + incidental (unintended) beneficiaries cannot hold anyone + modification OK until vesting (knowledge + action) + promisee can enforce K against promisor o Assignment: All rights can be assigned UNLESS prohibited by law, unique personal service, or substantial change o MUST have present transfer but NOT necessarily writing/consideration o Assignee can hold obligor unless notice o Assignor out of picture once assign the rights o Delegation: All duties can be assigned UNLESS prohibited by law, unique personal service, or substantial change o Must have present transfer but NOT necessarily writing/consideration o Obligee MUST accept BUT delegator remains liable TERMS I. PAROL EVIDENCE RULE Rule: Written integration = NO extrinsic evidence Exceptions: CL: clarify ambiguity, fraud/duress, or subsequent agreement (no such thing as unamendable K) UCC: usage of trade, course of dealings, course of performance II. PERFORMANCE (goods/UCC) Seller: PERFECT tender + single delivery Non-Carrier -> Seller’s Place of business Carrier -> Destination (deliver to buyer’s place of business) = FOB (buyer $/risk); FAS (seller $/risk) Shipment (deliver to shipper) = C&F (K price = cost and freight); CIF (K price = CI + freight) Buyer: Pay (concurrent w/ delivery ) + must give time to get cash if demanded III. RISK OF LOSS – ALWAYS ON EXAM ******* NO Breach: Non-Carrier: Seller Merchant -> Risk passes on possession Seller Non-Merchant -> Risk passes on tender Carrier: C&F or CIF -> risk on Buyer FOB or FAS -> Risk on Seller It doesn’t specify delivery to particular location risk of loss passes to buyer on giving to carrier Breach: Risk on SELLER UNLESS Acceptance despite breach Cured the breach 1) Within proper time OR 2) addt’l time if reasonable belief would accept non-conforming goods (prior history OR new model old price) Trial Period: “Sale or Return” (Risk on buyer during trial) OR “Sale on Approval” (Risk on seller during trial) Building Contracts: New building (risk on builder) Old Building (risk on owner) CONDITIONS I. TYPES Timing: Precedent (occur before duty arises), concurrent (2 precedent); subsequent (not occur during K period) Burden of Proof: On P for precedent or concurrent; On D for subsequent Formation: Express, Implied, Constructive II. SATISFACTION OR EXCUSE CONTRACTS MINI REVIEW Page |4 Satisfaction: CL: Substantial Performance UCC: Perfect Tender Excuse: Prevention -> if you prevent condition from occurring you waive the condition Anticipatory Breach -> excuses condition - can sue NOW (executory bilateral K + unequivocal) Breach -> breach by one party excuses condition of the other party to perform Excuse by Substantial Performance -> If performance is precondition to other party perform (constructively). Substantial perform excuses condition of perfectness under CL (UCC – perfect tender) Divisibility/Installment -> Performance divided into 2 or more parts + # of parts same for both + performance of each part is equivalent of the other = entitled to $ of units performed even if not all Installment -> Have to show substantial impairment of part or all to reject part or all Waiver -> AFTER condition is broken statement that won’t require condition Estoppel -> BEFORE condition is to occur statement wont’ require condition ******WARRANTIES – ALWAYS ON EXAM I. TYPES Constructive Warranty of Title: Will give good title (imposed on merchants AND non-merchants by law) Constructive Warranty of Infringement: No copyright, trademark etc infringement (merchants ONLY) Implied Warranty of Merchantability: Goods will be fit for ORDINARY PURPOSE (merchants ONLY) Implied Warranty of Fitness for Particular Purpose: Buyer has PARTICULAR purpose + Seller has reason to know + buyer relying on seller (merchants AND non-merchants) Express Warranties: Affirmation of fact through language (distinguish “puffing”) (innocent misrep still breach) II. DISCLAIMERS ALL warranties can be disclaimed Merchantability -> Must be express and use word conspicuously Implied Warranties (Merch or Fitness) -> can use “AS IS” clause Federal Consumer Protection Law: no disclaimer of implied if full written warranty issued; no ty-ins unless totally w/o costs for parts and labor; lemon problem (consumer chooses remed) III. BENEFICIARIES Warranties extend to FAMILY, HOUSEHOLD, OR GUESTS in the HOME DISCHARGE (EXCUSE OF PERFORMANCE) I. 12 WAYS TO NOT BE IN BEACH 1. Performance perfectly 2. Tender if tender goods can’t be sued (tender = ready, willing, and able to perform) 3. Condition Subsequent Occurs cut off duty to perform 4. Impossibility Objectively performance can’t be done (no one could perform) not subjective (this D can’t do) CL illness = discharge in SERVICE contracts UCC destruction of ID’ed goods, transportation failure (when K about what carrier to use MUST tender/accept