Prentice hall Biology Worksheets
advertisement
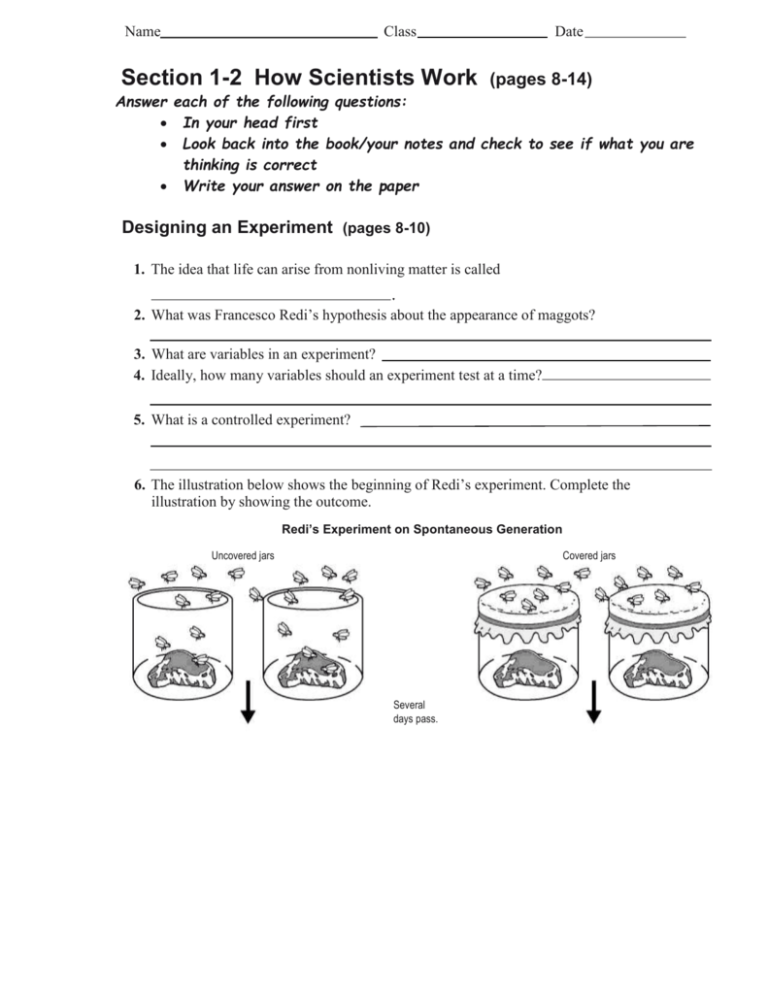
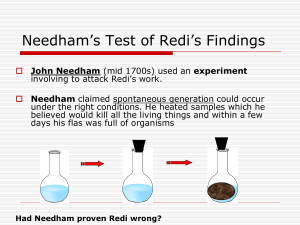
Name Class Section 1-2 How Scientists Work Date (pages 8-14) Answer each of the following questions: In your head first Look back into the book/your notes and check to see if what you are thinking is correct Write your answer on the paper Designing an Experiment (pages 8-10) 1. The idea that life can arise from nonliving matter is called 2. What was Francesco Redi’s hypothesis about the appearance of maggots? 3. What are variables in an experiment? 4. Ideally, how many variables should an experiment test at a time? 5. What is a controlled experiment? 6. The illustration below shows the beginning of Redi’s experiment. Complete the illustration by showing the outcome. Redi’s Experiment on Spontaneous Generation Uncovered jars Covered jars Several days pass. Variables In a controlled experiment, only one variable is changed. This is called the manipulated variable. The variable that changes in response to the manipulated variable is called the responding variable. The variables that are kept constant are called controlled variables. Identify the manipulated variable, the responding variable, and two of the controlled variables in the experiment shown. Types of Variables Manipulated Variable Responding Variable Gravy is boiled. Gravy is boiled. Flask is open. Flask is sealed. Controlled Variables Gravy is teeming with microorganisms. Gravy is free of microorganisms. Use the diagram and table to answer the question. 7. Suppose the scientist had put one type of gravy in the flask he left open and another in the flask he sealed. Would this be a well-designed controlled experiment? Explain. ______________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 8. In Redi’s experiment, what were the manipulated variable and the responding variable? 9. For what do scientists use the data from a controlled experiment? 10. When scientists look for explanations for specific observations, what do they assume about nature? Repeating Investigations (pages 10-12) 11. Why do scientists assume that experimental results can be reproduced? 12. What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek discover? 13. What did John Needham conclude from his test of Redi’s findings? 14. What did Spallanzani do to improve upon Redi’s and Needham’s work? ________________________________________________________________________ Pasteur’s Test of Spontaneous Generation The theory of spontaneous generation stated that life could arise from nonliving matter. Louis Pasteur did an experiment that disproved this theory. He put boiled broth in a flask that allowed air but not microorganisms to reach the broth. A year later, he broke the neck of the flask. Color the broth in the flask in which microorganisms grew. 1 Year Passes Use the diagram to answer the questions. 15. Would the results of this experiment have changed if Pasteur had let the unbroken flask sit for three years instead of one? Why or why not? ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ When Experiments Are Not Possible (page 13) 16. In animal field studies, why do scientists usually try to work without making the animals aware that humans are present? 17. When a controlled experiment is not possible, why do scientists try to identify as many relevant variables as possible? How a Theory Develops (pages 13-14) 18. 19. In science, what is a theory? Is the following sentence true or false? A theory may be revised or replaced by a more useful explanation.