Dear Parents
advertisement

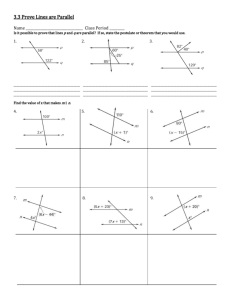
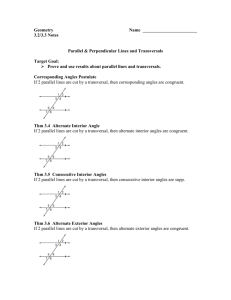
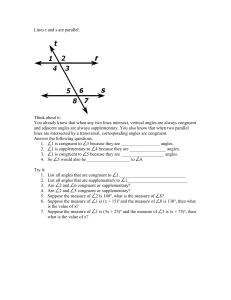
Math 8 Unit 6 Traversing Congruency Volume 1 Issue 6 References Helpful Links: http://www.studystack.com/s tudytable-56459 http://www.mathnstuff.com/ math/spoken/here/2class/26 0/trans.htm http://www.studyzone.org/m testprep/math8/g/8parallelan glepairsl.cfm Mathematics Course 3 Textbook Connection: Chapter 7, Lessons: 2 & 5 and Lab 7-2 Mathematics Course 3 Textbook Online: http://go.hrw.com/resour ces/go_mt/hm3/so/c3ch7 aso.pdf http://my.hrw.com/ma th06_07/nsmedia/hom ework_help/msm3/ms m3_ch07_02_homewor khelp.html Dear Parents Below you will find a list of concepts that your child will use and understand while completing Unit 6 Traversing Congruency. Also included are references, vocabulary and examples that will help you assist your child at home. Concepts Students will Use and Understand Parallel lines have the same slope and perpendicular lines have opposite, reciprocal slopes. When two lines intersect, vertical angles are congruent and adjacent angles are supplementary. When parallel lines are cut by a transversal, corresponding, alternate interior and alternate exterior angles and congruent. The length of segments formed by two non-parallel transversals cutting parallel line is proportional to the distances of the parallel lines from the intersection of the transversal. Parallel lines can be constructed using the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal. Vocabulary Adjacent angles- angles in the same plane that have a common vertex and a common side, but no common interior points. Alternate exterior angles- pairs of angles formed when a third line (transversal) crosses 2 lines. These angles are on opposite sides of the transversal and are outside the 2 lines. Alternate interior angles- pairs of angles formed when a third line (transversal) crosses 2 lines. These angles are on opposite sides of the transversal and are inside the 2 lines. Coincidental- two equivalent linear equations overlap when graphed. Complimentary angles- Two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. Congruent- having the same size, shape and measure. Two figures are congruent if all of their corresponding measures are equal. Equiangular- The property of a polygon whose angles are all congruent. Equilateral- the property of a polygon whose sides are all congruent. Intersecting lines- Two lines in a plane that cross each other. Unless two lines are coincidental, parallel or skew, they will intersect at one point. Linear pair- adjacent, supplementary angles. Excluding their common side, a linear pair forms a straight line. Opposite Reciprocals- reciprocals are 2 numbers that have a product of 1; opposites are positive and negative Parallel lines- two lines that lie in the same plane and do not intersect. Perpendicular lines- two lines that intersect at a right angle. Reflection line- a line that is the perpendicular bisector of the segment with endpoints at a pre-image point and the image of that point after reflection. Regular polygon- a polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular. Same-side exterior angles (Consecutive interior)- pairs of angles formed when a transversal crosses 2 lines. These angles are on the same side of the transversal and outside the 2 lines. The angles are supplementary. Same-side interior angles- pairs of angles formed when a transversal crosses 2 lines. These angles are on the same side of the transversal and inside the 2 lines. The angles are supplementary. Skew lines- two lines that do not lie in the same plane (cannot be parallel or intersect). Supplementary angles- two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Transversal- a line that crosses two or more lines. Vertical angles- two nonadjacent angles formed by interesting lines or segments. http://intermath.coe.uga.edu/ Math 8 Unit 6 Traversing Congruency Symbols congruent perpendicular Example 1 Name all angles that are congruent to angle 3. 2 and 7 are what type of angles? parallel Example 2 Additional Links http://www.cliffsnotes. com/WileyCDA/CliffsRe viewTopic/Proportional -Parts-ofTriangles.topicArticleId -18851,articleId18813.html Find the value of m. m 3 m+5 4 Example 3 What is the slope of a line parallel to a line with the equation of 4x + y = 7? http://www.analyzema th.com/Slope/Slope.ht ml What is the slope of a line perpendicular to a line with the equation of y=2x+8? Key Example 1 Angle 2, 6 and 7. They are alternate exterior angles. Example 2 m m 5 3 4 4m=3m+15 Example 3 Parallel: m=-4 Perpendicular: m= 1 2 m=15