reasonable substitute), or failure of presupposed condition (e.g., oil – allocate) 5. Commercial Frustration event occurring AFTER K formation, but before K performance + unforeseen + affecting either party’s ability to perform OR the value of performance (hurricane) 6. Rescission executory x 2 + cancel (performance still remaining on both sides and cancel) 7. Cancellation executory x 1 + cancel (one party has performed and cancel) 8. Novation substitution of new party + consent by ALL 3 = discharge of original party’s duties after novation 9. Accord/Satisfaction (Compromise) Parties do something different that will satisfy existing terms Accord = Executory promise (the compromise) Satisfaction = Performance of the accord If no satisfaction, the non-breaching party can sue on EITHER the accord or the original promise 10. Account Stated Unliquidated claim (no fixed $ agreed to before) + amt “offered” in payment + amt accepted 11. Lapse/Laches If neither party acts w/in reasonable time after K term, then K lapses and neither is in breach (occurs BEFORE running of statute of limitations) 12. Judgment/Merger If you get jdgmt for breach and give damages can’t sue again for original K amt CONTRACTS MINI REVIEW Page |5 BREACH AND REMEDIES I. BREACH Common Law: Substantial Performance (mat’l breach -> excuse other party; minor breach -> no excuse) UCC: Perfect Tender bracketed by good faith II. REMEDIES Land (rent or sale): Specific Performance (both sides can get) UNLESS transferred to BFP Damages Types: Goal: Put the non-breaching party in position would have been in w/o the breach Expectation: Those that flow directly and immediately as a natural consequence of the D's actions Generally Damages = K price +/- (EITHER FMV (can’t cover) OR Sale/purchase price (cover/resell) + Incidentals – Expenses Saved Consequential: Those that do not always flow from the D's conduct – D only liable for foreseeable damages Foreseeable: When the parties made the K did the D know of the special circumstances that would cause them to a reasonable person to foresee the result Nominal: Hurt but not legally injured (get $1) Stipulated/Liquidated: Agreed on amt or method to calculate in advance K can NOT provide for PENALTY TEST: at time of K amt is 1) difficult to determine + 2) provision is reasonable forecast Punitive: NOT allowed in private K law (b/c goal to put in place would be in w/o breach) III. BAD SELLER FOR GOODS No Goods Tendered: Buyer can 1. Cover (reasonable + seasonable) damages = K price – purchase price 2. Sue for K damages = K price - FMV (at time of discovery of breach) 3. Specific Performance (only when inadequate remedy at law – unique goods or can’t cover) Tender Non-Conforming Goods: buyer has 2 options 1. Reject Single Delivery K (assumed) Non perfect goods unless curable (in original time or reas belief) Installment K Substantial Impairment 2. Accept Knowingly: Can still get damages = Value non-conforming goods – Value of conforming goods Unknowing: Can reject acceptance (std: substantial impairment – not perfect tender b/c accepted) IV. BAD BUYER FOR GOODS Insolvent Buyer: Not a breach. Options - 1) not deliver unless get cash 2) stop delivery in transit (only lots – whole truck) 3) reclaim the goods (if go bankrupt 10 days of delivery – exclusive remedy if you use this) Wrongful Rejection: Options 1) sell to another (D=K price – substitute sale price) 2) K Damages if can’t resell (D=FMV – K price (w/o reselling) 3) lost profits (only if volume seller) – NOT specific performance V. BAD BUYER OR SELLER Anticipatory Repudiation/Breach: Neither party has performed + unequivocal Can suspend your performance and either sue now or sue later Right to Demand Assurances: When other side short of anticipatory breach must demand assurances in writing and if no response w/in 30 days becomes anticipatory repudiation Damages: Incidental/Consequential – Savings Incidental: Things connected to transaction (Buyers OR sellers) Consequentials: foreseeable to reasonable person (BUYERS ONLY) Mitigation: Duty to mitigate on BOTH sides **GET EXTRA CREDIT IF SAY NEED TO REDUCE TO PRESENT VALUE THIRD PARTY RIGHTS General Rule: Buyer gets title of seller – except buyer may ACHIEVE better title in some situations Accession: Added value to PERSONAL property (b/c can’t have fixtures on chattels) Cash: Even a thief can convey good title to cash Holder in Due Course: Takes free of personal defenses (including a claim of ownership) Intermingling (CL Confusion): Mandates a divvy (equal proportion). Following the divvy confusion gives finality (cows) **Entrustment: Owner (not bailee) + Merchant + Buyer in Ordinary Course = Gets title (watch) CONTRACTS MINI REVIEW Voidable Title: Intentional sale b/c of fraud, but later sold to BFP Estoppel: Detrimental Reliance Page |6